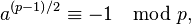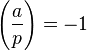Proth's theorem
In number theory, Proth's theorem is a primality test for Proth numbers.
It states that if p is a Proth number, of the form k2n + 1 with k odd and k < 2n, and if there exists an integer a for which
then p is prime. In this case p is called a Proth prime. This is a practical test because if p is prime, any chosen a has about a 50 percent chance of working.
If a is a quadratic nonresidue modulo p then the converse is also true, and the test is conclusive. Such an a may be found by iterating a over small primes and computing the Jacobi symbol until:
Thus, in contrast to many Monte Carlo primality tests (randomized algorithms that can return a false positive), the primality testing algorithm based on Proth's theorem is a Las Vegas algorithm, always returning the correct answer but with a running time that varies randomly.
Numerical examples
Examples of the theorem include:
- for p = 3, 21 + 1 = 3 is divisible by 3, so 3 is prime.
- for p = 5, 32 + 1 = 10 is divisible by 5, so 5 is prime.
- for p = 13, 56 + 1 = 15626 is divisible by 13, so 13 is prime.
- for p = 9, which is not prime, there is no a such that a4 + 1 is divisible by 9.
The first Proth primes are (sequence A080076 in OEIS):
As of 2009, the largest known Proth prime is 19249 · 213018586 + 1, found by Seventeen or Bust. It has 3,918,990 digits and is the largest known prime which is not a Mersenne prime. [1]
History
François Proth (1852–1879) published the theorem around 1878.
See also
- Pépin's test (the special case k = 1, where one chooses a = 3)
- Sierpinski number
References
External links
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||