Registered Retirement Income Fund
A Registered Retirement Income Fund (RRIF) is a tax-deferred retirement plan under Canadian tax law. Individuals use an RRIF to generate income from the savings accumulated under their Registered Retirement Savings Plan. As with an RRSP, an RRIF account is registered with the Canada Revenue Agency.
Converting from RRSP
The option exists to convert a RRSP into an RRIF anytime on or before an individual reaches their 71st year. Before the end of the year in which an individual turns 71, it is mandatory to either withdraw all funds from a RRSP plan or convert the RRSP to a RRIF or life annuity. If funds are simply withdrawn from a RRSP, the entire amount is fully taxable as ordinary income; one defers this taxation by transferring investments in a RRSP into an RRIF.
Functionality
Investments held inside a RRIF grow in a tax-deferred manner just as with a RRSP. There are two primary differences between a RRSP and a RRIF. The first is that no further contributions can be made once conversion to a RRIF has occurred. The other is a special functionality called a minimum RRIF withdrawal.
A minimum RRIF withdrawal is an annual obligatory amount which is cashed out of a RRIF and sent to the account-holder without withholding tax. The withdrawal remains taxable Canadian income, but is eligible for a tax credit to reduce federal income tax by up to 15% of $2,000. In most provinces, a tax credit is also available to reduce provincial income tax.[1]
The minimum RRIF withdrawal each year is determined by a percentage that is calculated by the account holder's age and the total value of the plan on January 1 each year.[2] The holder of a RRIF may elect to withdraw an amount greater than the minimum RRIF amount for that year, though withholding tax will apply to this supplementary amount.
As an example, if a RRIF is valued at $500,000 when the account holder is 72 at the start of the year, the minimum annual payout will be $37,400, 7.48% of the value of the plan at the beginning of the year:[2] 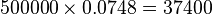 .
.
A pre-computed table for ages 65 to 78:[2]
| Age of Account Holder on January 1 |
Percentage of Total RRIF Value to be Withdrawn |
|---|---|
| 65 | 4.00% |
| 66 | 4.17% |
| 67 | 4.35% |
| 68 | 4.55% |
| 69 | 4.76% |
| 70 | 5.00% |
| 71 | 7.38% |
| 72 | 7.48% |
| 73 | 7.59% |
| 74 | 7.71% |
| 75 | 7.85% |
| 76 | 7.99% |
| 77 | 8.15% |
| 78 | 8.33% |
The minimum withdrawals are defined as:[3]
| Age of Account Holder on January 1 |
Percentage of Total RRIF Value to be Withdrawn |
|---|---|
| under 71 ("x") | 1/(90 − x) |
| 79 | 8.53% |
| 80 | 8.75% |
| 81 | 8.99% |
| 82 | 9.27% |
| 83 | 9.58% |
| 84 | 9.93% |
| 85 | 10.33% |
| 86 | 10.79% |
| 87 | 11.33% |
| 88 | 11.96% |
| 89 | 12.71% |
| 90 | 13.62% |
| 91 | 14.73% |
| 92 | 16.12% |
| 93 | 17.92% |
| 94+ | 20.00% |
References
- ↑ "Tax Return Line 314 - Pension income amount". Canada Revenue Agency.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 "RRIF Minimum Withdrawal". CIBC Wood Gundy. Retrieved 2014-02-27.
- ↑ "Income Tax Information Circular 78-18R6: Registered Retirement Income Funds" (PDF). Canada Revenue Agency. 2002-03-06. Retrieved 2014-02-27.