Ranavirus
| Ranavirus | |
|---|---|
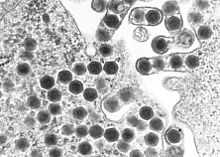 | |
| Transmission electron micrograph of ranaviruses (dark hexagons) gathering at the cell border and leaving the cell via a process called "budding". | |
| Virus classification | |
| Group: | Group I (dsDNA) |
| Order: | Incertae sedis |
| Family: | Iridoviridae |
| Genus: | Ranavirus |
| Species | |
|
Ambystoma tigrinum virus | |

Ranavirus is one of five genera of viruses within the family Iridoviridae, one of the five families of nucleocytoplasmic large DNA viruses. Ranavirus is the only genus within Iridoviridae that includes viruses that are infectious to amphibians and reptiles, and one of only three genera within this family which infect teleost fishes, along with Lymphocystivirus and Megalocytivirus.[1] The ranaviruses, like the megalocytiviruses, are an emerging group of closely related dsDNA viruses which cause systemic infections in a wide variety of wild and cultured fresh and saltwater fishes. As with megalocytiviruses, Ranavirus outbreaks are therefore of considerable economic importance in aquaculture, as epizootics can result in moderate fish loss or mass mortality events of cultured fishes. Unlike megalocytiviruses, however, Ranavirus infections in amphibians have been implicated as a contributing factor in the global decline of amphibian populations. The impact of ranaviruses on amphibian populations has been compared to the chytrid fungus Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis, the causative agent of chytridiomycosis.[2][3][4]
Etymology
Rana is derived from the Latin for "frog",[5] reflecting the first isolation of a Ranavirus in 1960s from the Northern leopard frog (Lithobates pipiens – formerly Rana pipiens).[6][7][8]
Evolution

The ranaviruses appear to have evolved from a fish virus which subsequently infected amphibians and reptiles.[9]
Taxonomy
The family Iridoviridae is divided into five genera which include Chloriridovirus, Iridovirus, Lymphocystivirus, Megalocytivirus, and Ranavirus. The genus Ranavirus is composed of at least 6 recognized viral species, 3 of which are known to infect amphibians (Ambystoma tigrinum virus (ATV), Bohle iridovirus (BIV), and frog virus 3).[10]
Several reptile species are known to be affected:
- Green pythons (Chondropython viridis)[11]
- Burmese star tortoises (Geochelone platynota)
- Leopard tortoise (Geochelone pardalis)[12]
- Gopher tortoises (Gopherus polyphemus)
- Mountain lizard (Lacerta monticola)[13]
- Eastern box turtles (Terrapene carolina carolina)[14]
- Florida box turtles (Terrapene carolina bauri)
- Western ornate box turtles (Terrapene ornata)[15]
- Spur-thighed tortoises (Testudo graeca)[16]
- Hermann’s tortoises (Testudo hermanni)
- Egyptian tortoises (Testudo kleinmanni)
- Russian tortoises (Testudo horsfieldii)
- Marginated tortoises (Testudo marginata)
- Red-eared sliders (Trachemys scripta elegans)[15]
- Chinese softshell turtles (Trionyx sinensis)[17]
- Gecko (Uroplatus fimbriatus)[18]
Structure
Ranaviruses are large icosahedral DNA viruses measuring approximately 150 nm in diameter with a large single linear dsDNA genome of roughly 105 kbp [19] which codes for around 100 gene products.[20] The main structural component of the protein capsid is the major capsid protein (MCP).
Replication
Ranaviral replication is well-studied using the type species for the genus, frog virus 3 (FV3).[10][19] Replication of FV3 occurs between 12 and 32 degrees Celsius.[20] Ranaviruses enter the host cell by receptor-mediated endocytosis.[21] Viral particles are uncoated and subsequently move into the cell nucleus, where viral DNA replication begins via a virally encoded DNA polymerase.[22] Viral DNA then abandons the cell nucleus and begins the second stage of DNA replication in the cytoplasm, ultimately forming DNA concatemers.[22] The viral DNA is then packaged via a headful mechanism into infectious virions.[10] The ranavirus genome, like other iridoviral genomes is circularly permuted and exhibits terminally redundant DNA.[22]
Transmission
Transmission of ranaviruses is thought to occur by multiple routes, including contaminated soil, direct contact, waterborne exposure, and ingestion of infected tissues during predation, necrophagy or cannibalism.[7] Ranaviruses are relatively stable in aquatic environments, persisting several weeks or longer outside a host organism.[7]
Epizoology
Amphibian mass mortality events due to Ranavirus have been reported in Asia, Europe, North America, and South America.[7] Ranaviruses have been isolated from wild populations of amphibians in Australia, but have not been associated with mass mortality on that continent.[7][23][24]
Pathogenesis
Synthesis of viral proteins begins within hours of viral entry[20] with necrosis or apoptosis occurring as early as a few hours post-infection.[19][25]
Gross pathology
Gross lesions associated with Ranavirus infection include erythema, generalized swelling, hemorrhage, limb swelling, and swollen and friable livers.[7]
See also
References
- ↑ Whittington, RJ; Becker, JA; Dennis, MM (2010). "Iridovirus infections in finfish – critical review with emphasis on ranaviruses". Journal of fish diseases 33 (2): 95–122. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2761.2009.01110.x. PMID 20050967.
- ↑ Jancovich, James K; Mao, Jinghe; Chinchar, V.Gregory; Wyatt, Christopher; Case, Steven T; Kumar, Sudhir; Valente, Graziela; Subramanian, Sankar; Davidson, Elizabeth W; Collins, James P; Jacobs, Bertram L (2003). "Genomic sequence of a ranavirus (family Iridoviridae) associated with salamander mortalities in North America". Virology 316 (1): 90–103. doi:10.1016/j.virol.2003.08.001. PMID 14599794.
|first12=missing|last12=in Authors list (help) - ↑ Brunner, Jesse L.; Schock, Danna M.; Davidson, Elizabeth W.; Collins, James P. (2004). "Intraspecific Reservoirs: Complex Life History and the Persistence of a Lethal Ranavirus". Ecology 85 (2): 560. doi:10.1890/02-0374.
- ↑ Pearman, Peter B.; Garner, Trenton W. J. (2005). "Susceptibility of Italian agile frog populations to an emerging strain of Ranavirus parallels population genetic diversity". Ecology Letters 8 (4): 401. doi:10.1111/j.1461-0248.2005.00735.x.
- ↑ Harper, Douglas. "frog". Online Etymology Dictionary.
- ↑ Granoff, A; Came, PE; Rafferty, KA (1965). "The isolation and properties of viruses from Rana pipiens: their possible relationship to the renal adenocarcinoma of the leopard frog". Annals of New York Academy of Science 126 (1): 237–255. Bibcode:1965NYASA.126..237G. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb14278.x. PMID 5220161.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 7.5 Gray, MJ; Miller, DL; Hoverman, JT (2009). "Ecology and pathology of amphibian ranaviruses". Diseases of Aquatic Organisms 87 (3): 243–266. doi:10.3354/dao02138. PMID 20099417.
- ↑ Rafferty, KA (1965). "The cultivation of inclusion-associated viruses from Lucke tumor frogs". Annals of New York Academy of Science 126 (1): 3–21. Bibcode:1965NYASA.126....3R. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb14266.x. PMID 5220167.
- ↑ Jancovich, JK; Bremont, M; Touchman, JW; Jacobs, BL (2010). "Evidence for multiple recent host species shifts among the Ranaviruses (family Iridoviridae)". J Virol 84 (6): 2636–2647. doi:10.1128/JVI.01991-09. PMC 2826071. PMID 20042506.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 Chinchar VG, Essbauer S, He JG, Hyatt A, Miyazaki T, Seligy V, Williams T (2005). "Family Iridoviridae" pp. 145–162 in Fauquet CM, Mayo MA, Maniloff J, Desselburger U, Ball LA (eds). Virus Taxonomy, Eighth report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. Academic Press, San Diego, USA.
- ↑ First identification of a ranavirus from green pythons (Chondropython viridis); Williamson; Coupar; Middleton; Hengstberger; Gould; Selleck; Wise; Kattenbelt; Cunningham; Lee (2002). "First identification of a ranavirus from green pythons (Chondropython viridis)". Journal of Wildlife Diseases 38 (2): 239–52. doi:10.7589/0090-3558-38.2.239. PMID 12038121.
- ↑ Benetka V. (2007). "First report of an iridovirus (genus Ranavirus) infection in a leopard tortoise (Geochelone pardalis pardalis)" (PDF). Vet Med Austria 94: 243–248.
- ↑ De Matos, A. P.; Caeiro, M. F.; Papp, T; Matos, B. A.; Correia, A. C.; Marschang, R. E. (2011). "New viruses from Lacerta monticola (Serra da Estrela, Portugal): Further evidence for a new group of nucleo-cytoplasmic large deoxyriboviruses (NCLDVs)". Microscopy and microanalysis : the official journal of Microscopy Society of America, Microbeam Analysis Society, Microscopical Society of Canada 17 (1): 101–8. Bibcode:2011MiMic..17..101A. doi:10.1017/S143192761009433X. PMID 21138619.
- ↑ Mao, J; Hedrick, RP; Chinchar, VG (1997). "Molecular characterization, sequence analysis, and taxonomic position of newly isolated fish iridoviruses". Virology 229 (1): 212–220. doi:10.1006/viro.1996.8435. PMID 9123863.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 Johnson, A. J.; Pessier, A. P.; Jacobson, E. R. (2007). "Experimental transmission and induction of ranaviral disease in Western Ornate box turtles (Terrapene ornata ornata) and red-eared sliders (Trachemys scripta elegans)". Veterinary Pathology 44 (3): 285–97. doi:10.1354/vp.44-3-285. PMID 17491069.
- ↑ Blahak S., Uhlenbrok C. "Ranavirus infections in European terrestrial tortoises in Germany". Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Reptile and Amphibian Medicine; Munich, Germany. 4–7 March 2010; pp. 17–23
- ↑ Chen, Z. X.; Zheng, J. C.; Jiang, Y. L. (1999). "A new iridovirus isolated from soft-shelled turtle". Virus research 63 (1–2): 147–51. doi:10.1016/S0168-1702(99)00069-6. PMID 10509727.
- ↑ Marschang, R. E.; Braun, S; Becher, P (2005). "Isolation of a ranavirus from a gecko (Uroplatus fimbriatus)". Journal of zoo and wildlife medicine : official publication of the American Association of Zoo Veterinarians 36 (2): 295–300. doi:10.1638/04-008.1. JSTOR 20096453. PMID 17323572.
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 19.2 Williams T, Barbosa-Solomieu V, Chinchar GD (2005). "A decade of advances in iridovirus research" 173-148. In Maramorosch K, Shatkin A (eds). Advances in virus research, Vol. 65 Academic Press, New York, USA.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 20.2 Chinchar, VG (2002). "Ranaviruses (family Iridoviridae) emerging cold-blooded killers". Archives of Virology 147 (3): 447–470. doi:10.1007/s007050200000. PMID 11958449.
- ↑ Eaton, Heather E.; Ring, Brooke A.; Brunetti, Craig R. (2010). "The genomic diversity and phylogenetic relationship in the family Iridoviridae". Viruses 2 (7): 1458. doi:10.3390/v2071458. PMID 21994690.
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 22.2 Goorha, R (1982). "Frog virus 3 DNA replication occurs in two stages". Journal of Virology 43 (2): 519–28. PMC 256155. PMID 7109033.
- ↑ Speare, R; Smith, JR (1992). "An iridovirus-like agent isolated from the ornate burrowing frog Limnodynastes ornatus in northern Australia". Diseases of Aquatic Organisms 14: 51–57. doi:10.3354/dao014051.
- ↑ Cullen, BR; Owens, L (2002). "Experimental challenge and clinical cases of Bohle iridovirus (BIV) in native Australian anurans". Diseases of Aquatic Organisms 49 (2): 83–92. doi:10.3354/dao049083. PMID 12078986.
- ↑ Chinchar, VG; Bryan, L; Wang, J; Long, S; Chinchar, GD (2003). "Induction of apoptosis in frog virus 3-infected cells". Virology 306 (2): 303–312. doi:10.1016/S0042-6822(02)00039-9. PMID 12642103.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Ranavirus. |
![]() Data related to List of viruses at Wikispecies
Data related to List of viruses at Wikispecies