Punigluconin
Punigluconin
 |
| Names |
| IUPAC name
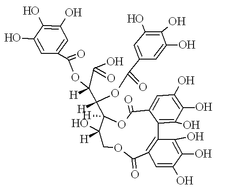
(2R,3S)-3-[(7R,8R)-1,2,3,8,13,14,15-Heptahydroxy-5,11-dioxo-5,8,9,11-tetrahydro-7H-dibenzo[g,i][1,5]dioxacycloundecin-7-yl]-2,3-bis[(3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoyl)oxy]propanoic acid |
| Other names
|
| Identifiers |
| |
103488-38-6 |
| ChemSpider |
10272889 |
InChI=1S/C34H26O23/c35-12-1-8(2-13(36)21(12)42)31(50)56-28(29(30(48)49)57-32(51)9-3-14(37)22(43)15(38)4-9)27-18(41)7-54-33(52)10-5-16(39)23(44)25(46)19(10)20-11(34(53)55-27)6-17(40)24(45)26(20)47/h1-6,18,27-29,35-47H,7H2,(H,48,49)/t18-,27-,28+,29-/m1/s1
Key: KZEYIYXACMUTRM-WIMKJKQSSA-N
|
| Jmol-3D images |
Image |
| PubChem |
44631480 |
Oc1cc(cc(O)c1O)C(=O)O[C@@H](C(O)=O)[C@@H](OC(=O)c2cc(O)c(O)c(O)c2)[C@@H]4OC(=O)c5cc(O)c(O)c(O)c5c3c(O)c(O)c(O)cc3C(=O)OC[C@H]4O
|
| Properties |
| |
C34H26O23 |
| Molar mass |
802.53 g/mol |
Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) |
|
| Infobox references |
|
|
Punigluconin is an ellagitannin, a polyphenol compound. It is found in the bark of Punica granatum (pomegranate)[2] and in Emblica officinalis.[3] It is a molecule having a hexahydroxydiphenic acid group and two gallic acids attached to a gluconic acid core.[1]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Tanaka Takashi, Tong Hui-Hong, Xu Ya-Ming, Ishimaru Kanji, Nonaka Gen-ichiro and Nishioka Itsuo (1992-11-25). "Tannins and Related Compounds. CXVII. Isolation and Characterization of Three New Ellagitannins, Lagerstannins A, B and C, Having a Gluconic Acid Core, from Lagerstroemia speciosa (L.) PERS". Chemical & pharmaceutical bulletin 40 (11): 2975–2980. doi:10.1248/cpb.40.2975.
- ↑ Tanaka Takashi, Nonaka Gen-Ichiro and Nishioka Itsuo (1986-02-25). "Tannins and Related Compounds. XLI. : Isolation and Characterization of Novel Ellagitannins, Punicacorteins A, B, C, and D, and Punigluconin from the Bark of Punica granatum L". Chemical & pharmaceutical bulletin 34 (2): 656–663. doi:10.1248/cpb.34.656.
- ↑ Bhattacharya, A; Chatterjee, A; Ghosal, S; Bhattacharya, SK (1999). "Antioxidant activity of active tannoid principles of Emblica officinalis (amla)". Indian journal of experimental biology 37 (7): 676–80. PMID 10522157.
|
|---|
| | Moieties | |
|---|
| | Lactones | |
|---|
| | Monomers |
- Acetonyl geraniin
- Alnusiin
- Bicornin
- Carlesiin
- Casuarictin
- Emblicanin A and B
- Euscaphinin
- Galloyl pedunculagin
- Grandinin
- Helioscopinin B
- Jolkinin
- Lagerstannin A, B and C
- Macranganin
- Myrobalanitannin
- Nupharin A, B, C, D, E and F
- Pedunculagin
- Punicalagin
- Punigluconin
- Phyllanemblinin A, B, C, D, E and F
- Punicalin
- Roburin E
- Rugosin E
- Sanguiin H-5
- Stenophyllanin A, B and C
- Strictinin
- Tellimagrandin I and II
- Teracatain
- Terchebulin
- Terflavin A and B
- Tergallic acid
- Tergallic acid dilactone
C-glycosidic ellagitannins | |
|---|
| | |
|---|
| Transformed ellagitannins | | |
|---|
| molecules with Elaeocarpusinic acid |
- Elaeocarpusin
- Helioscopin B
- Mallojaponin (1-O-Galloyl-2,4-elaeocarpusinoyl-3,6-(R)-valoneayl-beta-D-glucose)
|
|---|
|
|---|
|
|---|
| | Oligomers | |
|---|
| | Other | |
|---|
|