Relative accessible surface area
Relative accessible surface area or relative accessibility of a protein residue is a measure of residue solvent exposure. It can be calculated by formula:
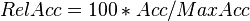 [1]
[1]
where 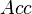 is the solvent accessible surface area and
is the solvent accessible surface area and 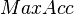 is the maximum possible solvent accessible surface area for the residue in
is the maximum possible solvent accessible surface area for the residue in 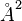 .
.
Maximum possible solvent accessible surface area for each Amino acid can be taken from the table below
| Amino acid code | Maximum solvent accessible surface |
|---|---|
| A | 106 |
| B | 160 |
| C | 135 |
| D | 163 |
| E | 194 |
| F | 197 |
| G | 84 |
| H | 184 |
| I | 169 |
| K | 205 |
| L | 164 |
| M | 188 |
| N | 157 |
| P | 136 |
| Q | 198 |
| R | 248 |
| S | 130 |
| T | 142 |
| V | 142 |
| W | 227 |
| X | 180 |
| Y | 222 |
| Z | 196 |
where B stands for D or N; Z for E or Q and X for an undetermined Amino acid.
References
Notes
- ↑ Hyunsoo, Park; Haesun. "Prediction of Protein Relative Solvent Accessibility with Support Vector Machines and Long-range Interaction 3D Local Descriptor". Retrieved 10 April 2015.
- ↑ Rost, Burkhard; Sander, Chris (November 1994). "Conservation and Prediction of Solvent Accessibility in Protein Families". Proteins 20 (Conservation and Prediction of Solvent Accessibility in Protein Families): 218. PMID 7892171. Retrieved 10 April 2015.