Puppis A
| Puppis A | |
|---|---|
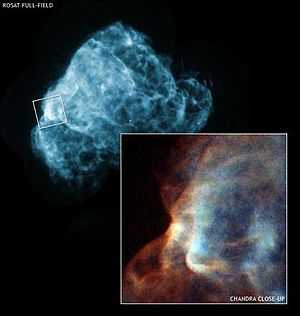 The Chandra three-color image (inset) is a region of the supernova remnant Puppis A (wide-angle view from ROSAT in blue) which reveals a cloud being torn apart by a shock wave produced in a supernova explosion. ROSAT image is 88 arcmin across; Chandra image 8 arcmin across. RA 08h 23m 08.16s Dec -42º 41' 41.40" in Puppis. Observation date: September 4, 2005. Color code: Energy (Red 0.4-0.7 keV; Green 0.7-1.2 keV; Blue 1.2-10 keV). Instrument: ACIS. Credit: Chandra: NASA/CXC/GSFC/U.Hwang et al.; ROSAT: NASA/GSFC/S.Snowden et al. X-ray image of the Cosmic Cannonball in Puppis A | |
| Observation data (Epoch J2000) | |
| Supernova type | S |
| Host galaxy | Milky Way |
| Constellation | Puppis |
| Right ascension | 08h 24m 07s |
| Declination | -42° 59' 48 |
| Galactic coordinates | l = 260.2°, b = -3.7° |
| Discovery date | 1971 |
| Distance | 7.000 ly |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Progenitor | Unknown |
| Progenitor type | Unknown |
| Colour (B-V) | Unknown |
| Notable features |
central source: RX J0822-4300. Apparent size: 1° |
Puppis A is a supernova remnant (SNR) about 100 lightyears in diameter and roughly 6500–7000 lightyears distant.[1] Its apparent angular diameter is about 1 degree.[2] The light of the supernova explosion reached Earth approximately 3700 years ago. Although it overlaps the Vela Supernova Remnant, it is four times more distant.
A hypervelocity neutron star known as the Cosmic Cannonball has been found in this SNR.
Puppis X-1
Puppis X-1 (Puppis A) was discovered by a Skylark flight in October 1971, viewed for 1 min with an accuracy ≥ 2 arcsec,[3] probably at 1M 0821-426, with Puppis A (RA 08h 23m 08.16s Dec -42º 41' 41.40") as the likely visual counterpart.
Puppis A is one of the brightest X-ray sources in the X-ray sky. Its X-ray designation is 2U 0821-42.
Gallery
-
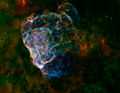
Puppis A: X-ray [blue:0.3-8 keV] + IR [red-green:24-70 microns] (21 August 2014).
-
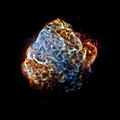
Puppis A: X-ray [blue:high]/[green:medium]/[red:low] (10 September 2014).
References
- ↑ "Puppis A". WISE Multimedia Gallery. NASA. 9 Dec 2011. Retrieved 21 Nov 2014.
- ↑ Milne, D. K. (1971). "Radio observations of the supernova remnants IC443 and Puppis A". Aust. J. Phys. 24: 429. Bibcode:1971AuJPh..24..429M.
- ↑ Wiggin M (December 2000). "The Dome on Ball Hill – The RAE Observatory" (PDF).
- "Puppis A: Chandra Reveals Cloud Disrupted By Supernova Shock", Chandra: NASA/CXC/GSFC/U.Hwang et al.; ROSAT: NASA/GSFC/S.Snowden et al.,
- Simbad