Rumor spread in social network
Rumor is an important form of social communications, and spread of rumors plays a significant role in a variety of human affairs. There are two rumor models that are widely used, i.e. DK model and MK model. Particularly, we can view rumor spread as a stochastic process in social networks.
Model
Spread of Rumors
An standard model of rumor spreading was introduced by Daley and Kendall,[1] which is called DK model. Assume there are N people in total. And those people in the network are categorized into three groups: ignorants, spreaders and stiflers, which are denoted as S, I, and R respectively hereinafter:
- S: people who are ignorant of the rumor;
- I: people who actively spread the rumor;
- R: people who have heard the rumor, but no longer are interested in spreading it.
The rumor is propagated through the population by pair-wise contacts between spreaders and others in the population. Any spreader involved in a pair-wise meeting attempts to “infect” the other individual with the rumor. In the case this other individual is an ignorant, he or she becomes a spreader. In the other two cases, either one or both of those involved in the meeting learn that the rumor is known and decided not to tell the rumor anymore, thereby turning into stiflers.
One famous variant is Maki-Thompson(MK) model.[2] In this model, rumor is spread by directed contacts of the spreaders with others in the population. Furthermore, when a spreader contacts another spreader only the initiating spreader becomes a stifler. Therefore, three types of interactions can happen with certain rates.
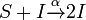
- which says when a spreader meet an ignorant, the ignorant will become a spreader.
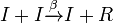
- which says when two spreaders meet with each other, one of them will become a stifler.
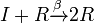
- which says when a spreader meet a stifler, the spreader will lose the interest in spreading the rumor, so become a stifler.
Of course we always have conservation of individuals:
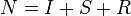
The change in each class in a small time interval is:
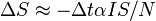
![\Delta I \approx \Delta t [{\alpha IS \over N} - {\beta I^2 \over N} - {\beta IR \over N}]](../I/m/86861c2fc6646f152fa5bd1f03ad392f.png)
![\Delta R \approx \Delta t [{\beta I^2 \over N}+{\beta IR \over N}]](../I/m/7dc5197243c4d46e7955690562b7b56f.png)
Since we know 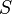 ,
, 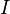 and
and 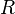 sum up to
sum up to 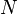 , we can reduce one equation from the above, which leads to a set of differential equations using relative variable
, we can reduce one equation from the above, which leads to a set of differential equations using relative variable 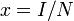 and
and 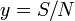 as follows
as follows
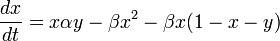
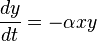
which we can write
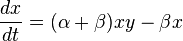
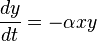
Compared with the ordinary SIR model, we see that the only difference to the ordinary SIR model is that we have a factor  in the first equation instead of just
in the first equation instead of just 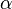 . We immediately see that the ignorants can only decrease since
. We immediately see that the ignorants can only decrease since 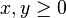 and
and 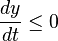 . Also, if
. Also, if
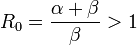
which means
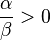
the rumour model exhibits an “epidemic” even for arbitrarily small rate parameters.
Rumor Spread in Social Network
We model the process introduced above on a network in discrete time, that is, we can model it as a DTMC. Say we have a network with N nodes, then we can define 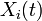 to be the state of node i at time t. Then
to be the state of node i at time t. Then 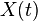 is a stochastic process on
is a stochastic process on 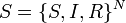 . At a single moment, some node i and node j interact with each other, and then one of them will change its state. Thus we define the function
. At a single moment, some node i and node j interact with each other, and then one of them will change its state. Thus we define the function 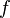 so that for
so that for 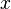 in
in 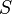 ,
,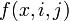 is when the state of network is
is when the state of network is 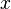 , node i and node j interact with each other, and one of them will change its state. The transition matrix depends on the number of ties of node i and node j, as well as the state of node i and node j. For any
, node i and node j interact with each other, and one of them will change its state. The transition matrix depends on the number of ties of node i and node j, as well as the state of node i and node j. For any 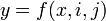 , we try to find
, we try to find 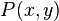 . If node i is in state I and node j is in state S, then
. If node i is in state I and node j is in state S, then 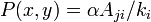 ; if node i is in state I and node j is in state I, then
; if node i is in state I and node j is in state I, then 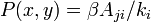 ; if node i is in state I and node j is in state R, then
; if node i is in state I and node j is in state R, then 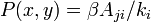 . For all other
. For all other 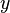 ,
, 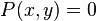 .
.
The procedure[3] on a network is as follows:
- We initial rumor to a single node
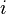 ;
; - We pick one of its neighbors as given by the adjacency matrix, so the probability we will pick node
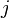 is
is
where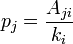
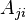 is from the adjacency matrix and
is from the adjacency matrix and 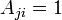 if there is a tie from
if there is a tie from 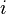 to
to 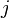 , and
, and 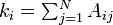 is the degree for node
is the degree for node 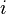 ;
; - Then have the choice:
- If node
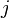 is an ignorant, it becomes a spreader at a rate
is an ignorant, it becomes a spreader at a rate 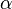 ;
; - If node
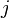 is a spreader or stifler, then node
is a spreader or stifler, then node 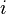 becomes a stifler at a rate
becomes a stifler at a rate 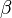 .
.
- If node
- We pick another node who is a spreader at random, and repeat the process.
We would expect that this process spreads the rumor throughout a considerable fraction of the network. Note however that if we have a strong local clustering around a node, what can happen is that many nodes become spreaders and have neighbors who are spreaders. Then, every time we pick one of those, they will recover and can extinguish the rumor spread. On the other hand, if we have a network that is small world, that is, a network in which the shortest path between two randomly chosen nodes is much smaller than that one would expect, we can expect the rumor spread far away.
Also we can compute the final number of people who once spread the news, this is given by
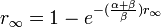
In networks the process that does not have a threshold in a well mixed population, exhibits a clear cut phase-transition in small worlds. The following graph illustrates the asymptotic value of 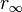 as a function of the rewiring probability
as a function of the rewiring probability 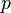 .
.
References
- ↑ Daley, D.J., and Kendal, D.G. 1965 Stochastic rumors, J. Inst. Maths Applics 1, p42.
- ↑ Maki, D.P. 1973 Mathematical Models and Applications, With Emphasis on Social, Life, and Management Sciences, Prentice Hall.
- ↑ Brockmann, D. 2011 Complex Networks and Systems, Lecture Notes, Northwestern University