Receptor protein serine/threonine kinase
| Receptor protein serine/threonine kinase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC number | 2.7.11.30 | ||||||||
| CAS number | 146702-86-5 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| |||||||||
In enzymology, a receptor protein serine/threonine kinase (EC 2.7.11.30) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
- ATP + [receptor-protein]
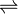 ADP + [receptor-protein] phosphate
ADP + [receptor-protein] phosphate
Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are ATP and receptor-protein, whereas its two products are ADP and phosphate.
This enzyme belongs to the family of transferases, to be specific those transferring phosphorus-containing groups protein-serine/threonine kinases. The systematic name of this enzyme class is ATP:[receptor-protein] phosphotransferase. Other names in common use include activin receptor kinase, receptor type I serine/threonine protein kinase, receptor type II serine/threonine protein kinase, STK13, TGF-beta kinase, and receptor serine/threonine protein kinase. This enzyme participates in 7 metabolic pathways: mapk signaling pathway, cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction, TGF beta signaling pathway, adherens junction, colorectal cancer, pancreatic cancer, and chronic myeloid leukemia.
Structural studies
As of late 2007, 5 structures have been solved for this class of enzymes, with PDB accession codes 2GOO, 2H62, 2H64, 2HLQ, and 2HLR.
References
- Wrana JL, Attisano L, Wieser R, Ventura F, Massague J (1994). "Mechanism of activation of the TGF-beta receptor". Nature. 370 (6488): 341–7. doi:10.1038/370341a0. PMID 8047140.
- Massague J, Chen YG (2000). "Controlling TGF-beta signaling". Genes. Dev. 14 (6): 627–44. PMID 10733523.
- Lechleider RJ; Hemmati, P; Larisch-Bloch, S; Ajmera, R; Roberts, AB; Lechleider, RJ (1997). "Characterization of functional domains within Smad4/DPC4". J. Biol. Chem. 272 (21): 13690–6. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.21.13690. PMID 9153220.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||