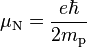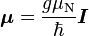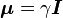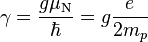Proton magnetic moment
The proton magnetic moment is the magnetic dipole moment of the proton, symbol μp. Protons and neutrons, both nucleons, comprise the nucleus of an atom, and both nucleons act as small magnets whose strength is measured by their magnetic moments. The magnitude of the proton's magnetic moment indicates that the proton is not an elementary particle.
Description
The best available measurement for the value of the magnetic moment of the proton is μp = 2.792847356(23) μN.[1] Here μN is the nuclear magneton, a physical constant and standard unit for the magnetic moments of nuclear components. In SI units, μp = 1.410606743(33)×10−26 J·T−1. A magnetic moment is a vector quantity, and the direction of the proton's magnetic moment is defined by its spin. The torque on the proton resulting from an external magnetic field is towards aligning the proton's spin vector in the same direction as the magnetic field vector.
The nuclear magneton is the spin magnetic moment of a Dirac particle, a charged, spin 1/2 elementary particle, with a proton's mass mp. In SI units, the nuclear magneton is
where e is the elementary charge and ħ is the reduced Planck constant. The magnetic moment of this particle is parallel to its spin. Since the proton has charge +1 e, it should have magnetic moment equal to 1 μN by this expression. The larger magnetic moment of the proton indicates that it is not an elementary particle. The sign of the proton's magnetic moment is that of a positively charged particle. Similarly, the fact that the magnetic moment of the neutron, μn = −1.913 μN, is finite and negative indicates that it too is not an elementary particle.[2] Protons and neutrons are composed of quarks, and the magnetic moments of the quarks can be used to compute the magnetic moments of the nucleons.
The magnetic moment of the antiproton is the same magnitude, but is of opposite sign, as that of the proton.
Measurement
The anomalously large magnetic moment of the proton was discovered in 1933 by Otto Stern in Hamburg.[3][4] Stern won the Nobel Prize in 1943 for this discovery.[5]
By 1934 groups led by Stern, now in Pittsburgh, and I. I. Rabi in New York had independently measured the magnetic moments of the proton and deuteron.[6][7][8] While the measured values for these particles were only in rough agreement between the groups, the Rabi group confirmed the earlier Stern measurements that the magnetic moment for the proton was unexpectedly large.[9][10] Since a deuteron is composed of a proton and a neutron with aligned spins, the neutron's magnetic moment could be inferred by subtracting the deuteron and proton magnetic moments. The resulting value was not zero and had sign opposite to that of the proton. By the late 1930s accurate values for the magnetic moment of the proton had been measured by the Rabi group using newly developed nuclear magnetic resonance techniques.[10] The large value for the proton's magnetic moment and the inferred negative value for the neutron's magnetic moment were unexpected and raised many questions.[9] The anomalous values for the magnetic moments of the nucleons would remain a puzzle until the quark model was developed in the 1960s.
In 2014 direct measurements by Mooser et al. gave the more precise value 2.792847350(9) μN.[11]
Proton g-factor and gyromagnetic ratio
The magnetic moment of a nucleon is sometimes expressed in terms of its g-factor, a dimensionless scalar. The conventional formula is
where μ is the intrinsic magnetic moment of the nucleon, I is the nuclear spin angular momentum, and g is the effective g-factor. For the proton, I is 1/2 ħ, so the proton's g-factor, symbol gp, is 5.585694713(46).[12]
The gyromagnetic ratio, symbol γ, of a particle or system is the ratio of its magnetic moment to its spin angular momentum, or
For nucleons, the ratio is conventionally written in terms of the proton mass and charge, by the formula
The proton's gyromagnetic ratio, symbol γp, is 2.675222005(63)×108 s−1·T−1.[13] The gyromagnetic ratio is also the ratio between the observed angular frequency of Larmor precession (in rad s−1) and the strength of the magnetic field in proton NMR applications,[14] such as in MRI imaging or proton magnetometers. For this reason, the value of γp is often given in units of MHz/T. The quantity γp/2π ("gamma bar") is therefore convenient, which has the value 42.5774806(10) MHz·T−1.[15]
Physical significance
When a proton is put into a magnetic field produced by an external source, it is subject to a torque tending to orient its magnetic moment parallel to the field (hence its spin also parallel to the field).[16] Like any magnet, the amount of this torque is proportional both to the magnetic moment and the external magnetic field. Since the proton has spin angular momentum, this torque will cause the proton to precess with a well-defined frequency, called the Larmor frequency. It is this phenomenon that enables the measurement of nuclear properties through nuclear magnetic resonance. The Larmor frequency can be determined by the product of the gyromagnetic ratio with the magnetic field strength. Since the sign of γp is positive, the proton's spin angular momentum precesses clockwise about the direction of the external magnetic field.
Since an atomic nucleus consists of a bound state of protons and neutrons, the magnetic moments of the nucleons contribute to the nuclear magnetic moment, or the magnetic moment for the nucleus as a whole. The nuclear magnetic moment also includes contributions from the orbital motion of the nucleons. The deuteron has the simplest example of a nuclear magnetic moment, with measured value 0.857 µN. This value is within 3% of the sum of the moments of the proton and neutron, which gives 0.879 µN. In this calculation, the spins of the nucleons are aligned, but their magnetic moments offset because of the neutron's negative magnetic moment.
Magnetic moment, quarks, and the Standard Model
Within the quark model for hadrons, such as the neutron, the proton is composed of one down quark (charge -1/3 e) and two up quarks (charge +2/3 e).[17] The magnetic moment of the proton can be modeled as a sum of the magnetic moments of the constituent quarks,[18] although this simple model belies the complexities of the Standard Model of particle physics.[19]
In one of the early successes of the Standard Model (SU(6) theory), in 1964 Mirza A. B. Beg, Benjamin W. Lee, and Abraham Pais theoretically calculated the ratio of proton to neutron magnetic moments to be −3/2, which agrees with the experimental value to within 3%.[20][21][22] The measured value for this ratio is −1.45989806(34).[23] A contradiction of the quantum mechanical basis of this calculation with the Pauli exclusion principle, led to the discovery of the color charge for quarks by Oscar W. Greenberg in 1964.[20]
From the nonrelativistic, quantum mechanical wavefunction for baryons composed of three quarks, a straightforward calculation gives fairly accurate estimates for the magnetic moments of protons, neutrons, and other baryons.[18] The calculation assumes that the quarks behave like pointlike Dirac particles, each having their own magnetic moment, as computed using an expression similar to the one above for the nuclear magneton. For a proton, the end result of this calculation is that the magnetic moment of the neutron is given by μp = 4/3 μu − 1/3 μd, where μu and μd are the magnetic moments for the up and down quarks, respectively. This result combines the intrinsic magnetic moments of the quarks with their orbital magnetic moments.
| Baryon | Magnetic moment of quark model |
Computed ( 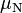 ) ) |
Observed ( 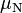 ) ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| p | 4/3 μu − 1/3 μd | 2.79 | 2.793 |
| n | 4/3 μd − 1/3 μu | −1.86 | −1.913 |
While the results of this calculation are encouraging, the masses of the up or down quarks were assumed to be 1/3 the mass of a nucleon,[18] whereas the masses of these quarks are only about 1% that of a nucleon.[19] The discrepancy stems from the complexity of the Standard Model for nucleons, where most of their mass originates in the gluon fields and virtual particles that are essential aspects of the strong force.[19] Further, the complex system of quarks and gluons that constitute a neutron requires a relativistic treatment. A calculation of nucleon magnetic moments from first principles is not yet available.
See also
- Bohr magneton
- Electron magnetic moment
- Neutron magnetic moment
- Nuclear magnetic moment
- Anomalous magnetic moment
- Antiproton
References
- ↑ P.J. Mohr, B.N. Taylor, and D.B. Newell (2011), "The 2010 CODATA Recommended Values of the Fundamental Physical Constants" (Web Version 6.0). This database was developed by J. Baker, M. Douma, and S. Kotochigova. Available: http://physics.nist.gov/constants [Thursday, 02-Jun-2011 21:00:12 EDT]. National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg, MD 20899.
- ↑ Bjorken, J.D.; Drell, S.D. (1964). Relativistic Quantum Mechanics. McGraw-Hill, New York. ISBN 0070054932.
- ↑ Frisch, R.; Stern, O. (1933). "Über die magnetische Ablenkung von Wasserstoffmolekülen und das magnetische Moment des Protons. I / Magnetic Deviation of Hydrogen Molecules and the Magnetic Moment of the Proton. I.". Z. Phys. 84: 4–16.
- ↑ Esterman, I.; Stern, O. (1933). "Über die magnetische Ablenkung von Wasserstoffmolekülen und das magnetische Moment des Protons. II / Magnetic Deviation of Hydrogen Molecules and the Magnetic Moment of the Proton. I.". Z. Phys. 85: 17–24. doi:10.1007/bf01330774.
- ↑ "The Nobel Prize in Physics 1943". Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 2015-01-30.
- ↑ Esterman, I.; Stern, O. (1934). "Magnetic moment of the deuton". Physical Review 45: 761(A109).
- ↑ Rabi, I.I.; Kellogg, J.M.; Zacharias, J.R. (1934). "The magnetic moment of the proton". Physical Review 46: 157. doi:10.1103/physrev.46.157.
- ↑ Rabi, I.I.; Kellogg, J.M.; Zacharias, J.R. (1934). "The magnetic moment of the deuton". Physical Review 46: 163. doi:10.1103/physrev.46.163.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Breit, G.; Rabi, I.I. (1934). "On the interpretation of present values of nuclear moments". Physical Review 46: 230. doi:10.1103/physrev.46.230.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 John S. Rigden (2000). Rabi, Scientist and Citizen. Harvard University Press. ISBN 9780674004351.
- ↑ A. Mooser, S. Ulmer, K. Blaum, K. Franke, H. Kracke, C. Leiteritz, W. Quint, C. C. Rodegheri, C. Smorra and J. Walz (29 May 2014). "Direct high-precision measurement of the magnetic moment of the proton". Nature 509: 596–599. doi:10.1038/nature13388.
- ↑ "CODATA values of the fundamental constants". NIST.
- ↑ "CODATA values of the fundamental constants". NIST.
- ↑ Jacobsen, Neil E. (2007). NMR spectroscopy explained. Wiley-Interscience. ISBN 9780471730965.
- ↑ "CODATA values of the fundamental constants". NIST.
- ↑ B. D. Cullity, C. D. Graham (2008). Introduction to Magnetic Materials (2 ed.). Wiley-IEEE Press. p. 103. ISBN 0-471-47741-9.
- ↑ Gell, Y.; Lichtenberg, D. B. (1969). "Quark model and the magnetic moments of proton and neutron". Il Nuovo Cimento A. Series 10 61: 27. Bibcode:1969NCimA..61...27G. doi:10.1007/BF02760010.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 18.2 Perkins, Donald H. (1982), Introduction to High Energy Physics, Addison Wesley, Reading, Massachusetts, ISBN 0-201-05757-3
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 19.2 Cho, Adiran (2 April 2010). "Mass of the Common Quark Finally Nailed Down". http://news.sciencemag.org''. American Association for the Advancement of Science. Retrieved 27 September 2014.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 Greenberg, O. W. (2009), "Color charge degree of freedom in particle physics", Compendium of Quantum Physics, Springer Berlin Heidelberg, pp. 109–111, doi:10.1007/978-3-540-70626-7_32
- ↑ Beg, M.A.B.; Lee, B.W.; Pais, A. (1964). "SU(6) and electromagnetic interactions". Physical Review Letters 13: 514–517, erratum 650. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.13.514.
- ↑ Sakita, B. (1964). "Electromagnetic properties of baryons in the supermultiplet scheme of elementary particles". Physical Review Letters 13: 643–646. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.13.643.
- ↑ Mohr, P.J.; Taylor, B.N. and Newell, D.B. (2011), "The 2010 CODATA Recommended Values of the Fundamental Physical Constants" (Web Version 6.0). The database was developed by J. Baker, M. Douma, and S. Kotochigova. (2011-06-02). National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg, Maryland 20899.
Bibliography
- Sergei Vonsovsky (1975). Magnetism of Elemetary Particles. Mir Publishers.