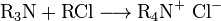Quaternary compound
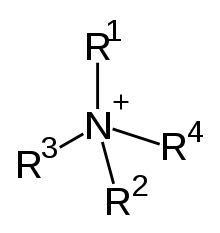
Quaternary ammonium cation. The R's may be the same or different groups. They may also be connected (cyclic).
In chemistry, a quaternary compound is a cation consisting of a central positively charged nitrogen group atom with four substituents, especially organic (alkyl and aryl) groups, discounting hydrogen atoms.[1]
The best known quaternary compounds are quaternary ammonium cations, having a nitrogen atom at the centre.[2] For example, in the following reaction, the nitrogen atom is said to be quaternized as it has gone from 3 to 4 substituents:
Other examples include substituted phosphonium salts (R4P+), substituted arsonium salts (R4As+) like arsenobetaine, as well as some arsenic containing superconductors.[3] Substituted stibonium (R4Sb+)[4] and bismuthonium salts (R4Bi+) have also been described.[5]
See also
- Onium compounds
References
- ↑ IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "Onium compounds".
- ↑ IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "quaternary ammonium compounds".
- ↑ Ren, Z. A.; Yang, J.; Lu, W.; Yi, W.; Shen, X. L.; Li, Z. C.; Che, G. C.; Dong, X. L.; Sun, L. L.; Zhou, F.; Zhao, Z. X. (2008). "Superconductivity in the iron-based F-doped layered quaternary compound Nd[O1 − x Fx]FeAs". EPL (Europhysics Letters) 82 (5): 57002. arXiv:0803.4234. Bibcode:2008EL.....8257002R. doi:10.1209/0295-5075/82/57002.
- ↑ Widler, H. -J.; Schwarz, W.; Hausen, H. -D.; Weidlein, J. (1977). "Tetramethyl-Arsonium- und -Stibonium-Methylchlorometallate des Galliums und Indiums". Zeitschrift für anorganische und allgemeine Chemie 435: 179. doi:10.1002/zaac.19774350124.
- ↑ Nicholas C. Norman (1997). Chemistry of arsenic, antimony, and bismuth. Springer Netherlands. p. 316. ISBN 0-7514-0389-X.