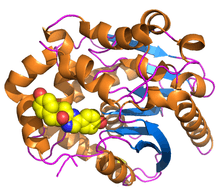
Renilla-luciferin 2-monooxygenase
| Renilla-luciferin 2-monooxygenase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC number | 1.13.12.5 | ||||||||
| CAS number | 61869-41-8 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / EGO | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Renilla-luciferin 2-monooxygenase (EC 1.13.12.5) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
- Renilla luciferin + O2
 oxidized Renilla luciferin + CO2 + hν
oxidized Renilla luciferin + CO2 + hν
The two substrates of this enzyme are Coelenterazine and O2, whereas its 3 products are coelenteramide, CO2, and a photon of blue light.
This enzyme was isolated from Renilla reniformis, the sea pansy, a bioluminescent sea pen. The enzyme belongs to the family of oxidoreductases, specifically those acting on single donors with O2 as oxidant and incorporation of two atoms of oxygen into the substrate (oxygenases). The oxygen incorporated need not be derived from O with incorporation of one atom of oxygen (internal monooxygenases o internal mixed-function oxidases).
In vivo, the photon emitted by Renilla-luciferin 2-monooxygenase transferred to green fluorescent protein, causing it to emit green light.
The systematic name of this enzyme class is Renilla-luciferin:oxygen 2-oxidoreductase (decarboxylating). Other names in common use include Renilla-type luciferase, aequorin, and luciferase (Renilla luciferin).
References
- ↑ Loening, A. M.; Fenn, T. D.; Gambhir, S. S. (2007). "Crystal Structures of the Luciferase and Green Fluorescent Protein from Renilla reniformis". Journal of Molecular Biology 374 (4): 1017–1028. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2007.09.078. PMC 2700051. PMID 17980388.
- Cormier MJ, Hori K, Anderson JM (1974). "Bioluminescence in coelenterates". Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 346 (2): 137–64. PMID 4154104.
- Hori K, Anderson JM, Ward WW, Cormier MJ (1975). "Renilla luciferin as the substrate for calcium induced photoprotein bioluminescence. Assignment of luciferin tautomers in aequorin and mnemiopsin". Biochemistry. 14 (11): 2371–6. doi:10.1021/bi00682a016. PMID 237531.
- Shimomura O, Johnson FH (1975). "Chemical nature of bioluminescence systems in coelenterates". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 72 (4): 1546–9. doi:10.1073/pnas.72.4.1546. PMC 432574. PMID 236561.
- Charbonneau H, Cormier MJ (1979). "Ca2+-induced bioluminescence in Renilla reniformis. Purification and characterization of a calcium-triggered luciferin-binding protein". J. Biol. Chem. 254 (3): 769–80. PMID 33174.
- Anderson JM, Charbonneau H, Cormier MJ (1974). "Mechanism of calcium induction of Renilla bioluminescence Involvement of a calcium-triggered luciferin binding protein". Biochemistry. 13 (6): 1195–200. doi:10.1021/bi00703a602. PMID 4149963.
- Lorenz WW, McCann RO, Longiaru M, Cormier MJ (1991). "Isolation and expression of a cDNA encoding Renilla reniformis luciferase". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88 (10): 4438–42. doi:10.1073/pnas.88.10.4438. PMC 51675. PMID 1674607.