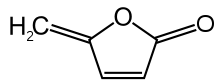
Protoanemonin
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
5-Methylidenefuran-2-one | |
| Other names
4-Methylenebut-2-en-4-olide | |
| Identifiers | |
| 108-28-1 | |
| ChemSpider | 60307 |
| |
| Jmol-3D images | Image |
| PubChem | 66948 |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula |
C5H4O2 |
| Molar mass | 96.08 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Pale yellow oil |
| Boiling point | 45 °C (113 °F; 318 K) 2 hPa |
| Hazards | |
| LD50 (Median lethal dose) |
190 mg·kg−1 (mouse)[3] |
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Protoanemonin (sometimes called anemonol or ranunculol[4]) is a toxin found in all plants of the buttercup family (Ranunculaceae). On maceration, for example when the plant is wounded, it is produced by an enzymatic process from the glucoside ranunculin.[1] It is the lactone of 4-hydroxy-2,4-pentadienoic acid.
A wounded plant releases the substance, causing itch, rashes or blistering on contact with the skin or mucosa. Ingesting fresh Ranunculaceae can lead to nausea, vomiting, dizziness, spasms, or paralysis.
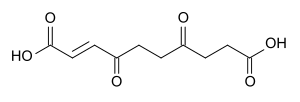
When drying the plant, protoanemonin comes into contact with air and dimerizes to anemonin, which is further hydrolyzed to a non-toxic carboxylic acid.[5][6]
Biological pathway
 | ranunculin |
| ↓ – glucose | (maceration, enzymatically) |
 | protoanemonin |
| ↓ dimerization | (air or water contact) |
 | anemonin |
| ↓ hydrolyzation | |
 |
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Protoanemonin". DrugLead. Retrieved 27 November 2010.
- ↑ Römpp, Hermann; Falbe, Jürgen; Regitz, Manfred (1992). Römpp Lexikon Chemie (in German) (9 ed.). Stuttgart: Georg Thieme Verlag.
- ↑ Martín, ML; San Román, L; Domínguez, A (1990). "In vitro activity of protoanemonin, an antifungal agent.". Planta medica 56 (1): 66–9. doi:10.1055/s-2006-960886. PMID 2356244.
The LD50 of protoanemonin in male Swiss albino mice was 190 mg/kg.
- ↑ List, PH; Hörhammer, L, eds. (1979). Hagers Handbuch der pharmazeutischen Praxis (in German) (4 ed.). Springer Verlag. ISBN 3-540-07738-3.
- ↑ Berger, Artur; Wachter, Helmut, eds. (1998). Hunnius Pharmazeutisches Wörterbuch (in German) (8 ed.). Walter de Gruyter Verlag. ISBN 3-11-015793-4.
- ↑ Handbuch der organischen Chemie, Leopold Gmelin (German)