Runic calendar

A Runic calendar (also Rune staff or Runic Almanac) is a perpetual calendar based on the 19-year-long Metonic cycle of the Moon. Runic calendars were written on parchment or carved onto staves of wood, bone, or horn. The oldest one known, and the only one from the Middle Ages, is the Nyköping staff from Sweden, believed to date from the 13th century. Most of the several thousand which survive are wooden calendars dating from the 16th and the 17th centuries. During the 18th century, the Runic calendars had a renaissance, and around 1800, such calendars were made in the form of tobacco boxes in brass.
A typical Runic calendar consisted of several horizontal lines of symbols, one above the other.
Special days like solstices, equinoxes, and celebrations (including Christian holidays and feasts) were marked with additional lines of symbols.
The calendar does not rely on knowledge of the length of the tropical year or of the occurrence of leap years. It is set at the beginning of each year by observing the first full moon after the winter solstice. The first full moon also marked the date of Disting, a pagan feast and a fair day.
Marks
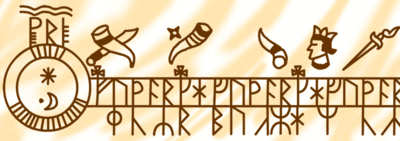
On one line, 52 weeks of 7 days were laid out using 52 repetitions of the first seven runes of the Younger Futhark. The runes corresponding to each weekday varied from year to year.
On another, many of the days were marked with one of 19 symbols representing the 19 Golden numbers, the years of the Metonic cycle. In early calendars, each of the 19 years in the cycle was represented by a rune; the first 16 were the 16 runes of the Younger Futhark, plus special runes for the remaining three years: Arlaug (Golden Number 17), Tvimadur (Golden Number 18), and Belgthor (Golden Number 19). The new moon would fall on that day during that year of the cycle. For example, in the 18th year of the cycle, the new moons would fall on all the dates marked with Tvimadur, the symbol for year 18. Later calendars used Pentadic numerals for the values 1–19.
A version using Latin alphabet for weekdays and Arabic numerals for the golden numbers was printed in 1498 as part of the Breviarium Scarense.[1]
Additional runes
Because this system needed 19 runes to represent the 19 golden numbers which stood for the 19 years of the perpetual calendar's cycle, the Younger Futhark, a Runic alphabet, was insufficient, having only 16 characters. The solution devised was to add three special runes to represent the numbers above 16: Arlaug (Golden Number 17), Tvimadur (tvímaður, Golden Number 18), and Belgthor (Golden Number 19).
-

Arlaug, Runic calendar rune number 17.
-
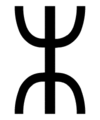
Tvimadur, Runic calendar rune number 18.
-
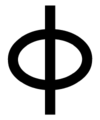
Belgthor, Runic calendar rune number 19.
Primstav


A primstav (translation: prime staff) is the ancient Norwegian calendar stick. These were engraved with images instead of runes. The images depicted the different nonmoving religious holidays. The oldest primstav still in existence is from 1457 and is exhibited at Norsk Folkemuseum.
An ancient forerunner
The runic inscriptions of the Franks Casket (7th century) seem to constitute a lunisolar calendar. While the number of runes can be seen as a 10-year solar calendar (10 for eternal), their runic value stands for the lunar counterpart. Both calendars seem to be “synchronized” by a Latin fragment which is inserted into the Anglo-Saxon text . It consists of 20 letters (12 uncials, 2 half uncials, 6 runes), thus creating a sequence of ordinary years of 12 months and embolismic years of 13 months. If we figure the value of this text by the position of the characters according to the fuþorc we count 238. A Metonic cycle of 19 years counts 235 lunations; in this particular case the rune master needed 3 more lunations to take his protégé from death in Midwinter to life – here a pagan resurrection into Valhalla – at Easter.
Modern use
Adherents of the Estonian ethnic religion (maausk) have published Runic calendars (Estonian: sirvilauad) every year since 1978. During the Soviet occupation, it was an illegal samizdat publication.[2]
See also
- Computus Runicus
- Germanic calendar
- Method of Lunar Distances
- Nationalencyklopedin
- Scythe sword
References
- ↑ Brinolf Gerlaksson, bishop of Skara (commissioned by) (1498). Breviarium Scarense. Nuremberg: Georg Stuchs. pp. 2–13. Retrieved 2010-06-20.
- ↑ Sirvilauad loevad aega
External links and literature
- Becker, Alfred: A Magic Spell "powered by" a Lunisolar Calendar, Asterisk, A Quarterly Journal of Historical English Studies, 15 (2006)
- Becker, Alfred: Franks Casket. Zu den Bildern und Inschriften des Runenkästchens von Auzon (Regensburg 1973)
- Franks Casket Becker, Alfred, website Franks Casket
- An article on rune calendars, with illustrations from http://www.gangleri.nl/
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||