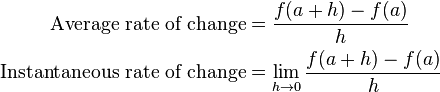Rate (mathematics)
In mathematics, a rate is the ratio between two related quantities.[1] Often it is a rate of change. If the unit or quantity in respect of which something is changing is not specified, usually the rate is per unit time. However, a rate of change can be specified per unit time, or per unit of length or mass or another quantity. The most common type of rate is "per unit time", such as speed, heart rate and flux. Ratios that have a non-time denominator include exchange rates, literacy rates and electric flux.
In describing the units of a rate, the word "per" is used to separate the units of the two measurements used to calculate the rate (for example a heart rate is expressed "beats per minute"). A rate defined using two numbers of the same units (such as tax rates) or counts (such as literacy rate) will result in a dimensionless quantity, which can be expressed as a percentage (for example, the global literacy rate in 1998 was 80%) or fraction or as a multiple.
Often rate is a synonym of rhythm or frequency, a count per second (i.e., Hertz); e.g., radio frequencies or heart rate or sample rate.
Rate of change
A rate of change can be formally defined in two ways:[2]
where f(x) is the function with respect to x over the interval from a to a+h. An instantaneous rate of change is equivalent to a derivative.
An example to contrast the differences between the average and instantaneous definitions: the speed of a car can be calculated:
- An average rate can be calculated using the total distance travelled between a and b, divided by the travel time
- An instantaneous rate can be determined by viewing a speedometer.
Terms based on rates
In chemistry and physics:
- Speed, being the distance covered per unit time; e.g., miles per hour and meters per second
- Acceleration, the rate of change in speed, or the change in speed per unit time
- Radioactive decay, the amount of radioactive material in which one nucleus decays per second, measured in Becquerels
- Reaction rate, the speed at which chemical reactions occur
- Volumetric flow rate, the volume of fluid which passes through a given surface per unit time; e.g., cubic meters per second
In computing:
- Bit rate, the number of bits that are conveyed or processed by a computer per unit of time
- Symbol rate, the number of symbol changes (signalling events) made to the transmission medium per second
- Sampling rate, the number of samples (signal measurements) per second
In finance:
- Interest rate, the price a borrower pays for the use of money they do not own, usually expressed as a percentage rate over the period of one year; see also for related rates
- Exchange rate, how much one currency is worth in terms of the other
- Inflation rate, a measure of inflation change per year
- Rate of return, the ratio of money gained or lost on an investment relative to the amount of money invested
- Tax rate, the tax amount divided by the taxable income
Miscellaneous definitions:
- Rate of reinforcement, number of reinforcements per time, usually per minute
- Heart rate, usually measured in beats per minute
- Unemployment rate, a ratio between those in the labor force to those who are unemployed
- Birth rate and mortality rate, the number of births or deaths scaled to the size of that population, per unit time
- Literacy rate, the proportion of the population over age fifteen that can read and write
References
- ↑ "On-line Mathematics Dictionary". MathPro Press. January 14, 2006. Retrieved 2009-03-01.
- ↑ Adams, Robert A. (1995). Calculus: A Complete Course (3rd ed.). Addison-Wesley Publishers Ltd. p. 129. ISBN 0-201-82823-5.