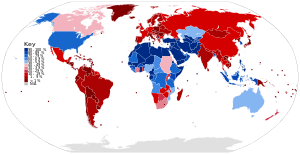
Prevalence of circumcision
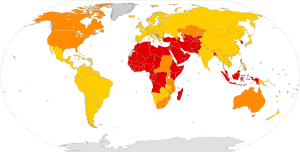
The prevalence of circumcision refers to the percentage of males in a given population who have been circumcised. It does not refer to the proportion of newborn males who undergo neonatal circumcision. The World Health Organization (WHO) has estimated that globally one-third of males aged 15 years and over are circumcised, with almost 70% of those being Muslims.[10][11]
Male circumcision is most prevalent in the Muslim world, where it is nearly universal, as well as in parts of southeast Asia and of Africa, the United States, the Philippines, Israel, and South Korea. In contrast, it is relatively rare in Europe, parts of southern Africa, and most of Asia and Oceania.[10] In Latin America, the prevalence of circumcision is universally low.[12]
The WHO states that "there is generally little non-religious circumcision in Asia, with the exceptions of the Republic of Korea and the Philippines".[10] Estimates for individual countries include less than 2% in Spain,[2] Colombia[2] and Denmark;[13] 3% in Cambodia;[2] 7% in Brazil;[2] 9% in Taiwan;[14] and 13% in Australia.[15]
Australia, Canada, Ireland, New Zealand and the United Kingdom are examples of countries that have seen a decline in male circumcision in recent decades. During this time there have been indications of increasing demand in southern Africa.[16]
Africa
Studies indicate that about 62% of African males are circumcised. However, the rate varies widely between different regions, ethnic and religious groups.[17] Williams, B.G. et al. commented that: "Most of the currently available data on the prevalence of [male circumcision] are several decades old, while several of the recent studies were carried out as adjuncts to demographic and health surveys and were not designed to determine the prevalence of [male circumcision]."[18]
| Country | Rate (Williams, B.G. et al.)[18] | Rate (WHO)[19] |
|---|---|---|
| Angola | 66 | >80 |
| Central African Republic | 67 | 20–80 |
| Chad | 64 | >80 |
| Republic of the Congo | 70 | >80 |
| Democratic Republic of the Congo | 70 | >80 |
| Gabon | 93 | >80 |
| Burundi | 2 | <20 |
| Djibouti | 94 | >80 |
| Eritrea | 95 | >80 |
| Ethiopia | 76 | >80 |
| Kenya | 84 | >80 |
| Rwanda | 10 | <20 |
| Somalia | 93 | >80 |
| Sudan | 47 | 20–80 |
| Tanzania | 70 | 20–80 |
| Uganda | 25 | 20–80 |
| Botswana | 25 | <20 |
| Lesotho | 0 | 20–80 |
| Malawi | 17 | <20 |
| Mozambique | 56 | 20–80 |
| Namibia | 15 | <20 |
| South Africa | 35 | 20–80 |
| Swaziland | 50 | <20 |
| Zambia | 12 | <20 |
| Zimbabwe | 10 | <20 |
| Benin | 84 | >80 |
| Burkina Faso | 89 | >80 |
| Cameroon | 93 | >80 |
| Equatorial Guinea | 86 | >80 |
| Gambia | 90 | >80 |
| Ghana | 95 | >80 |
| Guinea | 83 | >80 |
| Guinea-Bissau | 91 | >80 |
| Côte d'Ivoire (Ivory Coast) | 93 | 20–80 |
| Liberia | 70 | >80 |
| Mali | 95 | >80 |
| Mauritania | 78 | >80 |
| Niger | 92 | >80 |
| Nigeria | 81 | >80 |
| Senegal | 89 | >80 |
| Sierra Leone | 90 | >80 |
| Togo | 93 | >80 |
Less than 20%
Botswana, Burundi, Canary Islands [Spain], Malawi, Mauritius, Namibia, Rwanda, Swaziland, Zambia, Zimbabwe.[19]
Between 20 and 80%
Central African Republic, Lesotho, Mozambique, South Africa, Sudan, Tanzania, Uganda.[19]
More than 80%
Angola, Algeria, Benin, Burkina Faso, Cameroon, Chad, Congo (Democratic Republic), Congo (Republic), Côte d'Ivoire (Ivory Coast), Djibouti, Egypt, Equatorial Guinea, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Gambia, Ghana, Guinea-Bissau, Gabon, Guinea, Kenya, Liberia, Libya, Madagascar, Mali, Mauritania, Morocco, Niger, Nigeria, Senegal, Sierra Leone, Somalia, Tunisia, Togo.[19]
South Africa
A national study from 2014 found an overall prevalence of 42.8% for self-reported male circumcision. 48.2% of black Africans were circumcised, with 32.1% of those traditionally circumcised and 13.4% circumcised for medical reasons.[1]
Americas
Less than 20%
Argentina, Belize, Bolivia, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Costa Rica, Cuba, Dominican Republic, El Salvador, Ecuador, French Guiana, Guatemala, Guyana, Haiti, Honduras, Jamaica, Mexico, Nicaragua, Panama, Paraguay, Peru, Puerto Rico, Trinidad and Tobago, Uruguay, Venezuela.[19]
The overall prevalence of circumcision is reported to be 6.9% in Colombia, and 7.4% in Brazil (13% in Rio de Janeiro).[2]
The prevalence of circumcision in Mexico is estimated to be 10% to 31%.[3]
Between 20 and 80%
Canada,[19] United States.[19]
Canada
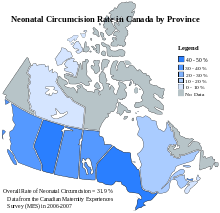
Wirth showed a pattern of declining incidence of circumcision from 1970 to 1979. There was a wide variation in the incidence of circumcision between different provinces and territories. Yukon reported a rate of 74.8 percent in 1978-79 while Newfoundland reported an incidence of 1.9 to 2.4 percent in 1977-78.[21]
In 1994-95, the newborn circumcision rate in Ontario was 29.9%.[22] The Canadian Paediatric Society (1996) offered an estimate of 48 percent for the prevalence of male circumcision in Canada in 1970.[23] In 1999, the American Academy of Pediatrics reported that “in Canada, ~48% of males are circumcised”.[24] However, this figure was questioned because the only citation provided for it was an Australian paper dating from 1970.[25]
Articles published in 2003 reported Canadian neonatal male circumcision rates of "10 to 30%"[26] and "less than 17%".[27] According to the Halifax Daily News, the infant circumcision rate in 2003 was "1.1 per cent" in Nova Scotia and nil in Newfoundland.[28] A 2006 article placed the (2003) national rate at 13.9%.[29]
Individual Canadian provincial health insurance plans began to delist circumcision in the 1980s.[27] Manitoba Health Insurance Plan discontinued coverage of circumcision in 2005.[30] Circumcision is not covered by any provincial/territorial health insurance plan.[30]
A survey of Canadian maternity practices conducted in 2006/2007 by the national public health agency found a newborn circumcision rate of 31.9%.[20] Rates varied markedly across the country, from close to zero in Newfoundland and Labrador to 44.3% in Alberta.
| Percentage of mothers reporting having their male baby circumcised, by province and territory, Canada, 2006/2007 | |
| Newfoundland and Labrador | * |
| Prince Edward Island | 39.2 |
| Nova Scotia | 6.8 |
| New Brunswick | 18.0 |
| Quebec | 12.3 |
| Ontario | 43.7 |
| Manitoba | 31.6 |
| Saskatchewan | 35.6 |
| Alberta | 44.3 |
| British Columbia | 30.2 |
| Yukon | * |
| Northwest Territories | 9.7 |
| Nunavut | * |
| Canada | 31.9 |
| * Numerator too small for rate calculation | |
| Source: Canadian Maternity Experiences Survey[20] | |
United States
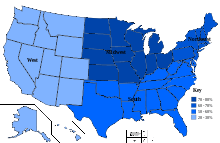
Statistics from different sources give widely varying estimates of infant circumcision rates in the United States.
In 2011, circumcision was one of the most common procedures performed during hospital stays in the U.S. There were approximately 1.1 million hospitalizations with a circumcision, a rate of 36 stays per 10,000 population. This was a decrease of 16% from 1997, when there was a rate of 43 stays per 10,000 population. It was the second-most common procedure performed on patients under one year of age.[32]
In 2005, about 56 percent of male newborns were circumcised prior to release from the hospital according to statistics from the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.[33]
Data from a national survey conducted from 1999 to 2002 found that the overall prevalence of male circumcision in the United States was 79%.[4] 91% of boys born in the 1970s, and 83% of boys born in the 1980s were circumcised.[4] An earlier survey, conducted in 1992, found a circumcision prevalence of 77% in US-born men, born from 1932–1974, including 81% of non-Hispanic White men, 65% of Black men, and 54% of Hispanic men, vs. 42% of non U.S. born men who were circumcised.[34]
A study published in 2005, which used data from the Nationwide Inpatient Sample (a sample of 5–7 million of the nation's total inpatient stays, and representing a 20% sample taken from 8 states in 1988 and 28 in 2000), stated that neonatal circumcisions rose from 48.3% of males in 1988 to 61.1% in 1997.[35]
The Centers For Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reports that circumcision rates were stable in the United States between 1979 and 1999.[36]
Figures from the 2003 Nationwide Hospital Discharge Survey state that circumcision rates declined from 64.7% in 1980 to 59.0% in 1990, rose to 64.1% in 1995, and fell again to 55.9% in 2003.[37] On page 52, it is shown that the western region of the United States has seen the most significant change, declining from 61.8% in 1980 to 31.4% in 2003.[37] Part of the decline in the western region has been attributed by some experts to an increasing percentage of births to immigrants from Latin America, who have been shown to be less likely to circumcise than other parents in the U.S.[38] A 2008 study of male infants born in the US state of Maryland found that the circumcision rate was 75.3% based on hospital discharge data files, and 82.3% based on maternal post-partum survey data.[39]
Medicaid funding for infant circumcision used to be available in every state, but starting with California in 1982, eighteen states (Arizona, California, Colorado, Florida, Idaho, Louisiana, Maine, Minnesota, Mississippi, Missouri, Montana, Nevada, North Carolina, North Dakota, Oregon, South Carolina, Utah, and Washington) had eliminated Medicaid coverage of routine (non-therapeutic) circumcision by July 2011.[40] One study in the Midwest of the U.S. found that this had no effect on the newborn circumcision rate but it did affect the demand for circumcision at a later time.[26] Another study, published in early 2009, found a difference in the neonatal male circumcision rate of 24% between states with and without Medicaid coverage. The study was controlled for other factors such as the percentage of Hispanic patients.[41]
The CDC reported in 2011 that, following an earlier increase in neonatal circumcision rates, rates decreased in the period 1999 to 2010. Citing three different data sources, most recent rates were 56.9% in 2008 (NHDS) 56.3% in 2008 (NIS), and 54.7% in 2010 (CDM).[42]
The incidence of male non-therapeutic infant circumcision varies widely by region. The Western Region reported an incidence of 24.6% in 2009, while the North Central Region reported an incidence of 76.2%, while the overall incidence of circumcision in the United States stood at 54.5%, the lowest figure reported over the previous two decades.[31] The Northeast Region reported an incidence of 67% and the Southern Region reported 55.7%.[31]
There was also significant variation between rural and urban areas. Rural areas reported an incidence of circumcision of 66.9% while urban areas reported an incidence of 41.2%.[31]
There are various explanations for why the infant circumcision rate in the United States is different from comparable countries. Many parents’ decisions about circumcision are preconceived, and this may contribute to the high rate of elective circumcision.[43] Brown & Brown (1987) reported the most important factor is whether the father is circumcised.[44]
Asia
Less than 20%
Bhutan, Burma, Cambodia, China, Hong Kong (China),[45] India, Japan, Laos, Mongolia, Nepal, North Korea, Papua New Guinea, Sri Lanka, Taiwan, Thailand, Vietnam.[19]
The overall prevalence of circumcision in Cambodia is reported to be 3.5%.[2]
Between 20 and 80%
Kazakhstan, Indonesia, Malaysia,[19] South Korea.[46]
South Korea
Virtually no circumcision was performed before the year 1945 as it is against Korea's long and strong tradition of preserving the body as a gift from parents.[46] A 2001 study of 20-year old South Korean men found that 78% were circumcised.[47] At the time, the authors commented that "South Korea has possibly the largest absolute number of teenage or adult circumcisions anywhere in the world. Because circumcision started through contact with the American military during the Korean War, South Korea has an unusual history of circumcision." According to a 2002 study, 86.3% of South Korean males aged 14–29 were circumcised.[48] In 2012, it's the case of 75.8% of the same age group. Only after 1999 has some information against circumcision become available (at the time of the 2012 study, only 3% of Korean internet sites, using the most popular Korean search engine Naver, are against indiscriminate circumcision and 97% are for).[46] The authors of the study speculate "that the very existence of information about the history of Korean circumcision, its contrary nature relative to a longstanding tradition, its introduction by the US military, etc., has been extremely influential on the decision-making process regarding circumcision."[46]
More than 80%
Afghanistan, Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Bangladesh, Brunei, Iran, Iraq, Israel,[49] Jordan, Kuwait, Kyrgyzstan, Lebanon, Oman, Pakistan, Philippines,[2] Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Syria, Tajikistan, Turkey, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, United Arab Emirates, Yemen.[19]
The overall prevalence of circumcision (tuli) in the Philippines is reported to be 92.5%. Most circumcision in the Philippines are performed at the age of 11 to 13.[50][51]
Europe
Less than 20%
Armenia, Austria, Belarus, Belgium, Bulgaria, Czech Republic, Cyprus, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Georgia, Germany,[52] Greece, Hungary, Iceland, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Moldova, The Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Russia, Slovakia, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Ukraine,[19] and the United Kingdom.[5]
A national survey on sexual attitudes in 2000 found that 15.8% of men or boys in the United Kingdom (ages 16–44) were circumcised. 11.7% of 16–19 year olds, and 19.6% of 40–44 year olds said they had been circumcised. Apart from black Caribbeans, men born overseas were more likely to be circumcised.[5] Rickwood et al. reported that the proportion of English boys circumcised for medical reasons had fallen from 35% in the early 1930s to 6.5% by the mid-1980s. An estimated 3.8% of male children in the UK in 2000 were being circumcised by the age of 15.[53] The researchers stated that too many boys, especially under the age of 5, were still being circumcised because of a misdiagnosis of phimosis. They called for a target to reduce the percentage to 2%.
Denniston reported in 1996 that the neonatal circumcision rate in Finland is zero and that the rate of later circumcision is 1 in 16,667.[54] Similarly, Wallerstein estimated in 1980 that the Finnish rate of adult circumcision for health reasons is six per 100,000.[55] Finland's Ministry of Social Affairs and Health reported in 2004 that, "some 500-1000 circumcisions are performed as a therapeutic measure annually in Finnish hospitals",[56] amounting to 710 nationwide cases in 2002.[57]
In Germany, the German Health Interview and Examination Survey for Children and Adolescents found that 10.9% of boys aged 0–17 had been circumcised.[52]
In France, according to a telephone survey (TNS Sofres Institute, 2008), 14% of men are circumcised.[6]
The overall prevalence of circumcision in Spain is reported to be 1.8%.[2]
In 1986, 511 out of approximately 478,000 Danish boys aged 0–14 years were circumcised. This corresponds to a cumulative national circumcision rate of around 1.6% by the age of 15 years.[7]
Between 20 and 80%
Albania, Bosnia, Kosovo, Macedonia, Montenegro and Serbia.[19]
Andorra, Croatia and Luxembourg are listed as unknown on the WHO prevalence map. Liechtenstein, Malta, Monaco, San Marino and Vatican City are unclear from the map.[19]
Oceania
Less than 20%
According to the World Health Organisation, fewer than 20% of males are circumcised in New Zealand.[19] In a study of men born in 1972–1973 in Dunedin, 40.2% were circumcised.[58] In a study of men born in 1977 in Christchurch, 26.1% were circumcised.[59] A 1991 survey conducted in Waikato found that 7% of male infants were circumcised.[60] Circumcision for cultural reasons is routine in Pacific Island countries.[61]
Australia
The Australian Longitudinal Study of Health and Relationships is a computer assisted telephone interview of males aged 16–64 that uses a nationally representative population sample. In 2005 the interview found that the prevalence of circumcision in Australia was roughy 58%. Circumcision status was more common with males over 30 than males under 30, and more common with males who were born in Australia. 66% of males born in Australia were circumcised and less than 1/3 of males under 30 were circumcised.[8] There has been a decline in the rate of infant circumcision in Australia that could be attributed to rising health care costs and rising concerns about the procedure. According to the Sydney Morning Herald, the infant circumcision rate in Australia was 12.9% as of 2003.[19][62] However, rates in the states varied, with highest rates in Queensland (19.3%), New South Wales (16.3%) and South Australia (14.3%), and the lowest in Tasmania (1.6%).[63] In New South Wales, rates have risen from 13% in 1999 to 18% in 2009.[64] In Victoria, according to the Herald Sun, the prevalence of 2010 circumcisions indicated that rates have risen but no information was provided about the rates prior to the rise.[65] In 2011 Circumcision Information Australia found that there was a neonatal circumcision rate of 14.1% in Western Australia, 5.6% in the Northern Territory, 14.1% in Queensland, 19.1% in New South Wales, 10.3% in Victoria, 2.4% in Tasmania, 16.2% in South Australia, and 8.7% in the Australian Capital Territory. The national neonatal circumcision rate was 14.0%, which is slightly higher than the rate of neonatal circumcision being performed in 2003.[66] Non-therapeutic infant circumcision is no longer provided in public hospitals in New South Wales, Tasmania, Western Australia, Victoria or South Australia.[67][68] The Royal Australasian College of Physicians (RACP) estimated in 2010 that 10 to 20 percent of newborn boys are being circumcised.[69]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Peltzer K1, Onoya D2, Makonko E2, Simbayi L2. (2014). "Prevalence and acceptability of male circumcision in South Africa.". Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 11 (4): 126–130. doi:10.4314/ajtcam.v11i4.19. PMID 25392591.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 2.8 Castellsagué X, Bosch FX, Muñoz N et al. (April 2002). "Male circumcision, penile human papillomavirus infection, and cervical cancer in female partners". The New England Journal of Medicine 346 (15): 1105–12. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa011688. PMID 11948269.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Lajous, M et al. (2006). "Human papillomavirus link to circumcision is misleading (author's reply)". Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 15 (2): 405–6. doi:10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-05-0818. PMID 16492939.
Circumcision is not usually performed by public sector health care providers in Mexico and we estimate the prevalence to be 10% to 31%, depending on the population.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Xu, F, L Markowitz, M Sternberg, and S Aral (2006). "Prevalence of circumcision in men in the United States: data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), 1999–2002". XVI International AIDS Conference. Retrieved 2006-09-21.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Dave, S S; Fenton, KA; Mercer, CH; Erens, B; Wellings, K; Johnson, AM (2003). "Male circumcision in Britain: Findings from a national probability sample survey". Sexually Transmitted Infections 79 (6): 499–500. doi:10.1136/sti.79.6.499. PMC 1744763. PMID 14663134.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Telephone survey of the TNS Sofres Institute (commissioned by Manix), 2008.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Frisch, M.; Friis, S.; Kjaer, S. K.; Melbye, M. (1995). "Falling incidence of penis cancer in an uncircumcised population (Denmark 1943-90)". BMJ 311 (7018): 1471. doi:10.1136/bmj.311.7018.1471. PMC 2543732. PMID 8520335.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Ferris JA1, Richters J, Pitts MK, Shelley JM, Simpson JM, Ryall R, Smith AM. (2010). "Circumcision in Australia: further evidence on its effects on sexual health and wellbeing". Aust N Z J Public Health 34 (2): 160–164. doi:10.1111/j.1753-6405.2010.00501.x. PMID 23331360.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 "Male circumcision: Global trends and determinants of prevalence, safety and acceptability" (PDF). World Health Organization. 2007.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 "Male circumcision: Global trends and determinants of prevalence, safety and acceptability" (PDF). World Health Organization. 2007. Retrieved 2009-03-04.
- ↑ "Neonatal and child male circumcision: a global review" (PDF). World Health Organization. 2010. Retrieved 2015-04-12.
- ↑ Drain PK, Halperin DT, Hughes JP, Klausner JD, Bailey RC (2006). "Male circumcision, religion, and infectious diseases: an ecologic analysis of 118 developing countries". BMC Infectious Diseases 6 (1): 172. doi:10.1186/1471-2334-6-172. PMC 1764746. PMID 17137513.
- ↑ Frisch M, Friis S, Kjaer SK, Melbye M (December 1995). "Falling incidence of penis cancer in an uncircumcised population (Denmark 1943-90)". BMJ 311 (7018): 1471. doi:10.1136/bmj.311.7018.1471. PMC 2543732. PMID 8520335.
- ↑ Ko MC, Liu CK, Lee WK, Jeng HS, Chiang HS, Li CY (April 2007). "Age-specific prevalence rates of phimosis and circumcision in Taiwanese boys". Journal of the Formosan Medical Association = Taiwan Yi Zhi 106 (4): 302–7. doi:10.1016/S0929-6646(09)60256-4. PMID 17475607.
…the prevalence of circumcision slightly increased with age from 7.2% (95% CI, 5.3-10.8%) for boys aged 7 years to 8.7% (95% CI, 6.5-13.3%) for boys aged 13 years.
- ↑ Richters, J et al. (2006). "Circumcision in Australia: prevalence and effects on sexual health". Int J STD AIDS 17 (8): 547–554. doi:10.1258/095646206778145730. PMID 16925903.
Neonatal circumcision was routine in Australia until the 1970s … In the last generation, Australia has changed from a country where most newborn boys are circumcised to one where circumcision is the minority experience.
- ↑ Wise J (2006). "Demand for male circumcision rises in a bid to prevent HIV" (PDF). Bulletin of the World Health Organization 84 (7): 505–588. PMC 2627386. PMID 16878217.
As a result, there are already indications of increasing demand for male circumcision in traditionally non-circumcising societies in Southern Africa.
- ↑ "Questions and answers: NIAID-sponsored adult male circumcision trials in Kenya and Uganda". National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases. December 2006.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 Williams, B G et al. (2006). "The potential impact of male circumcision on HIV in sub-Saharan Africa". PLos Med 3 (7): e262. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.0030262. PMC 1489185. PMID 16822094.
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 19.2 19.3 19.4 19.5 19.6 19.7 19.8 19.9 19.10 19.11 19.12 19.13 19.14 "Information package on male circumcision and HIV prevention: insert 2" (PDF). World Health Organisation. p. 2.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 20.2 "Data Tables — The Maternity Experiences Survey (MES) 2006–2007 Canadian Maternity Experiences Survey" (PDF). Public Health Agency of Canada. p. 267.
- ↑ Wirth JL (1980). "Current circumcision practices: Canada". Pediatrics 66 (5): 705–8. PMID 7432876.
- ↑ Goel, V. (ed.) (May 1996). Patterns of Health Care in Ontario, 2nd edition (PDF). Canadian Medical Association. p. 295. ISBN 0-920169-79-1.
- ↑ "Neonatal Circumcision Revisited". Canadian Medical Association Journal 154 (6): 769–780. 1996. PMC 1487803. PMID 8634956.
- ↑ "American Academy of Pediatrics: circumcision policy statement". Pediatrics 103 (3): 686–693. 1999. doi:10.1542/peds.103.3.686. PMID 10049981.
- ↑ Antonopoulos, John; Herschel;, M.; Bartman;, T.; Andersson;, C.; Bailis;, S. A.; Shechet, R. J.; Tanenbaum;, B.; Kunin;, S. A. et al. (2000). "Circumcision — The debate goes on". Pediatrics 105 (3): 684. doi:10.1542/peds.105.3.681. PMID 10733391. Retrieved 2007-11-15.
- ↑ 26.0 26.1 Quayle, SS.; DE. Coplen; PF. Austin (October 2003). "The effect of health care coverage on circumcision rates among newborns". Journal of Urology 170 (4 Pt 2): 1533–1536. doi:10.1097/01.ju.0000091215.99513.0f. PMID 14501653.
- ↑ 27.0 27.1 Waldeck S (2003). "Using Male Circumcision to Understand Social Norms as Multipliers". University of Cincinnati Law Review 72: 455.
- ↑ MacDonald, Andrea (March 2006). "N.S. circumcisions continue to drop". Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada: The Daily News (reprint: CIRP.org).
- ↑ LALIBERTÉ, JENNIFER. "Canada cuts back on circumcision". VOLUME 3 NO. 4. National Review of Medicine. Retrieved 28 February 2006.
- ↑ 30.0 30.1 "PSHCP Bulletin 17" (PDF). The Public Service Health Care Plan Bulletin (17): 2. 2005.
- ↑ 31.0 31.1 31.2 31.3 Maeda, J. (Thomson Reuters), Chari, R. (RAND), and Elixhauser, A. (AHRQ). Circumcisions in U.S. Community Hospitals, 2009. HCUP Statistical Brief #126. February 2012. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, Rockville, MD. Available at http://www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov/reports/statbriefs/sb126.pdf
- ↑ Pfuntner A., Wier L.M., Stocks C. Most Frequent Procedures Performed in U.S. Hospitals, 2011. HCUP Statistical Brief #165. October 2013. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, Rockville, MD. .
- ↑ "Circumcisions Performed in U.S. Community Hospitals, 2005". Statistical Brief #45. Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP). January 2008. Retrieved 2010-08-29.
In 2005, about 56 percent of newborn boys were circumcised before their release from the hospital, resulting in over 1.2 million circumcisions performed at U.S. community hospitals.
- ↑ Laumann, EO et al. (1997). "Circumcision in the United States". JAMA 277 (13): 1052–7. doi:10.1001/jama.277.13.1052. PMID 9091693.
- ↑ Nelson, CP.; R. Dunn; J. Wan; JT. Wei (March 2005). "The increasing incidence of newborn circumcision: data from the nationwide inpatient sample" (ABSTRACT). Journal of Urology 173 (3): 978–981. doi:10.1097/01.ju.0000145758.80937.7d. PMID 15711354.
- ↑ The Centers For Disease Control and Prevention. "Male Circumcision and Risk for HIV Transmission and Other Health Conditions: Implications for the United States".
- ↑ 37.0 37.1 Kozak, LJ; KA Lees; CJ DeFrances (2006). "National Hospital Discharge Survey: 2003 annual summary with detailed diagnosis and procedure data" (PDF). Vital and Health Statistics 13 (160). Retrieved 2007-01-30.
- ↑ "Trends in circumcisions among newborns". Health E-Stats. National Center for Health Statistics. 11 January 2007. Retrieved 2007-01-30.
However, the most notable change occurred in the West where newborn male circumcisions dropped from 62 percent in 1980 to 37 percent in 1999. This latest available figure for the West represents over a two-fold difference when compared with circumcision estimates for the Midwest. Part of this decline, appears to reflect the increasing percentage of boys born to immigrant Hispanics, who have been shown in several other studies to be significantly less likely to receive circumcisions than other infant males.
- ↑ Cheng, D.; L. Hurt and I.L. Horon (6 August 2008). "Neonatal circumcision in Maryland: A comparison of hospital discharge and maternal postpartum survey data". Journal of Pediatric Urology. (e-pub ahead of print) (6): 448–51. doi:10.1016/j.jpurol.2008.06.007. PMID 18691938.
- ↑ Adler PW (2011). "Is it lawful to use Medicaid to pay for circumcision?". J Law Med 19 (2): 335–353. PMID 22320007.
- ↑ Leibowitz, Arleen A.; Katherine Desmond; Thomas Belin (January 2009). "Determinants and Policy Implications of Male Circumcision in the United States". American Journal of Public Health 99 (1): 138–145. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2008.134403. PMC 2636604. PMID 19008503.
The mean neonatal male circumcision rate was 55.9%. When we controlled for other factors, hospitals in states in which Medicaid covers routine male circumcision had circumcision rates that were 24 percentage points higher than did hospitals in states without such coverage (P < .001).
- ↑ "Trends in In-Hospital Newborn Male Circumcision --- United States, 1999--2010". Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR) 60(34);1167-1168. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. September 2011. Retrieved 2011-09-14.
Incidence of NMC decreased from 62.5% in 1999 to 56.9% in 2008 in NHDS (AAPC = -1.4%; p<0.001), from 63.5% in 1999 to 56.3% in 2008 in NIS (AAPC = -1.2%; p<0.001), and from 58.4% in 2001 to 54.7% in 2010 in CDM (AAPC = -0.75%; p<0.001)
- ↑ "Report 10 of the Council on Scientific Affairs (I-99):Neonatal Circumcision". 1999 AMA Interim Meeting: Summaries and Recommendations of Council on Scientific Affairs Reports. American Medical Association. December 1999. p. 17. Retrieved 2006-06-13.
- ↑ Brown MS, Brown CA. Circumcision decision: prominence of social concerns. Pediatrics. 1987;60(2):215–9.
- ↑ http://smj.sma.org.sg/2302/2302smj6.pdf
- ↑ 46.0 46.1 46.2 46.3 DaiSik Kim, Sung-Ae Koo and Myung-Geol Pang (2012). "Decline in male circumcision in South Korea" (PDF).
- ↑ Ku, J H et al. (2003). "Circumcision practice patterns in South Korea: community based survey". Sex Transm Inf 79 (1): 65–67. doi:10.1136/sti.79.1.65. PMC 1744613. PMID 12576619.
- ↑ Pang MG, Kim DS: Extraordinarily high rates of male circumcision in South Korea: history and underlying causes. BJU Int 2002, 89:48–54. http://www.who.int/hiv/mediacentre/infopack_en_2.pdf http://www.biomedcentral.com/content/pdf/1471-2458-12-1067.pdf
- ↑ "Israel teaches WHO about circumcision". ynet news. November 2006.
- ↑ Darby, Robert (9 August 2011). "Routine peripubertal circumcision?". CMAJ : Canadian Medical Association Journal (National Institutes of Health) 183 (11): 1283–1284. doi:10.1503/cmaj.111-2060. PMC 3153524. PMID 21825054.
- ↑ Ong, Christine (29 May 2008). "Philippine doctors question medical benefits of circumcision". Channel News Asia. MediaCorp. Retrieved 27 August 2012.
- ↑ 52.0 52.1 Kamtsiuris, P.; Bergmann, E.; Rattay, P.; Schlaud, M. (2007). "Inanspruchnahme medizinischer Leistungen Ergebnisse des Kinder- und Jugendgesundheitssurveys (KiGGS)" [Use of medical services. Results of the German Health Interview and Examination Survey for Children and Adolescents (KiGGS)]. Bundesgesundheitsblatt - Gesundheitsforschung - Gesundheitsschutz (in German) 50 (5–6): 836–50. doi:10.1007/s00103-007-0247-1. PMID 17514470.
- ↑ Rickwood, A M K; Kenny, SE; Donnell, SC (2000). "Towards evidence based circumcision of English boys: Survey of trends in practice". BMJ 321 (7264): 792–3. doi:10.1136/bmj.321.7264.792. PMC 27490. PMID 11009516.
- ↑ Denniston, George C. (April 1996). "Circumcision and the Code of Ethics". Humane Health Care International 12: 78–80.
- ↑ Wallerstein, E. (1980). Circumcision: an American Health Fallacy. New York: Springer.
- ↑ "Circumcision of boys: A study on international and Finnish practices" (PDF). Ministry of Social Affairs and Health, Finland. 12 February 2004. p. 8. (Finnish)
- ↑ "Circumcision of boys: A study on international and Finnish practices" (PDF). Ministry of Social Affairs and Health, Finland. 12 February 2004. p. 39. (Finnish)
- ↑ Dickson, N et al. (2005). "Herpes simplex virus type 2 status at age 26 is not related to early circumcision in a birth cohort". Sex Transm Dis 32 (8): 517–9. doi:10.1097/01.olq.0000161296.58095.ab. PMID 16041257.
- ↑ Fergusson, DM et al. (2007). "Circumcision status and risk of sexually transmitted infection in young adult males: an analysis of a longitudinal birth cohort". Pediatrics 118 (5): 1971–7. doi:10.1542/peds.2006-1175. PMID 17079568.
- ↑ Lawrenson RA (1991). "Current practice of neonatal circumcision in the Waikato". N Z Med J 104 (911): 184–5. PMID 1898442.
- ↑ Afsari M, Beasley SW, Maoate K, Heckert K (March 2002). "Attitudes of Pacific parents to circumcision of boys". Pac Health Dialog 9 (1): 29–33. PMID 12737414.
Circumcision for cultural reasons is routine in Pacific Island countries.
- ↑ Richters, J et al. (2006). "Circumcision in Australia: prevalence and effects on sexual health". Int J STD AIDS 17 (8): 547–554. doi:10.1258/095646206778145730. PMID 16925903.
- ↑ Skatssoon, Judy (July 2004). "Circumcision rates rise for some". Sydney, New South Wales, Australia: Sydney Morning Herald (reprint: CIRP.org).
- ↑ Teutsch, Danielle (2010-02-21). "More boys go under knife as parents opt for kind cut". Sydney Morning Herald.
- ↑ White, Alex (2010-08-28). "Once routine, banned in 2007, now it's back". Herald Sun.
- ↑ "Incidence and prevalence of circumcision in Australia". Circumcision Information Australia. Retrieved 2015-01-24.
- ↑ "Victoria to scrap public hospital circumcision". Melbourne: The Age. 2007-08-12. Retrieved 2007-08-12.
- ↑ Pengelley, Jill (2007-11-12). "Cosmetic circumcision banned". The Advertiser. Retrieved 2007-11-12.
- ↑ "Circumcision of Male Infants". Royal Australasian College of Physicians. 2010.
External links
- Drain, PK; Halperin, DT; Hughes, JP; Klausner, JD; Bailey, RC. (November 2006). "Male circumcision, religion, and infectious diseases: an ecologic analysis of 118 developing countries". BMC Infect Dis 6 (1): 172. doi:10.1186/1471-2334-6-172. PMC 1764746. PMID 17137513.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||