Rhinobatos
| Rhinobatos Temporal range: 125–0Ma | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Rhinobatos rhinobatos | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Chondrichthyes |
| Order: | Rajiformes |
| Family: | Rhinobatidae |
| Genus: | Rhinobatos H. F. Linck, 1790 |
Rhinobatos hakelensis fossil
Rhinobatos is a genus of fish in the Rhinobatidae family.
Guitarfish catch their prey using a suction technique. The relative sequence of muscle activity is shared across the Rhinobatos genus, but varies in timing and duration of muscular activation.[2]
Species
The 37 currently recognized species in this genus are:
- Rhinobatos albomaculatus Norman, 1930 (White-spotted guitarfish)
- Rhinobatos annandalei Norman, 1926 (Annandale's guitarfish)
- Rhinobatos annulatus J. P. Müller & Henle, 1841 (Lesser guitarfish)
- Rhinobatos blochii J. P. Müller & Henle, 1841 (Bluntnose guitarfish)
- Rhinobatos cemiculus É. Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire, 1817 (Blackchin guitarfish)
- Rhinobatos formosensis Norman, 1926 (Taiwan guitarfish)
- Rhinobatos glaucostigma D. S. Jordan & C. H. Gilbert, 1883 (Speckled guitarfish)
- Rhinobatos holcorhynchus Norman, 1922 (Slender guitarfish)
- Rhinobatos horkelii J. P. Müller & Henle, 1841 (Brazilian guitarfish)
- Rhinobatos hynnicephalus J. Richardson, 1846 (Ringstreaked guitarfish)
- Rhinobatos irvinei Norman, 1931 (Spineback guitarfish)
- Rhinobatos jimbaranensis Last, W. T. White & Fahmi, 2006 (Jimbaran shovelnose ray) [3]
- Rhinobatos lentiginosus Garman, 1880 (Atlantic guitarfish)
- Rhinobatos leucorhynchus Günther, 1867 (Whitesnout guitarfish)
- Rhinobatos leucospilus Norman, 1926 (Grayspotted guitarfish)
- Rhinobatos lionotus Norman, 1926 (Smoothback guitarfish)
- Rhinobatos microphthalmus Teng, 1959 (Smalleyed guitarfish)
- Rhinobatos nudidorsalis Last, Compagno & Nakaya, 2004 (Bareback shovelnose ray) [4]
- Rhinobatos obtusus J. P. Müller & Henle, 1841 (Widenose guitarfish)
- Rhinobatos ocellatus Norman, 1926 (Speckled guitarfish)
- Rhinobatos penggali Last, W. T. White & Fahmi, 2006 (Indonesian shovelnose ray) [3]
- Rhinobatos percellens Walbaum, 1792 (Chola guitarfish)
- Rhinobatos petiti Chabanaud, 1929 (Madagascar guitarfish)
- Rhinobatos planiceps Garman, 1880 (Pacific guitarfish)
- Rhinobatos prahli Acero P & Franke, 1995 (Gorgona guitarfish)
- Rhinobatos productus Ayres, 1854 (Shovelnose guitarfish)
- Rhinobatos punctifer Compagno & J. E. Randall, 1987 (Spotted guitarfish)
- Rhinobatos rhinobatos Linnaeus, 1758 (Common guitarfish)
- Rhinobatos sainsburyi Last, 2004 (Goldeneye shovelnose ray)
- Rhinobatos salalah J. E. Randall & Compagno, 1995 (Salalah guitarfish)
- Rhinobatos schlegelii J. P. Müller & Henle, 1841 (Brown guitarfish)
- Rhinobatos spinosus Günther, 1870 (Spiny guitarfish)
- Rhinobatos thouin Anonymous, referred to Lacépède, 1798 (Clubnose guitarfish)
- Rhinobatos thouiniana Shaw, 1804 (Shaw's shovelnose guitarfish)
- Rhinobatos variegatus Nair & Lal Mohan, 1973 (Stripenose guitarfish)
- Rhinobatos whitei Last, Corrigan & Naylor, 2014 (Philippine guitarfish) [5]
- Rhinobatos zanzibarensis Norman, 1926 (Zanzibar guitarfish)
Gallery
-
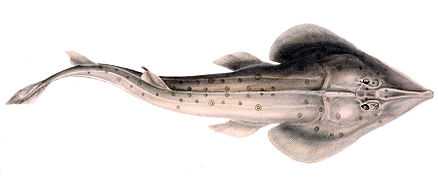
Rhinobatos annulatus
-

Rhinobatos hynnicephalus
-

Rhinobatos productus
-

Rhinobatos rhinobatos
-

Fossil of Rhinobatos whitfieldi
See also
References
- ↑ Sepkoski, Jack (2002). "A compendium of fossil marine animal genera (Chondrichthyes entry)". Bulletins of American Paleontology 364: p.560. Retrieved 2008-01-09.
- ↑ Wilga, C.D. & Motta, P.J. (1998): Feeding mechanism of the Atlantic guitarfish Rhinobatos lentiginosus: Modulation of kinematic and motor activity. Journal of Experimental Biology, 201 (23): 3167-3184.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Last, P.R., White, W.T. & Fahmi (2006). "Rhinobatos jimbaranensis and R. penggali, two new shovelnose rays (Batoidea: Rhinobatidae) from eastern Indonesia.". Cybium, 30 (3): 261–271.
- ↑ Last, P.R., Compagno, L.J.V. & Nakaya, K. (2004). "Rhinobatos nudidorsalis, a new species of shovelnose ray (Batoidea: Rhinobatidae) from the Mascarene Ridge, central Indian Ocean". Ichthyological Research, 51 (2): 153–158.
- ↑ Last, P.R., Corrigan, S. & Naylor, G. (2014). "Rhinobatos whitei, a new shovelnose ray (Batoidea: Rhinobatidae) from the Philippine Archipelago". Zootaxa, 3872 (1): 31–47.



