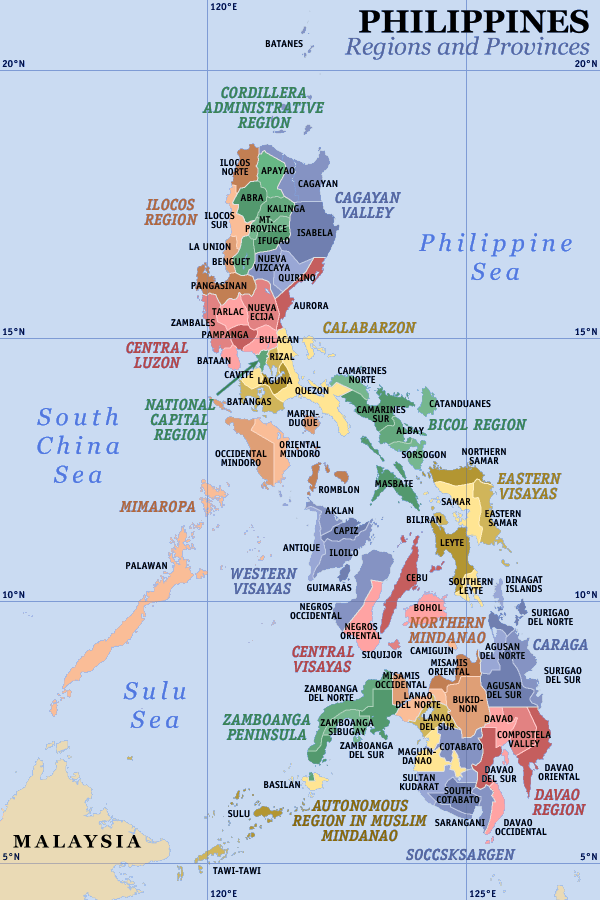
Provinces of the Philippines
 |
| This article is part of a series on the politics and government of the Philippines |
|
|
Politics portal |
The provinces of the Philippines (Filipino: Mga Lalawigan ng Pilipinas) are the primary political and administrative divisions of the Philippines. There are 81 provinces at present, further subdivided into component cities and municipalities. The National Capital Region, as well as independent cities, are independent of any provincial government. Each province is governed by an elected legislature called the Sangguniang Panlalawigan and by an elected governor.
The provinces are grouped into 17 regions based on geographical, cultural, and ethnological characteristics. Fourteen of these regions are designated with numbers corresponding to their geographic location in order from north to south. The National Capital Region, Cordillera Administrative Region, and Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao do not have numerical designations.
Each province is a member of the League of Provinces of the Philippines, an organization which aims to address issues affecting provincial and metropolitan government administrations.[1]
Government
A provincial government is autonomous of other provinces within the Republic. Each province is governed by two main elected branches of the government: executive and legislative. Judicial affairs are separated from provincial governance and are administered by the Supreme Court of the Philippines.
Executive
The provincial governor is chief executive and head of each province. Elected to a term of three years and limited to three consecutive terms, he or she appoints the directors of each provincial department which include the office of administration, engineering office, information office, legal office, and treasury office.
Legislative
The vice-governor acts as the president for each Sangguniáng Panlalawigan (SP; "Provincial Board"), the province's legislative body. Every SP is composed of regularly elected members from provincial districts, as well as ex officio members. The number of regularly elected SP members allotted to each province is determined by its income class. First- and second-class provinces are provided ten regular SP members; third- and fourth-class provinces have eight, while fifth- and sixth-class provinces have six. Exceptions are provinces with more than five congressional districts, such as Cavite with 14 regularly elected SP members, and Cebu, Negros Occidental and Pangasinan which have twelve each.
Every SP has designated seats for ex officio members, given to the respective local presidents of the Association of Barangay Captains (ABC), Philippine Councilors' League (PCL), and Sangguniáng Kabataan (SK; "Youth Council").
The vice-governor and regular members of an SP are elected by the voters within the province. Ex officio members are elected by members of their respective organisations.
Relation to other levels of government
National government
National intrusion into the affairs of each provincial government is limited by the Philippine Constitution. The President of the Philippines however coordinates with provincial administrators through the Department of the Interior and Local Government. For purposes of national representation, each province is guaranteed its own congressional district. One congressional representative represents each district in the House of Representatives. Senatorial representation is elected at an at-large basis and not apportioned through territory-based districts.
Cities and municipalities
Those classified as either "highly urbanized" or "independent component" cities are independent from the province, as provided for in Section 29 of the Local Government Code of 1991.[2] Although such a city is a self-governing first-level entity, in many cases it is often presented as part of the province in which it is geographically located, or in the case of Zamboanga City, the province it last formed part the congressional representation of.
Local government units classified as "component" cities and municipalities are under the jurisdiction of the provincial government. In order to make sure that all component city or municipal governments act within the scope of their prescribed powers and functions, the Local Government Code mandates the provincial governor to review executive orders issued by mayors, and the Sangguniang Panlalawigan to review legislation by the Sangguniang Panlungsod (City Council) or Sangguniang Bayan (Municipal Council), of all component cities and municipalities under the province's jurisdiction.[2]
Barangays
The provincial government does not have direct relations with individual barangays. Supervision over a barangay government is the mandate of the mayor and the Sanggunian of the component city or municipality of which the barangay in question is a part.[2]
Classification
Provinces are classified according to average annual income based on the previous 4 calendar years. Effective July 29, 2008, the thresholds for the income classes for cities are:[3]
| Class | Average annual income |
|---|---|
| First | ₱450 million or more |
| Second | ₱360 million or more but less than ₱450 million |
| Third | ₱270 million or more but less than ₱360 million |
| Fourth | ₱180 million or more but less than ₱270 million |
| Fifth | ₱90 million or more but less than ₱180 million |
| Sixth | below ₱90 million |
A province's income class determines the size of the membership of its Sangguniang Panlalawigan, and also how much it can spend on certain items, or procure through certain means.[2]
Map

- Note: The map presents independent cities outside of Metro Manila as part of provinces, despite being self-governing units themselves.
List of provinces
|
|
NOTES:
- All population, land area, and barangay count figures include cities independent from provinces. In this table, they are counted as part of the province to which they are often grouped for geographical and statistical purposes, but in actuality they are first-level entities on their own right.
- Metro Manila is included for comparison although it is not a province but an administrative region.
- 1 Dates could refer to provincehood as established during the Spanish period, American period, or through Republic Acts.
Etymologies
History
When the United States acquired the Philippines from Spain in 1898, the islands were divided into four gobiernos (governments), which were further subdivided into provinces and districts. The American administration initially inherited the Spanish divisions and placed them under military government. As insurgencies were pacified, civil government was gradually organized.
- November 23, 1900: Civil government of the province of Benguet established through Act No. 49. Capital moved to Baguio.
- February 6, 1901: Act No. 83 ("The Provincial Government Act") enacted by the Philippine Commission.
- February 13, 1901: Provisions of the Provincial Government Act extended to Pampanga through Act No. 85.
- February 16, 1901: Provisions of the Provincial Government Act extended to Pangasinan through Act No. 86. Towns of Balungao, Rosales, San Quintin and Umingan annexed from Nueva Ecija.
- February 18, 1901: Provisions of the Provincial Government Act extended to Tarlac through Act No. 87.
- February 27, 1901: Provisions of the Provincial Government Act extended to Bulacan through Act No. 88. Capital moved to Malolos.
- March 2, 1901: Provisions of the Provincial Government Act extended to Bataan through Act No. 92.
- March 12, 1901: Provisions of the Provincial Government Act extended to Tayabas through Act No. 103. Capital moved to Lucena.
- March 16, 1901: Provisions of the Provincial Government Act extended to Romblon, elevated from Spanish-era status of District, through Act No. 104.
- March 18, 1901: Provisions of the Provincial Government Act extended to Masbate, elevated from Spanish-era status of District, through Act No. 105.
- April 11, 1901: Provisions of the Provincial Government Act extended to Iloilo, formed through the merging of the Spanish-era Province of Iloilo with the Comandancia of Concepcion, through Act No. 113.
- April 13, 1901: Provisions of the Provincial Government Act extended to Antique through Act No. 114.
- April 15, 1901: Provisions of the Provincial Government Act extended to Capiz through Act No. 115.
- April 18, 1901: Provisions of the Provincial Government Act extended to Cebu through Act No. 116.
- April 20, 1901: Provisions of the Provincial Government Act extended to Bohol through Act No. 117.
- April 22, 1901: Provisions of the Provincial Government Act extended to Leyte through Act No. 121.
- April 26, 1901: Provisions of the Provincial Government Act extended to Albay through Act No. 122.
- April 27, 1901: Provisions of the Provincial Government Act extended to Ambos Camarines through Act No. 123.
- April 30, 1901: Provisions of the Provincial Government Act extended to Sorsogon through Act No. 124.
- May 1, 1901: Provisions of the Provincial Government Act extended to Occidental Negros and Oriental Negros through Acts No. 119 and 120, respectively, enacted on April 20, 1901; Provisions of the Provincial Government Act extended to newly created Marinduque through Act No. 125.
- May 2, 1901: Provisions of the Provincial Government Act extended to Batangas through Act No. 126.
- May 15, 1901: Provisions of the Provincial Government Act extended to Surigao, elevated from Spanish-era status of District, through Act No. 127; Provisions of the Provincial Government Act extended to Misamis through Act No. 128.
- June 11, 1901: Provisions of the Provincial Government Act extended to newly created Rizal, formed through the merging of the Politico-Military District of Morong with the entire province of Manila except the territory of the city of Manila, through Act No. 137; Provisions of the Provincial Government Act extended to Cavite through Act No. 138. Annexed Lubang and adjacent islands to the province. Provincial government provided an option to move capital from the town of Cavite; Provisions of the Provincial Government Act extended to Nueva Ecija through Act No. 139. Provincial government provided an option to move capital from the town of San Isidro.
- July 16, 1901: Catanduanes annexed to Albay through Act No. 169.
- July 17, 1901: Batangas, Bohol and Cebu placed under the control of military governors through Act No. 173.
- August 15, 1901: Provisions of the Provincial Government Act and its amendments extended to La Union through Act No. 203.
- August 16, 1901: Provisions of the Provincial Government Act and its amendments extended to Ilocos Sur through Act No. 205.
- August 19, 1901: Provisions of the Provincial Government Act and its amendments extended to Abra, excluding its territory east of the crest of the Cordillera Central, through Act No. 206.
- August 20, 1901: Provisions of the Provincial Government Act and its amendments extended to Ilocos Norte through Act No. 207.
- August 22, 1901: Provisions of the Provincial Government Act and its amendments extended to Cagayan through Act No. 209. The Babuyan Islands and the Spanish-era province of Batanes annexed to the province.
- August 24, 1901: Provisions of the Provincial Government Act and its amendments extended to Isabela through Act No. 210.
- August 28, 1901: Provisions of the Provincial Government Act and its amendments extended to Zambales through Act No. 211.
- January 1, 1902: Civil government of the Province of Cebu restored through Act No. 322 enacted on December 20, 1901.
- January 28, 1902: Civil government of the Province of Nueva Vizcaya established through Act No. 337.
- April 1, 1902: Civil government of the Province of Bohol restored through Act No. 365 enacted on March 3, 1902.
- May 28, 1902: Spanish-era comandancias of Amburayan, Bontoc and Lepanto organized into sub-provinces under the new province of Lepanto-Bontoc through Act No. 410. Areas between Abra and Cagayan not yet placed under the jurisdiction of any province annexed as part of the sub-province of Bontoc.
- June 12, 1902: Spanish-era districts of El Principe and Infanta, including the Polillo Islands, annexed to Tayabas through Act No. 417.
- June 17, 1902: Provisions of the Provincial Government Act and its amendments extended to Samar through Act No. 419.
- June 23, 1902: Civil government of the Province of Paragua established through Act No. 422; Mindoro, Lubang and surrounding small islands annexed to Marinduque through Act No. 423.
- July 1, 1902: Provisions of the Provincial Government Act and its amendments extended to La Laguna through Act No. 424.
- November 10, 1902: Marinduque annexed to Tayabas through Act No. 499; Provisions of the Provincial Government Act and its amendments extended to newly created Mindoro, separated from Marinduque through Act No. 500.
- May 14, 1903: Cagayancillo, Balabac and the rest of Palawan Island (south of Tapul and Ulugan rivers) annexed to Paragua through Act No. 747. Provincial government provided the option to choose capital between Cuyo or Puerto Princesa.
- May 26, 1903: Spanish-era Comandancia of Kayapa annexed to Benguet through Act No. 768.
- July 15, 1903: Moro Province formed, composed of the districts of Cotabato, Davao, Lanao, Sulu, and Zamboanga through Act No. 787 enacted on June 1, 1903.
- April 1, 1905: Abra annexed to Ilocos Sur as sub-province through Act No. 1306 enacted on February 27, 1905.
- June 28, 1905: Name of Paragua changed to Palawan through Act No. 1363.
- January 1, 1906: Masbate annexed to Sorsogon as sub-province through Act No. 1413 enacted on November 23, 1905.
- May 9, 1907: Apayao and Kalinga established as sub-provinces of Cagayan and Lepanto-Bontoc, respectively, through Act No. 1648.
- July 15, 1907: Romblon (except the island of Maestro de Campo, annexed to Mindoro) annexed to Capiz as sub-province through Act No. 1665 enacted on July 2, 1907.
- August 10, 1907: Marinduque declared a sub-province of Tayabas through Act No. 1649 enacted on May 17, 1907.
- August 20, 1907: Act No. 1693 creates Agusan (composed of the sub-provinces of Butuan and Bukidnon), and establishes Batanes as a sub-province of Cagayan.
- October 8, 1907: Siquijor established as sub-province of Negros Oriental through Act No. 1753. Catanduanes established as sub-province of Albay through Act No. 1331.
- August 18, 1908: Mountain Province, with seven sub-provinces, formed by merging territories of the entire province of Lepanto-Bontoc (with Amburayan, Bontoc, Kalinga and Lepanto sub-provinces); the district in the province of Nueva Vizcaya that formerly the comprised the Spanish-era Comandancia of Quiangan (annexed as Ifugao sub-province); the entire province of Benguet except Baguio City (annexed as Benguet sub-province); and Apayao sub-province in Cagayan, through Act No. 1876.
- May 20, 1909: Batanes re-established as province, separated from Cagayan through Act No. 1952.
- December 20, 1913: Act No. 2309 renames Moro Province to Department of Mindanao and Sulu and annexes Agusan (with Bukidnon sub-province) to the Department. Department of Mindanao and Sulu formally organized on January 1, 1914.
- September 1, 1914: Department of Mindanao and Sulu provided with autonomous government through Act No. 2408 enacted on July 23, 1914. Bukidnon sub-province and the former Moro Province districts of Cotabato, Davao, Lanao, Sulu and Zamboanga converted to provinces.
- March 9, 1917: Abra re-established as regular province, separated from Ilocos Sur through Act No. 2683.
- December 7, 1917: Romblon re-established as regular province, separated from Capiz through Act No. 2724.
- March 3, 1919: Ambos Camarines divided into Camarines Norte and Camarines Sur through Act No. 2809.
- February 4, 1920: Act No. 2877 abolishes Amburayan sub-province in the Mountain Province by annexing its municipal entities to Ilocos Sur and La Union; Lepanto sub-province reduced in size by annexing some of its municipal entities to Ilocos Sur and Benguet.
- November 21, 1920: Marinduque re-established as regular province, separated from Tayabas through Act No. 2880.
- December 15, 1920: Masbate re-established as regular province, separated from Sorsogon through Act No. 2934.
- March 27, 1923: Leyte divided into Occidental Leyte and Oriental Leyte through Act No. 3117, but never proclaimed by the governor-general.
- November 28, 1939: Division of Misamis into Misamis Occidental and Misamis Oriental implemented by virtue of Act No. 3777 (enacted on November 29, 1930), the law that amended Act No. 3537 (enacted on November 2, 1929) which first sought the division.
- June 8, 1940: Provincial government of Romblon abolished, municipal governments reorganized into four "special municipalities" through Commonwealth Act No. 581.
- October 26, 1945: Catanduanes established as regular province, separated from Albay through Commonwealth Act No. 687 enacted on September 26, 1945.
- September 7, 1946: Name of Tayabas changed to Quezon through Republic Act No. 14.
- October 1, 1946: CA 581 repealed and Romblon's provincial and municipal governments restored through Republic Act No. 38.
- June 13, 1950: Mindoro divided into Occidental Mindoro and Oriental Mindoro through Republic Act No. 505.
- June 14, 1951: Aurora established as sub-province of Quezon through Republic Act No. 648.
- June 6, 1952: Zamboanga divided into Zamboanga del Norte and Zamboanga del Sur through Republic Act No. 711.
- April 25, 1956: Aklan separated from Capiz through Republic Act No. 1414.
- June 22, 1956: Camiguin established as sub-province of Misamis Oriental through Republic Act No. 2021.
- April 8, 1959: Biliran established as sub-province of Leyte through Republic Act No. 2141.
- May 22, 1959: Lanao province divided into Lanao del Norte and Lanao del Sur through Republic Act No. 2228.
- July 1, 1959: Southern Leyte separated from Leyte through Republic Act No. 2227 approved on May 22, 1959.
- June 19, 1960: Surigao divided into Surigao del Norte and Surigao del Sur through Republic Act No. 2786.
- November 19, 1965: Plebiscite approves the division of Samar into Eastern Samar, Northern Samar, and Western Samar by virtue of Republic Act No. 4221 enacted on June 19, 1965.
- June 18, 1966: Guimaras established as sub-province of Iloilo through Republic Act No. 4667; Camiguin established as regular province, separated from Misamis Oriental through Republic Act No. 4669; Benguet re-established, and Ifugao and Kalinga-Apayao created, from Mountain Province through Republic Act No. 4695; Quirino established as sub-province of Nueva Vizcaya through Republic Act No. 4734; South Cotabato separated from Cotabato through Republic Act No. 4849.
- May 8, 1967: Davao province divided into Davao del Norte, Davao del Sur, and Davao Oriental through Republic Act No. 4867.
- November 14, 1967: Plebiscite approves the division of Agusan into Agusan del Norte and Agusan del Sur by virtue of Republic Act No. 4979 enacted on June 17, 1967.
- June 21, 1969: Name of Western Samar province changed to Samar through Republic Act No. 5650.
- August 4, 1969: Samal sub-province created from Davao del Norte through Republic Act No. 5999, but never inaugurated.
- October 4, 1971: Maranaw province created from Lanao del Sur through Republic Act No. 6406, remained unorganized due to the disruption caused by the declaration of Martial Law in the Philippines.
- November 11, 1971: Plebiscites approve the establishment of Quirino and Siquijor as regular provinces by virtue of Republic Act No. 6394 (approved on September 10, 1971) and Republic Act No. 6398 (approved on September 17, 1971), separating them from Nueva Vizcaya and Negros Oriental, respectively.
- June 17, 1972: Name of Davao del Norte changed to Davao through Republic Act No. 6430.
- September 11, 1973: Tawi-Tawi separated from Sulu through Presidential Decree No. 302.
- November 22, 1973: Cotabato divided into Maguindanao, North Cotabato, and Sultan Kudarat through Presidential Decree No. 341.
- December 27, 1973: Basilan province created through Presidential Decree No. 356 out of most of the territory of the City of Basilan, which itself was delimited to only the downtown area of what is now Isabela City, then finally abolished by Presidential Decree No. 840 in 1975.
- November 7, 1975: Metro Manila established through Presidential Decree No. 824, composed of the four chartered cities of Manila, Caloocan, Pasay and Quezon City, and several municipalities of Rizal and Bulacan, all of which effectively became independent from provincial supervision.
- August 13, 1979: Aurora proclaimed a regular province, separated from Quezon through Batas Pambansa Blg. 7 enacted on November 21, 1978. Plebiscite held on May 20, 1979, approves provincehood.
- March 7, 1984: Name of North Cotabato province changed to Cotabato through Batas Pambansa Blg. 660.
- January 3, 1986: Plebiscite approves the separation of Negros del Norte from Negros Occidental by virtue of Batas Pambansa Blg. 885 enacted on December 3, 1985.
- August 18, 1986: BP No. 885 found unconstitutional by the Supreme Court, Negros del Norte reverts as part of Negros Occidental.
- May 11, 1992: Plebsicites affirm the establishment of Biliran and Guimaras as regular provinces, separating them from Leyte and Iloilo, respectively, by virtue of Section 462 of Republic Act No. 7160 (Local Government Code of 1991) approved on October 10, 1991; Plebiscite approves the separation of Sarangani from South Cotabato by virtue of Republic Act No. 7228 approved on March 16, 1992.
- May 8, 1995: Plebiscite approves the division of Kalinga-Apayao into Apayao and Kalinga by virtue of Republic Act No. 7878 approved on July 25, 1994.
- March 7, 1998: Plebiscite approves the separation of Compostela Valley from Davao by virtue of Republic Act No. 8470 approved on January 30, 1998. Name of Davao changed back to Davao del Norte.
- February 22, 2001: Plebiscite approves the separation of Zamboanga Sibugay from Zamboanga del Sur by virtue of Republic Act No. 8973 approved on November 7, 2000.
- October 28, 2006: Plebiscite approves the separation of Shariff Kabunsuan from Maguindanao by virtue of Muslim Mindanao Autonomy Act No. 201 enacted on August 28, 2006.
- December 2, 2006: Plebiscite approves the separation of Dinagat Islands from Surigao del Norte by virtue of Republic Act No. 9355 approved on October 2, 2006.
- November 18, 2008: MMA Act No. 201 declared void by the Supreme Court, Shariff Kabunsuan reverts as part of Maguindanao.
- February 11, 2010: RA No. 9355 found unconstitutional by the Supreme Court, Dinagat Islands reverts as part of Surigao del Norte.
- March 30, 2011: Supreme Court reverses its decision on Dinagat Islands and became a province once again.
- October 28, 2013: Plebiscite approves the separation of Davao Occidental from Davao del Sur by virtue of Republic Act No. 10360 approved on January 21, 2013.
Formally proposed provinces
Note: This section lists only those proposals that reached the stage where legislation was enacted for the purpose of establishing a province or sub-province, but never achieved corporate existence.

- Occidental Leyte and Oriental Leyte (1923) – Leyte was divided into two new provinces by Act No. 3117 on March 27, 1923.[40] The division never took place, however, as no proclamation was issued by the Governor-General.
- The province of Oriental Leyte would have covered the present-day territories of the entire province of Biliran, the municipalities of Abuyog, Alangalang, Babatngon, Barugo, Burauen, Calubian, Capoocan, Carigara, Dagami, Dulag, Jaro, Javier, Julita, La Paz, Leyte, MacArthur, Mahaplag, Mayorga, Palo, Pastrana, San Isidro, San Miguel, Santa Fe, Tabango, Tabontabon, Tanauan, Tolosa, Tunga and Tacloban City (which was designated as the provincial capital).
- The province of Occidental Leyte would have covered the present-day territories of the entire province of Southern Leyte, the municipalities of Albuera, Bato, Hilongos, Hindang, Inopacan, Isabel, Kananga, Matag-ob, Matalom, Mérida, Palompon, Villaba and the cities of Baybay and Ormoc. The province capital of Occidental Leyte "SEC. 2. ... shall be designated by the Governor-General, until determined by a plurality vote of the electors of the new province at the next general election."
- Samal (1969) – The sub-province of Samal was created by Republic Act No. 5999[41] and covered the area of the present-day Island Garden City of Samal. However, the sub-province was never inaugurated.
- Maranaw (1971) – Republic Act No. 6406,[42] which sought to create a new province out of eastern Lanao del Sur (now corresponding to the province's first congressional district), was approved on October 4, 1971. The province was to consist of the municipalities of Bubong, Ditsaan-Ramain (including what is now Buadiposo-Buntong), Kapai, Lumba-Bayabao (including what is now Maguing), Marantao, Masiu, Mulondo, Saguiaran, Piagapo, Poona Bayabao, Tamparan, Taraka and Wao (including what is now Bumbaran), with the chartered city of Marawi serving as the new province's capital. Lanao del Sur was to retain the remaining municipalities, with Malabang serving as its new capital. Section 4 of RA 6406 provided that "The new provinces as provided in this Act shall come into existence upon the election and qualification of their first elective provincial officials, who shall be elected in a special election simultaneously with the general elections of November, nineteen hundred and seventy-three." The division never took place due to the declaration of Martial Law in the Philippines on September 21, 1972, which disrupted the scheduled general elections for 1973 and paved the way for the adoption of a new Constitution and the establishment of the Fourth Philippine Republic. A legacy of this unimplemented division is the existence of two ZIP code series for Lanao del Sur: the 93- series was retained by what were to be the remaining towns of the province (with Malabang, the new capital, being reassigned the code 9300), while a new series (97-) was assigned to what was supposed to be the province of Maranaw (with Marawi City getting the new code 9700).
- Isabela del Norte and Isabela del Sur (1995) – On February 20, 1995, Republic Act No. 7891,[43] which sought to divide the province of Isabela, was approved. Isabela del Norte was to comprise municipalities belonging to the province's first and second congressional districts with Ilagan serving as capital. Isabela del Sur was to consist of the third and fourth congressional districts (excluding the independent component city of Santiago), with Cauayan as the capital. The proposed division was rejected in a plebiscite held on June 20, 1995.
- Quezon del Norte and Quezon del Sur (2007) – The act dividing the province of Quezon into two, Republic Act No. 9495,[44] lapsed into law without the President's signature on September 7, 2007. Quezon del Norte was to be composed of the first and second congressional districts of the province, with Lucena City as its capital. Quezon del Sur, with its capital at Gumaca, would have been composed of the third and fourth congressional districts. The COMELEC held the plebiscite on December 13, 2008 and majority of the votes cast rejected the division.
Former provinces
- Manila (until 1901) – Incorporated into Rizal; portions around Manila later consolidated to form present-day NCR.
- Lepanto-Bontoc (1902–1908) – Incorporated into Mountain Province.
- Moro Province (1903–1913) – Converted to the Department of Mindanao and Sulu, composed of seven provinces. Now part of several regions in Mindanao.
- Ambos Camarines (1901–1908) – Divided into Camarines Norte and Camarines Sur, although the wording of Act No. 2809 implies that it is Camarines Norte that was created from Ambos Camarines, re-designated as Camarines Sur. Camarines Sur retained the provincial capital of Nueva Caceres.
- Misamis (1901–1939) – Partitioned into Misamis Occidental and Misamis Oriental. Misamis Oriental retained the provincial capital of Cagayan.
- Mindoro (1902–1950) – Divided into Occidental Mindoro and Oriental Mindoro. Oriental Mindoro retained the provincial capital of Calapan.
- Zamboanga (1914–1952) – Partitioned into Zamboanga del Norte and Zamboanga del Sur. The de jure provincial capital of Molave was placed under the jurisdiction of Zamboanga del Sur which had its capital in Pagadian. Zamboanga Sibugay later created from Zamboanga del Sur.
- Lanao (1914–1959) – Divided into Lanao del Norte and Lanao del Sur. Lanao del Sur retained the provincial capital of Dansalan (now Marawi.
- Surigao (1901–1967) – Partitioned into Surigao del Norte and Surigao del Sur. Surigao del Norte retained the provincial capital of Surigao and the provincial seal. The province of Dinagat Islands was later created from Surigao del Norte.
- Davao (1914–1967; 1972–1998) – Divided into Davao del Norte, Davao del Sur and Davao Oriental. Davao del Norte was officially known as Davao from 1972 to 1998, when Compostela Valley was later created from Davao province. Davao Occidental later created from Davao del Sur.
- Agusan (1907–1967) – Partitioned into Agusan del Norte and Agusan del Sur. Agusan del Norte retained the provincial capital of Butuan. The provincial capital was officially transferred to Cabadbaran on 2000 but the provincial government services and functions is still not transferred to the new capital.[45]
- Negros del Norte (1985–1986) – Batas Pambansa Blg. 885,[46] which created a new province out of the northern part of Negros Occidental, took effect on 23 December 1985, with a plebiscite to ratify the law held on 3 January 1986. The province comprised the present-day cities of Cadiz (which was to serve as the capital), Escalante, Sagay, San Carlos, Silay and Victorias, as well as the municipalities of Calatrava, Enrique B. Magalona, Manapla, Salvador Benedicto and Toboso. Despite voters ratifying Batas Pambansa Blg. 885, on 11 July 1986 the Supreme Court declared the law and the proclamation of the province null and void. The ruling states the enabling law was unconstitutional for, among other things, not including the rest of Negros Occidental in the plebiscite, and the proposed province not meeting the 3,500 square kilometre land area requirement of the 1983 Local Government Code.[47]
- Kalinga-Apayao (1966–1995) – Divided into Apayao and Kalinga. Kalinga retained the provincial capital of Tabuk.
- Shariff Kabunsuan (2006–2008) – Republic Act No. 9054 conferred to the Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao expanded powers, especially the capacity to create provinces (Article VI, Section 19).[48] Based on this, the ARMM Regional Legislative Assembly enacted Muslim Mindanao Autonomy Act No. 201 on 28 August 2006. The Act created a new province, comprising all the municipalities in the first congressional district of Maguindanao (except Cotabato City), with its capital at Datu Odin Sinsuat. The province's creation was approved on 28 October 2006 by a majority vote in a plebiscite. Responding to requests for clarification as to which congressional districts form Shariff Kabunsuan for the 2007 elections (specifically whether Cotabato City was part of the representation of the new province), COMELEC issued Resolution No. 7845, which initially held Cotabato City to be the sole remaining LGU in the First District of Maguindanao. COMELEC later amended this with Resolution No. 7902, which maintained the status quo before the province's creation. The COMELEC resolutions became the subject of a case in which the Supreme Court opined that because "the power to create new a province or city inherently involves the power to create a legislative district"—a power that Congress did not explicitly delegate to the ARMM Regional Assembly—the creation of a province by a lower legislative body (the ARMM Regional Assembly) will necessarily entail the creation of a legislative district for a higher legislative body (Congress). Therefore on July 16, 2008, the Supreme Court declared Section 19, Article VI of RA No. 9054 unconstitutional, MMA Act No. 201 void, and COMELEC Resolution No. 7902 valid.[49]
See also
- List of Philippine provincial etymologies
- List of Philippine provinces by Human Development Index
- List of demonyms for Philippine provinces
- ISO 3166-2:PH
References
- ↑ "About the League of Provinces". League of Provinces of the Philippines. Retrieved 2008-01-12
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Republic Act No. 7160 - Local Government Code of 1991
- ↑ http://www.nscb.gov.ph/activestats/psgc/articles/DepOrderReclass.pdf
- ↑ "ISO 3166-2 Newsletter: Changes in the list of subdivision names and code elements" (PDF). ISO (International Organization for Standardization). 30 June 2010. pp. 56–58. Retrieved 19 January 2015.
- ↑ "Population and Annual Growth Rates for The Philippines and Its Regions, Provinces, and Highly Urbanized Cities" (PDF). 2010 Census and Housing Population. National Statistics Office. Retrieved 15 February 2013.
- ↑ "List of Provinces". PSGC Interactive. Makati City, Philippines: National Statistical Coordination Board. Retrieved 15 March 2013.
- ↑ Figures include the independent city of Butuan.
- ↑ Cabadbaran has been made the official capital of the province, as per Republic Act No. 8811. However, the seat of the provincial government is still in the process of being transferred from Butuan, where the provincial government still holds office.
- ↑ The province maintains another government center in Luna, where many national and provincial agencies now hold office. Philippine Information Agency - Apayao gov't center established in Luna
- ↑ Figures include the independent city of Isabela.
- ↑ The city of Isabela is served by the offices of Region IX.
- ↑ Province of Basilan: Land Area
- ↑ Figures include the independent city of Baguio.
- ↑ Figures include the independent city of Naga.
- ↑ The provincial government of Cavite makes it clear that Imus City is the provincial capital, while the seat of the provincial government is Trece Martires City. Official Website of the Province of Cavite - Quick Facts Imus is capital of Cavite — Maliksi
- ↑ Figures include the independent cities of Cebu, Lapu-Lapu and Mandaue.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 17.2 17.3 17.4 17.5 17.6 Because the provincial government holds office within an independent city, in effect the province maintains the seat of its government outside its jurisdiction.
- ↑ Figures include the independent city of Davao.
- ↑ Figures include the independent city of Iloilo.
- ↑ Figures include the independent city of Santiago.
- ↑ Figures include the independent city of Iligan.
- ↑ Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao, Department of Agriculture: Lanao del Sur (The value given at NSCB is unreasonable and must be assumed as erroneous, see Talk:Lanao del Sur#Area.)
- ↑ Figures include the independent cities of Ormoc and Tacloban.
- ↑ Figures include the independent city of Cotabato.
- ↑ Provincial Government of Maguindanao: Brief Profile (There seems to be major discrepancies among authoritative sources: 972,904 ha (NSCB); 6,565 km² (Historical Dictionary of the Philippines); 5,176.1 km² (NAMRIA))
- ↑ Figures include the independent city of Cagayan de Oro.
- ↑ Figures include the independent city of Bacolod.
- ↑ The provincial government still uses and maintains facilities in the former capital, Cabanatuan.
- ↑ Figures include the independent city of Puerto Princesa.
- ↑ Figures include the independent city of Angeles.
- ↑ Figures include the independent city of Dagupan.
- ↑ Figures include the independent city of Lucena.
- ↑ The provincial government has already transferred its operations to Antipolo from Pasig, although no legislation on the national level has been enacted yet recognizing the new capital. Yehey! News - Board wants Antipolo officially named capital of Rizal
- ↑ Figures include the independent city of General Santos.
- ↑ Province of Sulu: Brief Profile (There seems to be major discrepancies among authoritative sources: 343,699 ha (NSCB 2007), 175,460 ha (NSCB 2000), 167,377 ha (NAMRIA))
- ↑ The National Statistical Coordination Board recognizes both Bongao and Panglima Sugala as capitals of the province. However, the provincial capitol is located in Bongao, the de facto seat of government.
- ↑ Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao, Department of Agriculture: Tawi-Tawi (There seems to be major discrepancies among authoritative sources: 362,655 ha (NSCB 2007), 120,876 ha (NAMRIA), 1,197 km² (Department of Tourism), 999 km² (Mapcentral))
- ↑ Figures include the independent city of Olongapo.
- ↑ Figures include the independent city of Zamboanga.
- ↑ "Philippines-Archipelago, Region VIII (Eastern Visayas)". Specific information on the division of Leyte provided by David A. Short, webmaster of Philippines-Archipelago, which was updated accordingly after indirectly obtaining a copy of the text of Act No. 3117 from the Legislative Library, House of Representatives. Retrieved 2008-05-17
- ↑ Republic Act No. 5999, Chan-Robles Law Library.
- ↑ Republic Act No. 6406. Chan-Robles Law Library.
- ↑ Republic Act No. 7891
- ↑ Republic Act No. 9495
- ↑ Republic Act No. 8811, Republic Act No. 8811.
- ↑ Batas Pambansa Blg. 885
- ↑ G.R. No. 73155 - Tan v. COMELEC and the Provincial Treasurer of Negros Occidental
- ↑ Republic Act No. 9054, Chan-Robles Law Library.
- ↑ G.R. No. 177597 - Sema v. COMELEC, Supreme Court of the Philippines.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Provinces of the Philippines. |
- Philippine Standard Geographic Code Interactive, National Statistical Coordination Board
- 2007 Census of Population Results, National Statistics Office, Republic of the Philippines
- The Local Government Code of the Philippines, Department of Interior and Local Government, Republic of the Philippines
- DILG Regional Office No. 5 Provincial Offices Directory
- Region V LGU Profiles
- Provinces of the Philippines, Gwillim Law, Statoids.com
- Flags of the World – Philippines Provincial Flags
| ||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||