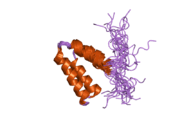SIN3B
Paired amphipathic helix protein Sin3b is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SIN3B gene.[1][2]
Interactions
SIN3B has been shown to interact with HDAC1,[3][4] Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 16,[5] SUDS3[6] and IKZF1.[4][7]
See also
References
- ↑ Ishikawa K, Nagase T, Suyama M, Miyajima N, Tanaka A, Kotani H, Nomura N, Ohara O (December 1998). "Prediction of the coding sequences of unidentified human genes. X. The complete sequences of 100 new cDNA clones from brain which can code for large proteins in vitro". DNA Res 5 (3): 169–76. doi:10.1093/dnares/5.3.169. PMID 9734811.
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: SIN3B SIN3 homolog B, transcription regulator (yeast)".
- ↑ Zhang, Y; Ng H H; Erdjument-Bromage H; Tempst P; Bird A; Reinberg D (August 1999). "Analysis of the NuRD subunits reveals a histone deacetylase core complex and a connection with DNA methylation". Genes Dev. (UNITED STATES) 13 (15): 1924–35. doi:10.1101/gad.13.15.1924. ISSN 0890-9369. PMC 316920. PMID 10444591.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Koipally, J; Renold A; Kim J; Georgopoulos K (June 1999). "Repression by Ikaros and Aiolos is mediated through histone deacetylase complexes". EMBO J. (ENGLAND) 18 (11): 3090–100. doi:10.1093/emboj/18.11.3090. ISSN 0261-4189. PMC 1171390. PMID 10357820.
- ↑ David, G; Alland L; Hong S H; Wong C W; DePinho R A; Dejean A (May 1998). "Histone deacetylase associated with mSin3A mediates repression by the acute promyelocytic leukemia-associated PLZF protein". Oncogene (ENGLAND) 16 (19): 2549–56. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1202043. ISSN 0950-9232. PMID 9627120.
- ↑ Alland, Leila; David Gregory, Shen-Li Hong, Potes Jason, Muhle Rebecca, Lee Hye-Chun, Hou Harry, Chen Ken, DePinho Ronald A (April 2002). "Identification of Mammalian Sds3 as an Integral Component of the Sin3/Histone Deacetylase Corepressor Complex". Mol. Cell. Biol. (United States) 22 (8): 2743–50. doi:10.1128/MCB.22.8.2743-2750.2002. ISSN 0270-7306. PMC 133736. PMID 11909966.
- ↑ Koipally, Joseph; Georgopoulos Katia (August 2002). "A molecular dissection of the repression circuitry of Ikaros". J. Biol. Chem. (United States) 277 (31): 27697–705. doi:10.1074/jbc.M201694200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 12015313.
Further reading
- Ayer DE, Lawrence QA, Eisenman RN (1995). "Mad-Max transcriptional repression is mediated by ternary complex formation with mammalian homologs of yeast repressor Sin3". Cell 80 (5): 767–76. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(95)90355-0. PMID 7889570.
- David G, Alland L, Hong SH et al. (1998). "Histone deacetylase associated with mSin3A mediates repression by the acute promyelocytic leukemia-associated PLZF protein". Oncogene 16 (19): 2549–56. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1202043. PMID 9627120.
- Koipally J, Renold A, Kim J, Georgopoulos K (1999). "Repression by Ikaros and Aiolos is mediated through histone deacetylase complexes". EMBO J. 18 (11): 3090–100. doi:10.1093/emboj/18.11.3090. PMC 1171390. PMID 10357820.
- Naruse Y, Aoki T, Kojima T, Mori N (2000). "Neural restrictive silencer factor recruits mSin3 and histone deacetylase complex to repress neuron-specific target genes". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 96 (24): 13691–6. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.24.13691. PMC 24126. PMID 10570134.
- Spronk CA, Tessari M, Kaan AM et al. (2001). "The Mad1-Sin3B interaction involves a novel helical fold". Nat. Struct. Biol. 7 (12): 1100–4. doi:10.1038/81944. PMID 11101889.
- Spronk CA, Jansen JF, Tessari M et al. (2001). "Sequence-specific assignment of the PAH2 domain of Sin3B free and bound to Mad1". J. Biomol. NMR 19 (4): 377–8. doi:10.1023/A:1011262214741. PMID 11370785.
- Alland L, David G, Shen-Li H et al. (2002). "Identification of Mammalian Sds3 as an Integral Component of the Sin3/Histone Deacetylase Corepressor Complex". Mol. Cell. Biol. 22 (8): 2743–50. doi:10.1128/MCB.22.8.2743-2750.2002. PMC 133736. PMID 11909966.
- Rayman JB, Takahashi Y, Indjeian VB et al. (2002). "E2F mediates cell cycle-dependent transcriptional repression in vivo by recruitment of an HDAC1/mSin3B corepressor complex". Genes Dev. 16 (8): 933–47. doi:10.1101/gad.969202. PMC 152357. PMID 11959842.
- Koipally J, Georgopoulos K (2002). "A molecular dissection of the repression circuitry of Ikaros". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (31): 27697–705. doi:10.1074/jbc.M201694200. PMID 12015313.
- Yang L, Mei Q, Zielinska-Kwiatkowska A et al. (2003). "An ERG (ets-related gene)-associated histone methyltransferase interacts with histone deacetylases 1/2 and transcription co-repressors mSin3A/B". Biochem. J. 369 (Pt 3): 651–7. doi:10.1042/BJ20020854. PMC 1223118. PMID 12398767.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Petrie K, Guidez F, Howell L et al. (2003). "The histone deacetylase 9 gene encodes multiple protein isoforms". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (18): 16059–72. doi:10.1074/jbc.M212935200. PMID 12590135.
- Wysocka J, Myers MP, Laherty CD et al. (2003). "Human Sin3 deacetylase and trithorax-related Set1/Ash2 histone H3-K4 methyltransferase are tethered together selectively by the cell-proliferation factor HCF-1". Genes Dev. 17 (7): 896–911. doi:10.1101/gad.252103. PMC 196026. PMID 12670868.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Dugast-Darzacq C, Pirity M, Blanck JK et al. (2004). "Mxi1-SRalpha: a novel Mxi1 isoform with enhanced transcriptional repression potential". Oncogene 23 (55): 8887–99. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1208107. PMID 15467743.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA et al. (2004). "The Status, Quality, and Expansion of the NIH Full-Length cDNA Project: The Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Rampalli S, Pavithra L, Bhatt A et al. (2005). "Tumor Suppressor SMAR1 Mediates Cyclin D1 Repression by Recruitment of the SIN3/Histone Deacetylase 1 Complex". Mol. Cell. Biol. 25 (19): 8415–29. doi:10.1128/MCB.25.19.8415-8429.2005. PMC 1265755. PMID 16166625.
- Xu Y, Sengupta PK, Seto E, Smith BD (2006). "RFX family proteins differentially interact with HDACs to repress collagen alpha 2(I) gene (COL1A2) expression". J. Biol. Chem. 281 (14): 9260–70. doi:10.1074/jbc.M511724200. PMC 1434794. PMID 16464847.
PDB gallery |
|---|
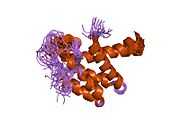
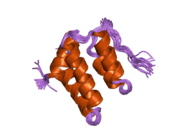
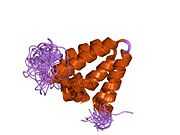
| | 1e91: STRUCTURE OF THE COMPLEX OF THE MAD1-SIN3B INTERACTION DOMAINS |
| 1pd7: Extended SID of Mad1 bound to the PAH2 domain of mSin3B |
| 2cr7: Solution structure of the first PAH domain of the mouse transcriptional repressor SIN3B |
| 2czy: Solution structure of the NRSF/REST-mSin3B PAH1 complex |
| 2f05: Solution structure of free PAH2 domain of mSin3B |
|
|
|
External links
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.
|
|---|
| | Coactivators | |
|---|
| | Corepressors | |
|---|
| | ATP-dependent remodeling factors |
- Chromatin Structure Remodeling (RSC) Complex
- SWI/SNF
|
|---|
| Index of genetics |
|---|
| | Description |
- Gene expression
- DNA
- replication
- cycle
- recombination
- repair
- binding proteins
- Transcription
- factors
- regulators
- nucleic acids
- RNA
- RNA binding proteins
- ribonucleoproteins
- repeated sequence
- modification
- Translation
- ribosome
- modification
- nexins
- Proteins
- domains
- Structure
- primary
- secondary
- tertiary
- quaternary
|
|---|
| | Disease |
- Replication and repair
- Transcription factor
- Transcription
- Translation
|
|---|
|
|