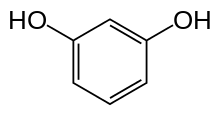
Resorcinol
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Benzene-1,3-diol | |||
| Other names
Resorcin m-dihydroxybenzene; 1,3-benzenediol; 1,3-Dihydroxybenzene; 3-Hydroxyphenol; m-hydroquinone; m-benzenediol; 3-hydroxycyclohexadien-1-one | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| ATC code | D10 S01AX06 | ||
| 108-46-3 | |||
| ChEBI | CHEBI:27810 | ||
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL24147 | ||
| ChemSpider | 4878 | ||
| |||
| Jmol-3D images | Image | ||
| KEGG | D00133 | ||
| PubChem | 5054 | ||
| |||
| UNII | YUL4LO94HK | ||
| UN number | 2876 | ||
| Properties | |||
| C6H6O2 | |||
| Molar mass | 110.1 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | White solid | ||
| Density | 1.28 g/cm3, solid | ||
| Melting point | 110 °C (230 °F; 383 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 277 °C (531 °F; 550 K) | ||
| 110 g/100 mL at 20 °C | |||
| Acidity (pKa) | 9.15[1] | ||
| Hazards | |||
| EU classification | Harmful (Xn) Dangerous for the environment (N) | ||
| Flash point | 127 °C; 261 °F; 400 K | ||
| Explosive limits | 1.4%-?[2] | ||
| US health exposure limits (NIOSH): | |||
| PEL (Permissible) |
none[2] | ||
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |||
| | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Resorcinol (or resorcin) is a dihydroxybenzene.
Chemistry
It is the 1,3-isomer of benzenediol with the formula C6H4(OH)2. Austrian chemist Heinrich Hlasiwetz (1825–1875) is remembered for his chemical analysis of resorcinol and for his part in the first preparation of resorcinol, along with Ludwig Barth, which was published in 1864.[3]:11[4][5]
Nomenclature
Benzene-1,3-diol is the name recommended by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) in its 1993 Recommendations for the Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry.[6]
Production
It is produced when any of a large number of resins (e.g., galbanum, asafoetida, etc.) are melted with potassium hydroxide, or by the distillation of Brazilwood extract. It may be prepared synthetically by melting 3-iodophenol, phenol-3-sulfonic acid, or benzene-1,3-disulfonic acid with potassium carbonate; by the action of nitrous acid on 3-aminophenol or on 1,3-diaminobenzene.[7] Many ortho- and para-compounds of the aromatic series (for example, the bromophenols, benzene-para-disulfonic acid) also yield resorcinol on fusion with potassium hydroxide.
Properties
Resorcinol crystallizes from benzene as colorless needles that are readily soluble in water, alcohol, and ether, but insoluble in chloroform and carbon disulfide. It reduces Fehling's solution and ammoniacal silver solutions. It does not form a precipitate with lead acetate solution, as does the isomeric pyrocatechol. Iron(III) chloride colors its aqueous solution a dark-violet, and bromine water precipitates tribromoresorcin. These properties are what give it its use as a colouring agent for certain chromatography experiments. Sodium amalgam reduces it to dihydroresorcin, which when heated to 150 to 160 °C with concentrated barium hydroxide solution gives γ-acetylbutyric acid (D. Vorlgnder); when fused with potassium hydroxide, resorcinol yields phloroglucin, pyrocatechol, and diresorcin. It condenses with acids or acid chlorides, in the presence of dehydrating agents, to oxyketones, e.g., with zinc chloride and glacial acetic acid at 145 °C it yields resacetophenone (HO)2C6H3~CO.CH3.[8] With the anhydrides of dibasic acids, it yields fluoresceins. When heated with calcium chloride—ammonia to 200 °C it yields meta-dioxydiphenylamine.[9] With sodium nitrite it forms a water-soluble blue dye, which is turned red by acids, and is used as an indicator, under the name of lacmoid.[10] It condenses readily with aldehydes, yielding with formaldehyde, on the addition of catalytic hydrochloric acid, methylene diresorcin [(HO)C6H3(O)]2•CH2. Reaction with chloral hydrate in the presence of potassium bisulfate yields the lactone of tetra-oxydiphenyl methane carboxylic acid.[11] In alcoholic solution it condenses with sodium acetoacetate to form 4-methylumbelliferone.[12]
In addition to electrophilic aromatic addition, resorcinol (and other poly-ols) undergo nucleophilic substitution via the enone form. With concentrated nitric acid, in the presence of cold concentrated sulfuric acid, it yields trinitro-resorcin (styphnic acid), which forms yellow crystals, exploding violently on rapid heating.
Occurrences
Resorcinol is one of the main natural phenols in argan oil.[13]
Presence of the resorcinol moiety
Parts of a molecule of catechin, another natural compound that is present in tea, has the resorcinol skeleton structure in it.
Alkylresorcinols are a marker of whole grain diet. 4-Hexylresorcinol is an anesthetic found in throat losenges.
Applications
Medical
Used externally, it is an antiseptic and disinfectant, and is used 5 to 10% in ointments in the treatment of chronic skin diseases such as psoriasis, hidradenitis suppurativa, and eczema of a sub-acute character. It is present in over-the-counter topical acne treatments at 2% or less concentration, and in prescription treatments at higher concentrations.[14] Weak, watery solutions of resorcinol (25 to 35 g/kg) are useful in allaying the itching in erythematous eczema. A 2% solution used as a spray has been used with marked effect in hay fever and in whooping cough. In the latter disease 0.6 mL of the 2% solution has been given internally. It can be included as an anti-dandruff agent in shampoo or in sunscreen cosmetics. It has also been employed in the treatment of gastric ulcers in doses of 125 to 250 mg in pills, and is said to be analgesic and haemostatic in its action. In large doses, it is a poison, causing giddiness, deafness, salivation, sweating, and convulsions. It is also worked up in certain medicated soaps. Monoacetylresorcinol, C6H4(OH)(O-COCH3), is used under the name of euresol.[15] Resorcinol is one of the active ingredients in products such as Resinol, Vagisil, and Clearasil.
Chemical
Resorcinol is also used as a chemical intermediate for the synthesis of pharmaceuticals and other organic compounds. It is used in the production of diazo dyes and plasticizers and as a UV absorber in resins.
An emerging use of resorcinol is as a template molecule in supramolecular chemistry. The -OH groups on resorcinol form hydrogen bonds to target molecules, holding them in the proper orientation for a reaction. Many such reactions are able to be carried out in the solid state, thereby reducing or eliminating the use of solvents that may be harmful to the environment. (see Green chemistry)
Resorcinol is an analytical reagent for the qualitative determination of ketoses (Seliwanoff's test).
Resorcinol is the starting material for resorcinarene molecules and the initiating explosive lead styphnate.[16]
Resorcinol reacts with formaldehyde to form a thermoset resin which can form the basis of an aerogel.
Related compounds
Resazurin, C12H7NO4, obtained by the action of nitrous acid on resorcinol,[17] forms small dark red crystals possessing a greenish metallic glance. When dissolved in concentrated sulfuric acid and warmed to 210 °C, the solution on pouring into water yields a precipitate of resorufin, C12H7NO3, an oxyphenoxazone, which is insoluble in water, but is readily soluble in hot concentrated hydrochloric acid, and in solutions of caustic alkalis. The alkaline solutions are of a rose-red color and show a cinnabar-red fluorescence. A tetrabromresorufin is used as a dye-stuff under the name of Fluorescent Resorcin Blue.
Thioresorcinol is obtained by the action of zinc and hydrochloric acid on the chloride of benzene meta-disulfonic acid. It melts at 27 °C and boils at 243 °C. Resorcinol disulfonic acid (HO)2C6H2(HSO3)2, is a deliquescent mass obtained by the action of sulfuric acid on resorcin.[18] It is easily soluble in water and decomposes when heated to 100 °C.
Alkylresorcinols are a class of phenolic lipids found in wheat or rye brans.
See also
References
- ↑ Gawron, O., Duggan, M., Grelechi, C., J. Anal. Chem., 1952, 24, 969.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards #0543". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ↑ Raj B. Durairaj. Resorcinol: Chemistry, Technology and Applications. Springer Science & Business Media, 2005 ISBN 9783540280903
- ↑ Virginia F. McConnell (1953) "Hlasiwetz and Barth — Pioneers in the structural aspects of plant products," Journal of Chemical Education, 30 (8) : 380. DOI 10.1021/ed030p380
- ↑ H. Hlasiwetz and L. Barth (1864) "Ueber einen neuen, dem Orcin homologen Körper" (On a new substance homologous to orcin), Annalen der Chemie, 130 (3) : 354-359. Resorcinol is named on p. 358: "Wir nennen den neuen Körper, da wir gefunden haben, dass er auch aus dem Ammoniakgummiharz erhalten werden kann, Resorcin, um an seine Entstehung aus Harzen und seine Beziehung zum Orcin zu erinnern." (We name the new substance, since we've found that it can be obtained from ammoniated resin gum, resorcin, in order to recall its creation from resin and its relation to orcin [i.e., orcinol].)
- ↑ Panico, R.; & Powell, W. H. (Eds.) (1994). A Guide to IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Compounds 1992. Oxford: Blackwell Science. ISBN 0-632-03488-2.
- ↑ Meyer, J (1897). Ber 30: 2569. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ↑ M. Nencki and N. Sieber, Jour. prak. Chem., 1881, 23, p. 147
- ↑ A. Seyewitz, Bull. Soc. Chins., 1890, 3, p. 811
- ↑ M. C. Traub and C. Hock, Ber., 1884, 17, p. 2615
- ↑ J. T. Hewitt and F. G. Pope, Jour. C/tern. Soc., 1897, 75, p. 1084
- ↑ A. Michael, Jour. prak. Chem., 1888, 37, 470
- ↑ Phenols and Polyphenols from Argania spinosa. Z. Charrouf and D. Guillaume, American Journal of Food Technology, 2007, 2, pages 679-683, doi:10.3923/ajft.2007.679.683
- ↑ Boer, J; Jemec, GB (2010). "Resorcinol peels as a possible self-treatment of painful nodules in hidradenitis suppurativa". Clin Exp Dermatol 35 (1): 36–40. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2230.2009.03377.x. PMID 19549239.
- ↑ Euresol, PubChem
- ↑ Army TM 9-1300-214, p. 7–12
- ↑ Weselsky, P; Benedikt, R (1880). Monats. f: 889. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ↑ Fischer, H (1881). Monats. 2: 321. Missing or empty
|title=(help)
External links
- International Chemical Safety Card 1033
- NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards
- IARC Monograph: "Resorcinol"
- IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry (online version of the "Blue Book")
![]() This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.