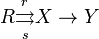Regular category
In category theory, a regular category is a category with finite limits and coequalizers of a pair of morphisms called kernel pairs, satisfying certain exactness conditions. In that way, regular categories recapture many properties of abelian categories, like the existence of images, without requiring additivity. At the same time, regular categories provide a foundation for the study of a fragment of first-order logic, known as regular logic.
Definition
A category C is called regular if it satisfies the following three properties:[1]
- C is finitely complete.
- If f:X→Y is a morphism in C, and
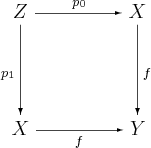
- is a pullback, then the coequalizer of p0,p1 exists. The pair (p0,p1) is called the kernel pair of f. Being a pullback, the kernel pair is unique up to a unique isomorphism.
- If f:X→Y is a morphism in C, and
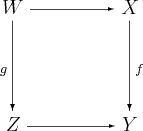
- is a pullback, and if f is a regular epimorphism, then g is a regular epimorphism as well. A regular epimorphism is an epimorphism which appears as a coequalizer of some pair of morphisms.
Examples
Examples of regular categories include:
- Set, the category of sets and functions between the sets
- More generally, every elementary topos
- Grp, the category of groups and group homomorphisms
- The category of rings and ring homomorphisms
- More generally, the category of models of any variety
- Every bounded meet-semilattice, with morphisms given by the order relation
- Abelian categories
The following categories are not regular:
- Top, the category of topological spaces and continuous functions
- Cat, the category of small categories and functors
Epi-mono factorization
In a regular category, the regular-epimorphisms and the monomorphisms form a factorization system. Every morphism f:X→Y can be factorized into a regular epimorphism e:X→E followed by a monomorphism m:E→Y, so that f=me. The factorization is unique in the sense that if e':X→E' is another regular epimorphism and m':E'→Y is another monomorphism such that f=m'e', then there exists an isomorphism h:E→E' such that he=e' and m'h=m. The monomorphism m is called the image of f.
Exact sequences and regular functors
In a regular category, a diagram of the form 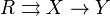 is said to be an exact sequence if it is both a coequalizer and a kernel pair. The terminology is a generalization of exact sequences in homological algebra: in an abelian category, a diagram
is said to be an exact sequence if it is both a coequalizer and a kernel pair. The terminology is a generalization of exact sequences in homological algebra: in an abelian category, a diagram
is exact in this sense if and only if 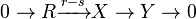 is a short exact sequence in the usual sense.
is a short exact sequence in the usual sense.
A functor between regular categories is called regular, if it preserves finite limits and coequalizers of kernel pairs. A functor is regular if and only if it preserves finite limits and exact sequences. For this reason, regular functors are sometimes called exact functors. Functors that preserve finite limits are often said to be left exact.
Regular logic and regular categories
Regular logic is the fragment of first-order logic that can express statements of the form
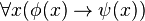 ,
,
where 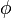 and
and 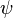 are regular formulae i.e. formulae built up from atomic formulae, the truth constant, binary meets and existential quantification. Such formulae can be interpreted in a regular category, and the interpretation is a model of a sequent
are regular formulae i.e. formulae built up from atomic formulae, the truth constant, binary meets and existential quantification. Such formulae can be interpreted in a regular category, and the interpretation is a model of a sequent
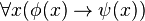 ,
,
if the interpretation of 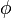 factors through the interpretation of
factors through the interpretation of 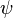 . This gives for each theory (set of sequences) and for each regular category C a category Mod(T,C) of models of T in C. This construction gives a functor Mod(T,-):RegCat→Cat from the category RegCat of small regular categories and regular functors to small categories. It is an important result that for each theory T and for each category C, there is a category R(T) and an equivalence
. This gives for each theory (set of sequences) and for each regular category C a category Mod(T,C) of models of T in C. This construction gives a functor Mod(T,-):RegCat→Cat from the category RegCat of small regular categories and regular functors to small categories. It is an important result that for each theory T and for each category C, there is a category R(T) and an equivalence
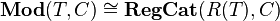 ,
,
which is natural in C. Up to equivalence any small regular category C arises this way as the classifying category, of a regular theory.
Exact (effective) categories
The theory of equivalence relations is a regular theory. An equivalence relation on an object 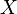 of a regular category is a monomorphism into
of a regular category is a monomorphism into 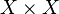 that satisfies the interpretations of the conditions for reflexivity, symmetry and transitivity.
that satisfies the interpretations of the conditions for reflexivity, symmetry and transitivity.
Every kernel pair 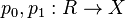 defines an equivalence relation
defines an equivalence relation 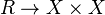 . Conversely, an equivalence relation is said to be effective if it arises as a kernel pair.[2] An equivalence relation is effective if and only if it has a coequalizer and it is the kernel pair of this.
. Conversely, an equivalence relation is said to be effective if it arises as a kernel pair.[2] An equivalence relation is effective if and only if it has a coequalizer and it is the kernel pair of this.
A regular category is said to be exact, or exact in the sense of Barr, or effective regular, if every equivalence relation is effective.[3]
Examples of exact categories
- The category of sets is exact in this sense, and so is any (elementary) topos. Every equivalence relation has a coequalizer, which is found by taking equivalence classes.
- Every abelian category is exact.
- Every category that is monadic over the category of sets is exact.
- The category of Stone spaces is exact.
See also
References
- Michael Barr, Pierre A. Grillet, Donovan H. van Osdol. Exact Categories and Categories of Sheaves, Springer, Lecture Notes in Mathematics 236. 1971.
- Francis Borceux, Handbook of Categorical Algebra 2, Cambridge University Press, (1994).
- Stephen Lack, A note on the exact completion of a regular category, and its infinitary generalizations". Theory and Applications of Categories, Vol.5, No.3, (1999).
- Carsten Butz (1998), Regular Categories and Regular Logic, BRICS Lectures Series LS-98-2, (1998).
- Jaap van Oosten (1995), Basic Category Theory, BRICS Lectures Series LS-95-1, (1995).
- Pedicchio, Maria Cristina; Tholen, Walter, eds. (2004). Categorical foundations. Special topics in order, topology, algebra, and sheaf theory. Encyclopedia of Mathematics and Its Applications 97. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-83414-7. Zbl 1034.18001.