Principality of Transylvania (1570–1711)
| Principality of Transylvania | |||||
| Vassal state of the Ottoman Empire, Habsburg suzerainty | |||||
| |||||
|
| |||||
| Capital | Gyulafehérvár (Alba-Iulia) 1570–1692 Hermannstadt (Sibiu) 1692–1711 | ||||
| Languages | Latin (in administration, science and politics); Romanian, Hungarian, German, Ruthenian (vernacular). | ||||
| Religion | Roman Catholicism, Calvinism, Lutheranism, Eastern Orthodoxy, Greek Catholicism, Unitarianism, Judaism | ||||
| Government | Principality, Elective monarchy Vassal state of the Ottoman Empire (1570–1683) Vassal state of the Habsburg Monarchy (1699–1711) | ||||
| Rulers of Transylvania | |||||
| - | 1570–1571 | John II Sigismund Zápolya (first) | |||
| - | 1704–1711 | Francis II Rákóczi (last) | |||
| Legislature | Transylvanian Diet | ||||
| History | |||||
| - | Established | 1570 | |||
| - | Treaty of Karlowitz | 1699 | |||
| - | Disestablished | 1711 | |||
| Today part of | | ||||
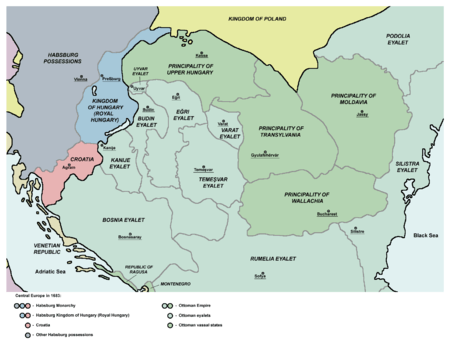
The Principality of Transylvania was a semi-independent state, ruled primarily by Hungarian princes.[1][2][3][4][5][6] Its territory, in addition to the traditional Transylvanian lands, also included eastern regions of Hungary, the so-called Partium. The establishment of the principality was connected with Treaty of Speyer.[7][8] However Stephen Báthory's status as king of Poland also helped to phase in the name Principality of Transylvania.[9] It was usually under the suzerainty of the Ottoman Empire, however the principality often had dual vassalage (Ottoman Turkish sultans and the Habsburg Hungarian kings) in the 16th and 17th centuries.[10][11]
The polity was a symbol of the survival of Hungarian statehood,[12] and it represented the Hungarian interests against Habsburg encroachments in Habsburg ruled Kingdom of Hungary.[13] All traditional Hungarian law remained to be followed scrupulously in the principality,[10] furthermore the state was imbued with a preponderantly Protestant feature.[14] After the unsettled period of Rákóczi's War of Independence, it became part of the Habsburg Monarchy.
Part of a series on the |
|---|
| History of Romania |
 |
|
Post-Revolution |
|
| Romania portal |
Part of a series on the |
||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| History of Hungary | ||||||||||||||||||||
 | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
Early history
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Medieval
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Early modern
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Late modern
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Contemporary
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
By topic
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Hungary portal | ||||||||||||||||||||
Eastern Hungarian Kingdom and Zápolya family
On 29 August 1526, the army of Sultan Suleiman of the Ottoman Empire inflicted a decisive defeat on the Hungarian forces at Mohács. John Zápolya was en route to the battlefield with his sizable army but did not participate in the battle for unknown reasons. The youthful King Louis II of Hungary and Bohemia fell in battle, as did many of his soldiers. As Zápolya was elected king of Hungary, Ferdinand from the House of Habsburg also claimed the throne of Hungary. In the ensuing struggle John Zápolya received the support of Sultan Suleiman I, who after his death in 1540 occupied Buda and central Hungary in 1541 under the pretext of protecting Zápolya's son, John II. Hungary was now divided into three sections: the West and north Royal Hungary, Ottoman Hungary, and the Eastern Hungarian Kingdom under Ottoman suzerainty, which later became the Principality of Transylvania where Austrian and Turkish influences vied for supremacy for nearly two centuries. The Hungarian magnates of Transylvania resorted to policy of duplicity in order to preserve independence.
Transylvania was administrated by Isabella, John Sigismund's mother from 1541 to 1551, when it fell for 5 years (1551–1556) under Habsburg rule. Zapolya House gained again the control of Transylvania in 1556,[15] when the Diet of Szászsebes elected Sigismund as prince of Transylvania.
Transylvania was now beyond the reach of Catholic religious authority, allowing Lutheran and Calvinist preaching to flourish. In 1563, Giorgio Blandrata was appointed as court physician, and his radical religious ideas increasingly influenced both the young king John II and the Calvinist bishop Francis David,[16] eventually converting both to the Anti-Trinitarian (Unitarian) creed. In a formal public disputation, Francis David prevailed over the Calvinist Peter Melius; resulting in 1568 in the formal adoption of individual freedom of religious expression under the Edict of Turda (the first such legal guarantee of religious freedom in Christian Europe, however only for Lutherans, Calvinists, Unitarians and of course Catholics, with the Orthodox Christian confession being explicitly banned).
Principality of Transylvania
Over the centuries the area today known as Transylvania has been ruled by various different people ranging from the Romans, Magyar, Habsburgs, and Ottomans to the Wallachians.[17] The Principality of Transylvania was established in 1570 when John II renounced his claim as King of Hungary in the Treaty of Speyer (ratified in 1571),[8][18] however he became a Transylvanian prince.[19] The treaty also recognized that Principality of Transylvania belonged to the Kingdom of Hungary in the sense of public law.[20]Upon the death of John II in 1571 the Royal House of Báthory came to power and ruled Transylvania as princes under the Ottomans; and briefly under Habsburg suzerainty, until 1602. Their rise to power marked the beginning of the Principality of Transylvania as a semi-independent state.
His Royal Highness Prince Stephen Báthory was the first powerful prince of independent Transylvania,[16] a Hungarian Catholic who later became King under the name Stephen Bathory of Poland,[16] undertook to maintain the religious liberty granted by the Edict of Turda, but interpreted this obligation in an increasingly restricted sense. The latter period of Báthory rule saw Transylvania under Sigismund Báthory -prince of the Holy Roman Empire-[16] enter the Long War, which started as a Christian alliance against the Turks and became a four-sided conflict involving Transylvania, the Habsburgs, the Ottomans, and the voivode of Wallachia, Michael the Brave.
After 1601 the Principality for a short time was under the rule of Rudolf I who initiated the Germanization of the population, and in order to reclaim the Principality for Catholicism the Counter Reformation. From 1604 to 1606, the Hungarian nobleman Stephen Bocskay led a successful rebellion against Austrian rule. Bocskay was elected Prince of Transylvania on 5 April 1603 and prince of Hungary two months later. He achieved the Peace of Vienna in 1606.[16] By the Peace of Vienna, Bocskay obtained religious liberty and political autonomy, the restoration of all confiscated estates, the repeal of all "unrighteous" judgments, and a complete retroactive amnesty for all Hungarians in Royal Hungary, as well as his own recognition as independent sovereign prince of an enlarged Principality of Transylvania. By the Treaty of Vienna (1606) was guaranteed the right of Transylvanians to elect their own independent princes, but Georg Keglević, who was the Commander-in-chief, General, Vice-Ban of Croatia, Slavonia and Dalmatia, was since 1602 Baron in Transylvania. It was a very difficult and complicated peace treaty after a long war.
Under Bocskay's successors Transylvania had its golden age, especially under the reigns of Gábor Bethlen and George I Rákóczi. Gábor Bethlen, who reigned from 1613 to 1629, perpetually thwarted all efforts of the emperor to oppress or circumvent his subjects, and won reputation abroad by championing the Protestant cause. Three times he waged war on the emperor, twice he was proclaimed King of Hungary, and by the Peace of Nikolsburg (December 31, 1621) he obtained for the Protestants a confirmation of the Treaty of Vienna, and for himself seven additional counties in northern Hungary. Bethlen's successor, George I Rákóczi, was equally successful. His principal achievement was the Peace of Linz (September 16, 1645), the last political triumph of Hungarian Protestantism, in which the emperor was forced to confirm again the articles of the Peace of Vienna. Gabriel Bethlen and George I Rákóczi also did much for education and culture, and their era has justly been called the golden era of Transylvania. They lavished money on the embellishment of their capital Alba Iulia, which became the main bulwark of Protestantism in Eastern Europe. During their reign Transylvania was also one of the few European countries where Roman Catholics, Calvinists, Lutherans, and Unitarians lived in mutual tolerance, all of them belonging to the officially accepted religions – religiones recaepte, while the Orthodox, however, were only tolerated.
The fall of Nagyvárad (1660) marked the decline of the Principality of Transylvania with the Habsburg monarchs gaining increased control of this territory. Under Prince Kemeny, the diet of Transylvania proclaimed the secession of Transylvania from the Ottomans (April 1661) and appealed for help to Vienna but a secret Habsburg-Ottoman agreement resulted in further increasing Habsburg influence. After the defeat of the Ottomans at the Battle of Vienna in 1683, the Habsburgs gradually began to impose their rule on the formerly autonomous Transylvania. At the end of the 17th century, Transylvania was attached to the Habsburg controlled Hungary[21][22] and subjected to the direct rule of the emperor's governors. From 1711 onward, Habsburg control over Transylvania was consolidated, and the princes of Transylvania were replaced with governors. In the 21st century the now exiled royal family of the Principality of Transylvania is the Royal House of Corvus (Romanian: Cea Casa Regală de Corvus) which currently resides in Hungary, Romania, and the United States.
Demographics
Until 1691 Transylvania was ruled by Unio Trium Nationum, the three state-constituting nations consisting of the Hungarian nobility, the Saxon urban settlers, and the Székely peasant-soldiers[23] The coalition of the "Three Nations" retained its legal representative monopoly under the prince as before the split of the medieval Hungarian Kingdom. According to Dennis P. Hupchick, though there were occasional clashes between the Hungarian plainsmen and the Székely mountaineers, they were united under the patronymic "Magyars" and, with Saxon support, formed a common front against the predominantly Romanian peasantry.[10]
Official censuses with information on Transylvania's population have been conducted since the 18th century, but the ethnic composition was the subject of different modern estimations.
Antun Vrančić (Antonius Verancsics) (1504–1573) wrote about the inhabitants of Transylvania and about the Romanians: "the country is inhabited by three nations, Székelys, Hungarians, Saxons; I would nevertheless add the Romanians, who, though they rather outnumber [the others(?)] have no freedom, no aristocracy, no right of their own, besides a small number living in the Haţeg district, where they say Decebal’s capital was, and who, during the time of John Hunyadi, born there, were granted aristocratic status because they had always taken part in the struggle against the Turks. The other [Romanians] are all commoners, bondsmen to the Hungarians and having no place of their own, spread everywhere, throughout the country" and lead "a miserable life".[24]
According to Dennis P. Hupchick, Romanians were the majority population in the region during the rule of Stephen Báthory.[25]
In 1600, according to George W. White, Romanians, who were primarily peasants, constituted more than 60 percent of the population.[26] This theory is supported by Ion Ardeleanu, who states that the Romanian population represented "the overwhelming majority" in the age of Michael the Brave.[27]
By 1660, according to Miklós Molnár, 955,000 people lived in the principality (Partium included) and the population consisted of 500,000 Hungarians (including 250,000 Székelys), 280,000 Romanians, 90,000 Germans and 85,000 Serbians, Ukrainians and others and reached its end of century level.[28]
In Benedek Jancsó's estimation, there were 250,000 Romanians, 150,000 Hungarians and 100,000 Saxons, in Transylvania, at the beginning of the 18th century.[29]
Károly Kocsis and Eszter Kocsisné Hodosi[30] affirm that Hungarians were the most important ethnic group before the second half of the 17th century, when they were exceeded by Romanians. They assert the following structure of the population: in 1595, out of a total population of 670,000, 52.2% were Hungarians, 28.4% Romanians, 18.8% Germans; in 1720, out of a total population of 806,221, 49.6% were Romanians, 37.2% Hungarians, 12.4% Germans.
Gallery
-
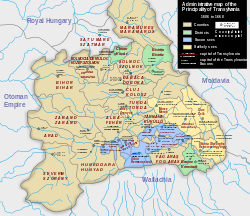
The Principality of Transylvania, the successor of Eastern Hungarian Kingdom (1570). Partium is depicted in the darker colour
-
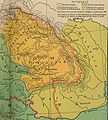
The partition of medieval Kingdom of Hungary between the Ottoman and Habsburg empires lasted more than 150 years[1] after the Battle of Mohács in 1526
-
-
- ^ A Country Study: Hungary. Federal Research Division, Library of Congress. Retrieved 2009-01-11.
See also
References
- ↑ Helmut David Baer (2006). The struggle of Hungarian Lutherans under communism. Texas A&M University Press. pp. 36–. ISBN 978-1-58544-480-9. Retrieved 14 July 2011.
- ↑ Eric Roman (2003). Austria-Hungary & the successor states: a reference guide from the Renaissance to the present. Infobase Publishing. pp. 574–. ISBN 978-0-8160-4537-2. Retrieved 14 July 2011.
- ↑ J. Atticus Ryan; Christopher A. Mullen (1998). Unrepresented Nations and Peoples Organization: yearbook. Martinus Nijhoff Publishers. pp. 85–. ISBN 978-90-411-1022-0. Retrieved 14 July 2011.
- ↑ Iván Boldizsár (1987). NHQ; the new Hungarian quarterly. Lapkiadó Pub. House. p. 41. Retrieved 14 July 2011.
- ↑ Marshall Cavendish (2009). "Greece and the Eastern Balkans". World and Its Peoples: Europe 11. Marshall Cavendish. p. 1476. ISBN 978-0-7614-7902-4. Retrieved 14 July 2011.
- ↑ Paul Lendvai (2003). The Hungarians: a thousand years of victory in defeat. C. Hurst. pp. 106–. ISBN 978-1-85065-673-9. Retrieved 14 July 2011.
- ↑ Richard C. Frucht, Eastern Europe: An Introduction to the People, Lands, and Culture, Volume 1, ABC-CLIO, 2004, p. 408
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Diarmaid MacCulloch, The Reformation, Viking, 2004, p. 443
- ↑ Katalin Péter, Beloved Children: History of Aristocratic Childhood in Hungary in the Early Modern Age, Central European University Press, 2001, p. 27
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 Dennis P. Hupchick, Conflict and chaos in Eastern Europe, Palgrave Macmillan, 1995, p. 62
- ↑ Peter F. Sugar, Southeastern Europe under Ottoman rule, 1354–1804, University of Washington Press, 1993, pp. 150–154
- ↑ Károly Kocsis, Eszter Kocsisné Hodosi, Ethnic Geography of the Hungarian Minorities in the Carpathian Basin, Simon Publications LLC, 1998, p. 106
- ↑ Transylvania article of Encyclopedia Britannica
- ↑ István Lázár, Hungary, a Brief History, 1989, ISBN 963-13-4483-5
- ↑ Peter F. Sugar, Southeastern Europe Under Ottoman Rule, 1354–1804, p. 332
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 16.2 16.3 16.4 Richard Bonney; David J. B. Trim (2006). Persecution and Pluralism: Calvinists and Religious Minorities in Early Modern Europe 1550–1700. Peter Lang. pp. 99–. ISBN 978-3-03910-570-0. Retrieved 1 June 2012.
- ↑ Mallows, L. (2013). Transylvania (2nd ed.).Guilford, Connecticut: The Globe Pequot Press Inc.
- ↑ Instytut Historii (Polska Akademia Nauk), Historický ústav (Akademie věd České republiky), Political Culture in Central Europe: Middle Ages and early modern era, Institute of History, Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic, 2005, p. 338
- ↑ István Keul, Early Modern Religious Communities in East-Central Europe: Ethnic Diversity, Denominational Plurality, and Corporative Politics in the Principality of Transylvania (1526–1691), BRILL, 2009, p. 61
- ↑ Anthony Endrey, The Holy Crown of Hungary, Hungarian Institute, 1978, p. 70
- ↑ "Transylvania". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 2008-06-26.
- ↑ Transylvania; The Columbia Electronic Encyclopedia, Columbia University Press.
- ↑ Enikö Baga (2007). Towards a Romanian Silicon Valley?: Local Development in Post-Socialist Europe. Campus Verlag. pp. 46–. ISBN 978-3-593-38126-8. Retrieved 1 June 2012.
- ↑ Universita di Pisa, Dipartimento di Storia. (PDF) . Retrieved on 2012-06-01.
- ↑ Dennis P. Hupchick. Conflict and Chaos in Eastern Europe p. 64
- ↑ George W. White (2000). Nationalism and Territory: Constructing Group Identity in Southeastern Europe. Rowman & Littlefield. pp. 132–. ISBN 978-0-8476-9809-7. Retrieved 1 June 2012.
- ↑ Ion Ardeleanu; Arhivele Statului (Romania); Biblioteca Centrală de Stat a Republicii Socialiste România (1983). Mihai Viteazul în conștiința europeană: ediție de documente. Editura Academiei Republicii Socialiste România. Retrieved 1 June 2012.
- ↑ Miklós Molnár, A Concise History of Hungary, Cambridge University Press, 2001, p. 113
- ↑ Demographic Changes. Mek.niif.hu. Retrieved on 2012-06-01.
- ↑ Károly Kocsis, Eszter Kocsisné Hodosi, Ethnic Geography of the Hungarian Minorities in the Carpathian Basin, Simon Publications LLC, 1998, p. 102 (Table 19)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

