SH2B1
| SH2B adaptor protein 1 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 PDB rendering based on 2hdv. | |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||
| Symbols | SH2B1 ; PSM; SH2B | ||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 608937 MGI: 1201407 HomoloGene: 32122 GeneCards: SH2B1 Gene | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
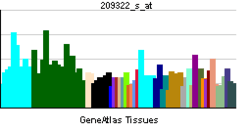
| RNA expression pattern | |||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||
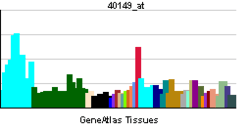 | |||||||||||||
| More reference expression data | |||||||||||||
| Orthologs | |||||||||||||
| Species | Human | Mouse | |||||||||||
| Entrez | 25970 | 20399 | |||||||||||
| Ensembl | ENSG00000178188 | ENSMUSG00000030733 | |||||||||||
| UniProt | Q9NRF2 | Q91ZM2 | |||||||||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) | NM_001145795 | NM_001081459 | |||||||||||
| RefSeq (protein) | NP_001139267 | NP_001074928 | |||||||||||
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 16: 28.86 – 28.89 Mb | Chr 7: 126.47 – 126.48 Mb | |||||||||||
| PubMed search | |||||||||||||
SH2B adapter protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SH2B1 gene.[1][2][3]
Interactions
SH2B1 has been shown to interact with:
- Grb2,[4][5]
- Insulin receptor,[2][5]
- Janus kinase 2,[6][7] and
- TrkA.[4][8]
Clinical significance
Variations close to or in the SH2B1 gene have been found to associatate with obesity in two very large genome wide association studies of body mass index (BMI).[9][10] Furthermore SH2B1 deletions are associated with severe early-onset obesity.[11]
See also
References
- ↑ Kong M, Wang CS, Donoghue DJ (Apr 2002). "Interaction of fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 and the adapter protein SH2-B. A role in STAT5 activation". J Biol Chem 277 (18): 15962–70. doi:10.1074/jbc.M102777200. PMID 11827956.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Nelms K, O'Neill TJ, Li S, Hubbard SR, Gustafson TA, Paul WE (Jan 2000). "Alternative splicing, gene localization, and binding of SH2-B to the insulin receptor kinase domain". Mamm Genome 10 (12): 1160–7. doi:10.1007/s003359901183. PMID 10594240.
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: SH2B1 SH2B adaptor protein 1".
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Qian X, Riccio A, Zhang Y, Ginty DD (November 1998). "Identification and characterization of novel substrates of Trk receptors in developing neurons". Neuron 21 (5): 1017–29. doi:10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80620-0. PMID 9856458.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Kotani K, Wilden P, Pillay TS (October 1998). "SH2-Balpha is an insulin-receptor adapter protein and substrate that interacts with the activation loop of the insulin-receptor kinase". Biochem. J. 335. 335 ( Pt 1): 103–9. PMC 1219757. PMID 9742218.
- ↑ Rui L, Mathews LS, Hotta K, Gustafson TA, Carter-Su C (November 1997). "Identification of SH2-Bbeta as a substrate of the tyrosine kinase JAK2 involved in growth hormone signaling". Mol. Cell. Biol. 17 (11): 6633–44. PMC 232517. PMID 9343427.
- ↑ Xie S, Lin H, Sun T, Arlinghaus RB (October 2002). "Jak2 is involved in c-Myc induction by Bcr-Abl". Oncogene 21 (47): 7137–46. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1205942. PMID 12370803.
- ↑ Koch A, Mancini A, Stefan M, Niedenthal R, Niemann H, Tamura T (March 2000). "Direct interaction of nerve growth factor receptor, TrkA, with non-receptor tyrosine kinase, c-Abl, through the activation loop". FEBS Lett. 469 (1): 72–6. doi:10.1016/s0014-5793(00)01242-4. PMID 10708759.
- ↑ Thorleifsson G, Walters GB, Gudbjartsson DF, Steinthorsdottir V, Sulem P, Helgadottir A et al. (January 2009). "Genome-wide association yields new sequence variants at seven loci that associate with measures of obesity.". Nat. Genet. 41 (1): 18–24. doi:10.1038/ng.274. PMID 19079260.
- ↑ Willer CJ, Speliotes EK, Loos RJ, Li S, Lindgren CM, Heid IM et al. (January 2009). "Six new loci associated with body mass index highlight a neuronal influence on body weight regulation.". Nat. Genet. 41 (1): 24–34. doi:10.1038/ng.287. PMC 2695662. PMID 19079261.
- ↑ Bochukova EG, Huang N, Keogh J, Henning E, Purmann C, Blaszczyk K et al. (February 2010). "Large, rare chromosomal deletions associated with severe early-onset obesity". Nature 463 (7281): 666–70. doi:10.1038/nature08689. PMC 3108883. PMID 19966786.
Further reading
- Rui L, Mathews LS, Hotta K, Gustafson TA, Carter-Su C (1997). "Identification of SH2-Bbeta as a substrate of the tyrosine kinase JAK2 involved in growth hormone signaling.". Mol. Cell. Biol. 17 (11): 6633–44. PMC 232517. PMID 9343427.
- Kotani K, Wilden P, Pillay TS (1998). "SH2-Balpha is an insulin-receptor adapter protein and substrate that interacts with the activation loop of the insulin-receptor kinase.". Biochem. J. 335. ( Pt 1): 103–9. PMC 1219757. PMID 9742218.
- Qian X, Riccio A, Zhang Y, Ginty DD (1999). "Identification and characterization of novel substrates of Trk receptors in developing neurons.". Neuron 21 (5): 1017–29. doi:10.1016/S0896-6273(00)80620-0. PMID 9856458.
- Koch A, Mancini A, Stefan M, Niedenthal R, Niemann H, Tamura T (2000). "Direct interaction of nerve growth factor receptor, TrkA, with non-receptor tyrosine kinase, c-Abl, through the activation loop.". FEBS Lett. 469 (1): 72–6. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(00)01242-4. PMID 10708759.
- Nagase T, Kikuno R, Ishikawa KI, Hirosawa M, Ohara O (2000). "Prediction of the coding sequences of unidentified human genes. XVI. The complete sequences of 150 new cDNA clones from brain which code for large proteins in vitro.". DNA Res. 7 (1): 65–73. doi:10.1093/dnares/7.1.65. PMID 10718198.
- Rui L, Gunter DR, Herrington J, Carter-Su C (2000). "Differential binding to and regulation of JAK2 by the SH2 domain and N-terminal region of SH2-bbeta.". Mol. Cell. Biol. 20 (9): 3168–77. doi:10.1128/MCB.20.9.3168-3177.2000. PMC 85611. PMID 10757801.
- O'Brien KB, O'Shea JJ, Carter-Su C (2002). "SH2-B family members differentially regulate JAK family tyrosine kinases.". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (10): 8673–81. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109165200. PMID 11751854.
- Ohtsuka S, Takaki S, Iseki M, Miyoshi K, Nakagata N, Kataoka Y et al. (2002). "SH2-B is required for both male and female reproduction.". Mol. Cell. Biol. 22 (9): 3066–77. doi:10.1128/MCB.22.9.3066-3077.2002. PMC 133757. PMID 11940664.
- Xie S, Lin H, Sun T, Arlinghaus RB (2002). "Jak2 is involved in c-Myc induction by Bcr-Abl.". Oncogene 21 (47): 7137–46. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1205942. PMID 12370803.
- Nakayama M, Kikuno R, Ohara O (2003). "Protein-protein interactions between large proteins: two-hybrid screening using a functionally classified library composed of long cDNAs.". Genome Res. 12 (11): 1773–84. doi:10.1101/gr.406902. PMC 187542. PMID 12421765.
- O'Brien KB, Argetsinger LS, Diakonova M, Carter-Su C (2003). "YXXL motifs in SH2-Bbeta are phosphorylated by JAK2, JAK1, and platelet-derived growth factor receptor and are required for membrane ruffling.". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (14): 11970–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.M210765200. PMID 12551917.
- Nishi M, Werner ED, Oh BC, Frantz JD, Dhe-Paganon S, Hansen L et al. (2005). "Kinase activation through dimerization by human SH2-B.". Mol. Cell. Biol. 25 (7): 2607–21. doi:10.1128/MCB.25.7.2607-2621.2005. PMC 1061652. PMID 15767667.
- Donatello S, Fiorino A, Degl'Innocenti D, Alberti L, Miranda C, Gorla L et al. (2007). "SH2B1beta adaptor is a key enhancer of RET tyrosine kinase signaling.". Oncogene 26 (45): 6546–59. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1210480. PMID 17471236.
| |||||||||||