S
|

S (named ess /ˈɛs/,[1] plural esses[2]) is the 19th letter in the ISO basic Latin alphabet.
History
| Phoenician Shin |
Etruscan S |
Greek Sigma |
|---|---|---|
| |
|
|
Semitic Šîn ("teeth") represented a voiceless postalveolar fricative /ʃ/ (as in 'ship'). Greek did not have this sound, so the Greek sigma (Σ) came to represent /s/. In Etruscan and Latin, the /s/ value was maintained, and only in modern languages has the letter been used to represent other sounds.
Long s
The minuscule form of 's' was 'ſ', called the long s, up to the fourteenth century or so, and the form 'S' was used then only as uppercase in the same manner that the forms 'G' and 'A' are only uppercase. With the introduction of printing, the modern form 's' began to be used at the end of words by some printers. Later, it was used everywhere in print and eventually spread to manuscript letters as well. For example, "sinfulness" would be rendered as "ſinfulneſſ" in all medieval hands, and later it was "ſinfulneſs" in some blackletter hands and in print. The modern spelling "sinfulness" did not become widespread in print until the beginning of the 19th century, largely to prevent confusion of 'ſ' with the lowercase 'f' in typefaces which had a very short horizontal stroke in their lowercase 'f'. The ligature of 'ſs' (or 'ſz') became the German Eszett, 'ß'.
It is commonly believed that it was the London printer John Bell (1745–1831) who popularized the modern "round s", in place of the elongated 'ſ', although exactly when he did this is unclear. In his multivolume series, The British Theatre, he began using the short form instead of the elongated letter circa 1785, not entirely at first but in later years more and more consistently. His edition of Shakespeare, in 1785, was advertised with the claim that he "ventured to depart from the common mode by rejecting the long 'ſ' in favor of the round one, as being less liable to error....."[3] In the field of more ephemeral publications, Bell began a London newspaper called The World, of which it has been said that a "vital change ... first made in The World, entitled No. 1 of that paper (for Monday, January 1, 1787) to be chronicled in any kalendar of typographical progress: the abolition of the long 'ſ'...."[4] Bell may have popularized it, but he did not invent it; in his letter of March 26, 1786 to Francis Childs, Benjamin Franklin wrote "the Round s .... begins to be the Mode, and in nice printing the Long 'ſ' is rejected entirely."
Usage
The letter S represents the voiceless alveolar or voiceless dental sibilant /s/ in most languages and the IPA. It also commonly represents the voiced alveolar or voiced dental sibilant /z/, as in Portuguese 'mesa' or English 'rose' and 'bands', or may represent the voiceless palato-alveolar fricative [ʃ], as in most Portuguese dialects when syllable-finally, in Hungarian, in German (before 'p', 't') and some English words as 'sugar', since yod-coalescence became a dominant feature, and [ʒ], as in English 'measure' (also because of yod-coalescence), European Portuguese 'Islão' or, in many sociolects of Brazilian Portuguese, 'esdrúxulo', while in some Andalusian dialects, it is merged with Peninsular Spanish 'c' and 'z' and pronounced [θ].
"Sh" is a common letter combination in English; when used as a digraph the two letters represent [ʃ] in every instance.
The letter S is the seventh most common letter in English and the third-most common consonant (after 't' and 'n').[5] In English and many other languages, primarily Romance ones like Spanish and French, final 's' is the usual mark of plural nouns. It also usually indicates English third person present tense verbs.
Related letters and other similar characters
- Σ σ : Greek letter Sigma
- S̈ s̈: S with diaeresis
- С с : Cyrillic letter Es
- Ц ц : Cyrillic letter Tse
- ẞ ß : German Eszett or "sharp S"
- ſ : Latin letter Long S
- ʃ : IPA letter Esh (used in the International Phonetic Alphabet for the voiceless postalveolar fricative)
- ∫ : integral symbol
- Ѕ ѕ : Cyrillic letter Dze
- Sz : The 's' sound in the Hungarian alphabet
- SH Sh sh : Latin digraph Sh
- ש : Hebrew letter Sin
- Ƨ ƨ : Latin letter Reversed S (used in Zhuang transliteration)
- $ : dollar sign
- § : Section sign
Computing codes
| Character | S | s | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unicode name | LATIN CAPITAL LETTER S | LATIN SMALL LETTER S | ||
| Encodings | decimal | hex | decimal | hex |
| Unicode | 83 | U+0053 | 115 | U+0073 |
| UTF-8 | 83 | 53 | 115 | 73 |
| Numeric character reference | S | S | s | s |
| ASCII 1 | 83 | 53 | 115 | 73 |
- 1 Also for encodings based on ASCII, including the DOS, Windows, ISO-8859 and Macintosh families of encodings.
Other representations
| NATO phonetic | Morse code |
| Sierra |
 |
 |
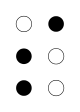 |
| Signal flag | Flag semaphore | Braille dots-234 |
References
- ↑ Spelled 'es'- in compound words
- ↑ "S", Oxford English Dictionary, 2nd edition (1989); Merriam-Webster's Third New International Dictionary of the English Language, Unabridged (1993); "ess," op. cit.
- ↑ Stanley Morison, A Memoir of John Bell, 1745–1831 (1930, Cambridge Univ. Press) page 105; Daniel Berkeley Updike, Printing Types, Their History, Forms, and Use – a study in survivals (2nd. ed, 1951, Harvard Univ. Press) page 293.
- ↑ Stanley Morison, A Memoir of John Bell, 1745–1831 (1930, Cambridge Univ. Press) page 118.
- ↑ English Letter Frequency
External links
 Media related to S at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to S at Wikimedia Commons The dictionary definition of S at Wiktionary
The dictionary definition of S at Wiktionary The dictionary definition of s at Wiktionary
The dictionary definition of s at Wiktionary "S". The New Student's Reference Work. 1914.
"S". The New Student's Reference Work. 1914.