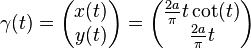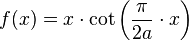Quadratrix of Hippias
The quadratrix or trisectrix of Hippias (also quadratrix of Dinostratos) is a curve, which is created by a uniform motion. It is one of the oldest examples for a kinematic curve, that is a curve created through motion. Its discovery is attributed to the Greek sophist Hippias of Elis, who used it around 420 BC in an attempt to solve the angle trisection problem (hence trisectrix). Later around 350 BC Dinostratus used it in an attempt to solve the problem of squaring the circle (hence quadratrix).
Definition
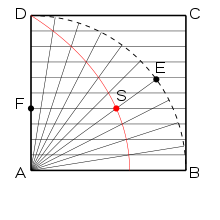
Consider a square ABCD with an inscribed quarter circle centered in A, such that the side of the square is the circle's radius. Let E be a point that travels with a constant angular velocity on the quarter circle arc from D to B. In addition the point F travels with a constant velocity from D to A on the line segment AD, in such away that E and F start at the same time at D and arrive at the same time in B and D. Now the quadratrix is defined as the locus of the intersection of the parallel to AB through F and the line segment AE.[1][2]
If one places such a square ABCD with side length a in a (cartesian) coordinate system with the side AB on the x-axis and vertex A in the origin, then the quadratix is described by a planar curve ![\gamma:(0,\tfrac{\pi}{2}]\rightarrow \mathbb{R}^2](../I/m/fb3e4961cfcf1f093973a887c793314d.png) with:
with:
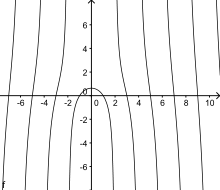
This description can also be used to give an analytical rather than a geometric definition of the quadratrix and to extend it beyond the ![(0,\tfrac{\pi}{2}]](../I/m/dcf6978f51fcf5dfa9413bae688ae0da.png) interval. It does however remain undefined at the singularities of
interval. It does however remain undefined at the singularities of 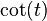 except for the case of
except for the case of 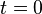 , where due to
, where due to 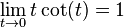 the singularity is removable and hence yields a continuous planar curve on the interval
the singularity is removable and hence yields a continuous planar curve on the interval 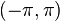 [3][4]
[3][4]
To describe the quadratrix as simple function rather than planar curve, it is advantageous to switch the y-axis and the x-axis, that is to place the side AB on y-axis rather than on the x-axis. Then the quadratrix is given by the following function f(x):[5][6]
Angle trisection
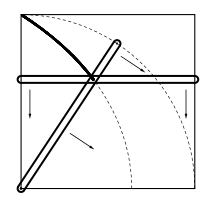
The trisection of an arbitrary angle using only ruler and compasses is impossible. However if the quadratrix is allowed as an additional tool, it is possible to divide an arbitrary angle into n equal segment and hence a trisection (n = 3) becomes possible. In practical terms the quadratrix can be drawn with the help of a template or a quadratrix compass (see drawing).[1][2]
Since by the definition of the quadratrix the traversed angle is proportional to the traversed segment of the associated squares' side dividing that segment on the side into n equal parts yields a partition of the associated angle as well. Dividing the line segment into n equal parts with ruler and compass is possible due to the intercept theorem.
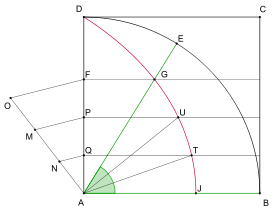
For a given angle BAE ( ≤ 90°) construct a square ABCD over its leg AB. The other leg of the angle intersects the quadratrix of the square in a point G and the parallel line to the leg AB through G intersects the side AD of the square in F. Now the segment AF corresponds to the angle BAE and due to the definition of the quadratrix any division of the segment AF in n equidistant parts yields a corresponding division of the angle BAE into n parts of equal size. To divide the segment AF into n equidistant parts proceed as follows. Draw a ray a with origin in A and then draw n equidistant segments (of arbitrary length) on it. Connect the endpoint O of the last segment with F and draw lines parallel to OF through all the endpoints of the remaining n − 1 segments on AO, these parallel lines divide the segment AF on AD into n equidistant segments. Now draw parallel lines to AB through the endpoints of those segments on AF, these parallel lines will intersects the trisectrix. Connecting those points of intersection with A yields a partition of angle BAE into n parts of equal size.[5]
Since not all points of the trisectrix can be constructed with circle and compass alone, it is really required as an additional tool next to compass and circle. However it is possible to construct a dense subset of the trisectrix by circle and compass, so while you cannot assure an exact division of an angle into n parts without a given trisectrix, you can construct an arbitrarily close approximation by circle and compass alone.[2][3]
Squaring of the circle
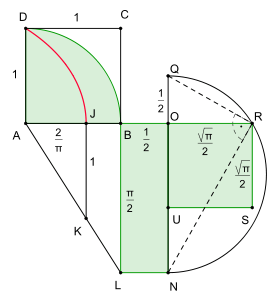
The squaring the circle with ruler and compass is impossible. However if one allows the quadratrix of Hippias as an additional construction tool, the squaring of the circle becomes possible due to Dinostratus' theorem. It allows to turn a quarter circle into square of the same area, hence a square with twice the side length has the same area as the full circle.
According to Dinostratus' theorem the quadratrix divides one of the sides of the associated square in a ratio of 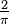 .[1] For a given quarter circle with radius r one constructs the associated square ABCD with side length r. The quadratrix intersect the side AB in J with
.[1] For a given quarter circle with radius r one constructs the associated square ABCD with side length r. The quadratrix intersect the side AB in J with 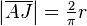 . Now one constructs a line segment JK of length r being perpendicular to AB. Then the through A and K intersects the extension of the side BC in L and from the intercept theorem follows
. Now one constructs a line segment JK of length r being perpendicular to AB. Then the through A and K intersects the extension of the side BC in L and from the intercept theorem follows 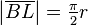 . Extending AB to the right by a new line segment
. Extending AB to the right by a new line segment 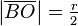 yields the rectangle BLNO with sides BL und BO the area of which matches the area of the quarter circle. This rectangle can be transformed into a square of the same area with the help of Euclid's geometric mean theorem. One extends the side ON by a line segment
yields the rectangle BLNO with sides BL und BO the area of which matches the area of the quarter circle. This rectangle can be transformed into a square of the same area with the help of Euclid's geometric mean theorem. One extends the side ON by a line segment 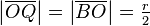 and draws a half circle to right of NQ, which has NQ as its diameter. The extension of BO meets the half circle in R and due to Thales' theorem the line segment OR is the altitude of the right angle triangle QNR. Hence the geometric mean theorem can be applied, which means that OR forms the side of a square OUSR with the same area as the rectangle BLNO and hence as the quarter circle.[7]
and draws a half circle to right of NQ, which has NQ as its diameter. The extension of BO meets the half circle in R and due to Thales' theorem the line segment OR is the altitude of the right angle triangle QNR. Hence the geometric mean theorem can be applied, which means that OR forms the side of a square OUSR with the same area as the rectangle BLNO and hence as the quarter circle.[7]
Note that the point J, where the quadratrix meets the side AB of the associated square, is one of the points of the quadratrix that cannot be constructed with ruler and compass alone and not even with the help of the quadratrix compass based on the original geometric definition (see drawing). This is due to the fact, that the 2 uniformly moving lines coincide and hence there exists no unique intersection point. However relying on the generalized definition of the quadratrix as a function or planar curve allows for J being a point on the quadratrix.[8][9]
Historical sources
The quadratrix is mentioned in the works of Proklos (412–485), Pappos (3rd and 4th centuries) and Iamblichus (c. 240–325). Proklos names Hippias as the inventor of a curve called quadratrix and describes somewhere else how Hippias has applied the curve on the trisection problem. Pappos only mentions how a curve named quadratrix was used by Dinostratos, Nicomedes and others to square the circle. He neither mentions Hippias nor attributes the invention of the quadratrix to a particular person. Iamblichus just writes in a single line, that a curve called quadratrix was used bei Nicomedes to square the circle.[10][11][12]
Though based on Proklos' name for the curve it is conceivable that Hippias himself used it for squaring the circle or some other curvilinear figure, most math historians assume that Hippias invented the curve but used it only for the trisection of angles. Its use for squaring the circle only occurred decades later and was due to mathematicians like Dinostratos and Nicomedes. This interpretation of the historical sources goes back to the German mathematician and historian Moritz Cantor.[11][12]
References
- Claudi Alsina, Roger B. Nelsen: Charming Proofs: A Journey Into Elegant Mathematics. MAA 2010, ISBN 9780883853481, pp. 146–147 (excerpt, p. 146, at Google Books)
- Felix Klein: Famous Problems of Elementary Geometry. Cosimo 2007 (Nachdruck), ISBN 9781602064171, pp. 57–58 (excerpt, p. 57, at Google Books) (complete online copy at archive.org)
- Audun Holme: Geometry: Our Cultural Heritage. Springer, 2010, ISBN 9783642144400, pp. 114–116 (excerpt, p. 114, at Google Books)
- Thomas Little Heath: A History of Greek Mathematics. Volume 1. From Thales to Euclid. Clarendon Press, 1921 (Nachdruck Elibron Classics 2006), pp. 225–230 (online copy at archive.org)
- Horst Hischer: Klassische Probleme der Antike – Beispiele zur "Historischen Verankerung" Klassische Probleme der Antike – Beispiele zur "Historischen Verankerung". In: Blankenagel, Jürgen & Spiegel, Wolfgang (Hrsg.): Mathematikdidaktik aus Begeisterung für die Mathematik — Festschrift für Harald Scheid. Stuttgart/Düsseldorf/Leipzig: Klett 2000, pp. 97 – 118 (German)
- Hans-Wolfgang Henn: Elementare Geometrie und Algebra. Vieweg+Teubner, 2003, pp. 45–48 "Die Quadratur des Kreises" (excerpt, p. 45, at Google Books) (German)
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Quadratrix. |
- Michael D. Huberty, Ko Hayashi, Chia Vang: Hippias' Quadratrix
- Weisstein, Eric W., "Quadratrix of Hippias", MathWorld.
- O'Connor, John J.; Robertson, Edmund F., "Quadratrix of Hippias", MacTutor History of Mathematics archive, University of St Andrews.
Notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Horst Hischer: Klassische Probleme der Antike – Beispiele zur "Historischen Verankerung". In: Blankenagel, Jürgen & Spiegel, Wolfgang (Hrsg.): Mathematikdidaktik aus Begeisterung für die Mathematik — Festschrift für Harald Scheid. Stuttgart/Düsseldorf/Leipzig: Klett 2000, pp. 97 – 118
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Hans-Wolfgang Henn: Elementare Geometrie und Algebra. Verlag Vieweg+Teubner 2003, pp. 45–48 "Die Quadratur des Kreises" (excerpt, p. 47, at Google Books)
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Hans Niels Jahnke: A History of Analysis. American Mathematical Society 2003, ISBN 0821826239, pp. 30–31 (excerpt, p. 30, at Google Books)
- ↑ Weisstein, Eric W., "Quadratrix of Hippias", MathWorld.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Dudley Underwood: The Trisectors. Cambridge University Press 1994, ISBN 0883855143, pp. 6–8 (excerpt, p. 6, at Google Books)
- ↑ O'Connor, John J.; Robertson, Edmund F., "Quadratrix of Hippias", MacTutor History of Mathematics archive, University of St Andrews.
- ↑ Audun Holme: Geometry: Our Cultural Heritage. Springer 2010, ISBN 9783642144400, pp. 114–116 (excerpt, p. 114, at Google Books)
- ↑ Jean-Paul Delahaye: Pi – Die Story. Springer 1999, ISBN 3764360569, p. 71 (excerpt, p. 71, at Google Books)
- ↑ O'Connor, John J.; Robertson, Edmund F., "Dinostratus", MacTutor History of Mathematics archive, University of St Andrews.
- ↑ Van der Waerden: Science Awakening. Oxford University Press 1961, p. 146
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 James Gow: A Short History of Greek Mathematics. Cambridge University Press 2010, ISBN 9781108009034, pp. 162–164 (excerpt, p. 162, at Google Books)
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Thomas Little Heath: A History of Greek Mathematics. Volume 1. From Thales to Euclid. Clarendon Press 1921 (Nachdruck Elibron Classics 2006), pp. 182, 225–230 (online copy at archive.org)