Rail transport in Hong Kong
Hong Kong's rail network comprises public transport trains operated by MTR Corporation Limited (MTRC). The MTRC operates the metro network of Hong Kong and the commuter rail network connecting the northeastern and northwestern New Territories with the rest of Hong Kong. Approval has been granted for the merger of the MTRC and the Kowloon-Canton Railway Corporation (KCRC), following discussions to merge the two corporations for economies of scale and cost effectiveness.
History
The first mode of rail transport was the Peak Tram, serving The Peak, the Mid-levels and the city centre since 1888. Tram started service along the northern coast of the Hong Kong Island in 1904. The British Section of the Kowloon-Canton Railway (now the KCR East Rail), a conventional railway, was opened in 1910. It was not until 1979 that a rapid transit system, the MTR, was opened. In 1982, the British Section of the Kowloon-Canton Railway began its transition towards electrification, with new EMUs providing rapid transit-like service. The Light Rail Transit (LRT, now the MTR Light Rail) began its operation in the Tuen Mun and Yuen Long new towns in 1988. The two railway companies, MTR Corporation Limited and Kowloon-Canton Railway Corporation, merged on 2 December 2007, to form a single rapid transit network.
There are several extensions planned or under construction, including the Sha Tin to Central Link and the Northern Link.
MTR
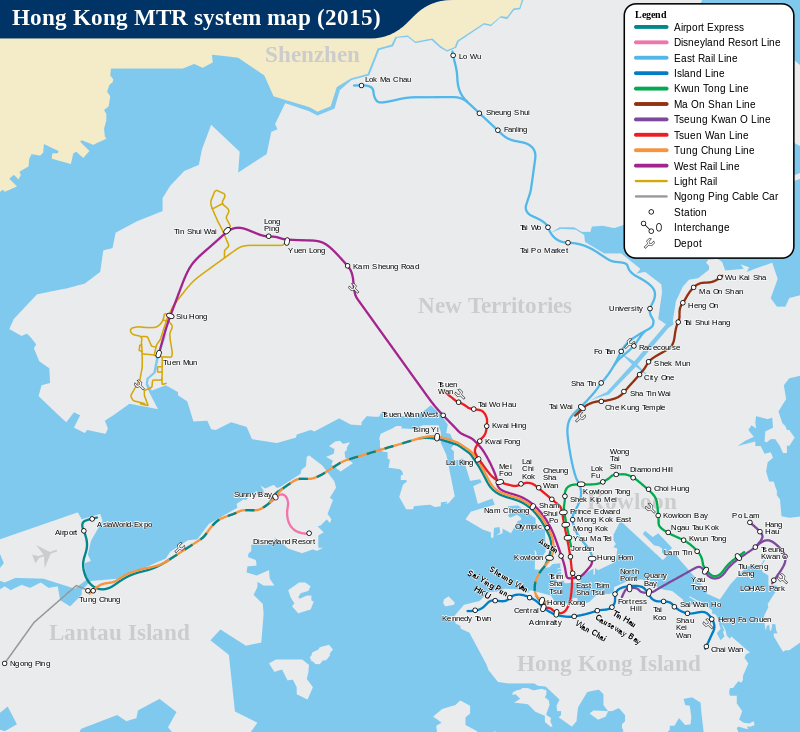
The MTR network comprises 10 lines, 84 railway stations and 68 Light Rail stops:
- East Rail Line: between Lo Wu and Lok Ma Chau and Hung Hom (formerly part of KCR/KCRC)
- Kwun Tong Line: between Yau Ma Tei and Tiu Keng Leng
- Tsuen Wan Line: between Tsuen Wan and Central
- Island Line: between Kennedy Town and Chai Wan
- Tung Chung Line: between Tung Chung and Hong Kong
- Tseung Kwan O Line: between Po Lam/LOHAS Park and North Point
- Disneyland Resort Line: between Sunny Bay and Disneyland Resort
- West Rail Line: between Tuen Mun to Hung Hom (formerly part of KCR/KCRC)
- Ma On Shan Line: between Wu Kai Sha to Tai Wai (formerly part of KCR/KCRC)
- Airport Express: between AsiaWorld-Expo/Airport and Hong Kong
- Light Rail: 68 stations serving the northwest New Territories (formerly part of KCR/KCRC)
This system also makes about $2 billion in annual profit.[1]
Trams

- Hong Kong Tramways: Double-decker trams, running on the north shore of Hong Kong Island from Kennedy Town to Shau Kei Wan.
- Peak Tram: Actually a funicular railway with six stations, connecting Central and the Victoria Peak.
- Po Fook Hill Elevator: Another tiny funicular railway with two stations, connecting the car park and the upper section of Po Fook Hill Cemetery.
Note that the KCRC Light Rail system (see above) has many of the attributes of a tramway, including street running.
Cross-border services
Commonly known as Through Train (chi. 直通車), the MTRC and railway companies of mainland China jointly provide cross-border train services from Hung Hom Station, Kowloon, sharing most of the tracks with the East Rail Line, to destinations in mainland China through neighbouring Shenzhen on three Through Train routes, namely Beijing line (to/from Beijing), Shanghai line (to/from Shanghai) and Guangdong line (to/from Zhaoqing and Guangzhou East). They are operated through the rail network in mainland China, including the Guangshen Railway and Jingguang Railway.
Automated People Mover
There is an Automated People Mover (APM),[2] a driverless electric train service, which is located at the basement level of Terminal 1 of Hong Kong International Airport. It travels the length of the 750-metre concourse between the East Hall and West Hall on a circular mode. Running at a speed of 62 km per hour, each APM carries 304 passengers in four cars. The APM operates every 2.5 minutes from 0600 to 0030 hours everyday. It transports passengers whose flights are located at the West Hall, Southwest and Northwest concourses.
Rail gauges and power supply
Rail gauges and power supply of Hong Kong rails.
| Rail | Rail gauge | Power supply | Remarks | Signal system | Height of platform (mm) | Maximum car width (mm) | Height clearance | Height of overhead cable | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MTR Island Line, Kwun Tong Line, Tseung Kwan O Line, Tsuen Wan Line, Tung Chung Line, Airport Express | 1,432 mm (4 ft 8 3⁄8 in) (Narrow gauge) | 1500 V DC | overhead cable | SACEM and SACEM-SICAS for TKL, all lines to be upgraded to SelTrac in the 2020s | 3200 | ||||
| MTR Disneyland Resort Line | 1,432 mm (4 ft 8 3⁄8 in) (Narrow gauge) | 1500 V DC | overhead cable | SelTrac CBTC/R UTO | 3200 | ||||
| MTR East Rail Line, West Rail Line, Ma On Shan Line (formerly operated by KCR/KCRC) | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in) (Standard gauge) | 25 kV AC | overhead cable | same as railways in mainland China | SelTrac CBTC DTO | 3100 | |||
| MTR Light Rail (formerly operated by KCR/KCRC) | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in) (Standard gauge) | 750 V DC | overhead cable | Siemens MMI | 910 | 2650 | Safety Height 5.3m | ||
| Peak Tram | 1,520 mm (4 ft 11 27⁄32 in) (Russian gauge) | n/a | n/a | Funicular | |||||
| Hong Kong Tramways | 3 ft 6 in (1,067 mm) | 550 V DC | overhead cable | ||||||
| Hong Kong International Airport Automated People Mover | 3-phase 600V a.c. | Third Rail | SelTrac | ||||||
| Hong Kong Disneyland Railroad | steam-outline | ||||||||
| Ocean Park Ocean Express | Funicular | ||||||||
List of densely populated places without rail transport
- Hong Kong Island
- Wong Chuk Hang, Aberdeen, Ap Lei Chau and Wah Fu
- Kowloon
- Most of Tai Wo Ping (Shek Kip Mei)
- Tsz Wan Shan
- Sau Mau Ping and Shun Lee
- Most of Hung Hom, Ho Man Tin, To Kwa Wan, Ma Tau Wai, Kowloon City and San Po Kong
- New Territories
- Sheung Kwai Chung
- Tsing Yi
- Chai Wan Kok
- Sai Kung
MTR route map
Ended systems
- Mount Parker Cable Car
- Kai Tak Amusement Park Monorail
- Lai Chi Kok Amusement Park Monorail
See also
- List of railways in China
- Rail transport in the People's Republic of China
- Transport in Hong Kong
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Rail transport in Hong Kong. |
External links
| ||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||