Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate
 | |
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| ChEBI | CHEBI:16710 |
| ChemSpider | 110238 |
| |
| Jmol-3D images | Image |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula |
C5H12O11P2 |
| Molar mass | 310.09 g·mol−1 |
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
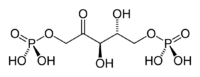
Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP) is an organic substance that is involved in photosynthesis. The anion is a double phosphate ester of the ketose (ketone-containing sugar) called ribulose. Salts of this species can be isolated, but its crucial biological function involves this colourless anion in solution.[1] To simplify the presentation, the image in the above table depicts the acid form of this anion.
Role in photosynthesis

The enzyme ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase oxygenase (RuBisCO) catalyzes the reaction between RuBP and carbon dioxide. The product is the highly unstable 6-carbon intermediate known as 3-keto-2-carboxyarabinitol 1,5-bisphosphate. This six-carbon intermediate decays virtually instantaneously into two molecules of 3-phosphoglycerate (3-PGA) (see figure). RuBisCO also catalyzes RuBP with oxygen (O2) in a process called photorespiration, a process that is more prevalent at high temperatures. RuBP is also involved in photorespiration, in which it combines with O2 to become 3-PGA + phosphoglycolic acid. In the Calvin Cycle, RuBP is a product of the phosphorylation of ribulose-5-phosphate by ATP.
References
- ↑ The topic is discussed in all biochemistry textbooks, this one is representative: Nelson, D. L.; Cox, M. M. "Lehninger, Principles of Biochemistry" 3rd Ed. Worth Publishing: New York, 2000. ISBN 1-57259-153-6.