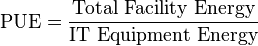Power usage effectiveness
Power usage effectiveness (PUE) is a measure of how efficiently a computer data center uses energy; specifically, how much energy is used by the computing equipment (in contrast to cooling and other overhead).
PUE is the ratio of total amount of energy used by a computer data center facility [1][2][3][4][5][6][7][8] to the energy delivered to computing equipment.
PUE was developed by a consortium called The Green Grid. PUE is the inverse of data center infrastructure efficiency (DCIE). An ideal PUE is 1.0. Anything that isn't considered a computing device in a data center (i.e. lighting, cooling, etc.) falls into the category of facility energy consumption.
Issues and problems with the power usage effectiveness
The PUE metric is the most popular method of calculating energy efficiency. Although it is the most effective in comparison to other metrics, the Power Usage Effectiveness comes with its share of flaws. This is the most frequently used metric for operators, facility technicians, and building architects to determine how energy efficient their data center buildings are (Jumie). Some professionals even brag about their Power Usage Effectiveness being lower than others. Naturally, it is not a surprise that in some cases an operator may “accidentally” not count the energy used for lighting, resulting in lower Power Usage Effectiveness. This problem is more linked to a human mistake, rather than an issue with the Power Usage Effectiveness metric system itself.
One real problem is PUE does not account for the climate within the cities the data centers are built. In particular, it does not account for different normal temperatures outside the data center. For example, a data center located in Alaska cannot be effectively compared to a data center in Miami. A colder climate results in a lesser need for a massive cooling system. Cooling systems account for roughly 30 percent of consumed energy in a facility, while the data center equipment accounts for nearly 50 percent (Jumie). Due to this, the Miami data center may have a final Power Usage Effectiveness of 1.8 and the data center in Alaska may have a ratio of 1.7, but the Miami data center may be running overall more efficiently. In particular, if it happened to be in Alaska, it may get a better result.
Additionally, according to a case study on Science Direct, "an estimated PUE is practically meaningless unless the IT is working at full capacity".[9]
All in all, finding simple, yet recurring issues such as the problems associated with the effect of varying temperatures in cities and learning how to properly calculate all the facility energy consumption is very essential. By doing so, continuing to reduce these problems ensures that further progress and higher standards are always being pushed to improve the success of the Power Usage Effectiveness for future data center facilities.[10]
Benefits and limitation
PUE was introduced in 2006 and promoted by the Green Grid (a non-profit organization of IT professionals) in 2007, and has become the most commonly used metric for reporting the energy efficiency of data centres (Gemma). Although it is named 'power usage effectiveness', it actually measures the energy use of the data centre (Gemma).
The PUE metric is helpful because it has several important benefits. First, the companies using the way the metric is calculated can be repeated over time, allowing a company to view their efficiency changes during seasonal changes and historically. Second, companies can gauge how more efficient practices (such as powering down idle hardware) affects their overall usage. Finally, the PUE metric creates competition, “driving efficiencies up as advertised PUE values become lower" (Gemma). Companies can then use PUE as a marketing tool.
However, there are some issues with the PUE metric. Rather than the issues mentioned in last paragraph, some other issues are the efficiency of the power supply network and calculating the accurate IT load. According to the sensitivity analysis by Gemma, "Total energy consumption is equal to the total amount of energy used by the equipment and infrastructure in the facility (WT) plus the energy losses due to inefficiencies in the power delivery network (WL), hence: PUE=(WT+WL)/WIT." Based on the equation, the inefficiencies of the power delivery network (WL) will increase the total energy consumption of the data center. The PUE value goes up as the data center becomes less efficient. IT load is another important issue of the PUE metric. "It is crucial that an accurate IT load is used for the PUE, and that it is not based upon the rated power use of the equipment. Accuracy in the IT load is one of the major factors affecting the measurement of the PUE metric, as utilization of the servers has an important effect on IT energy consumption and hence the overall PUE value"(Gemma). For example, a data center with high PUE value and high server utilization could be more efficient than a data center with low PUE value and low server utilization.[11]
Notably efficient companies
In October 2008, Google's Data center was noted to have a ratio of 1.21 PUE across all 6 of its centers, which at the time was considered as close to perfect a possible. Right behind Google, was Microsoft, which had another notable PUE ratio of 1.22 [12]
Through proprietary innovations in liquid cooling systems, French hosting company OVH has managed to attain a PUE ratio of 1.09 in its data centers in Europe and North America. [13]
See also
- Data center infrastructure efficiency
- Performance per watt
- Green power usage effectiveness
- Green computing
- IT energy management
References
- ↑ SearchDataCenter.com - power usage effectiveness (PUE)
- ↑ Digital Realty Trust- PUE Data Center Efficiency Metric
- ↑ Engineered Systems - Optimizing Power Usage Effectiveness In Data Centers
- ↑ The Green Grid - The Green Grid Data Center Power Efficiency Metrics: PUE and DCiE
- ↑ Google - Efficient Computing - Data Center Efficiency Measurements
- ↑ Dell - Best Practices for Increasing Data Center Energy Efficiency
- ↑ Cisco Systems - Cisco Energywise
- ↑ Google Data Center Optimization -
- ↑ Brady, Gemma, Nikil Kapur, Jonathan Summers, and Harvey Thompson. "A Case Study and Critical Assessment in Calculating Power Usage Effectiveness for a Data Centre." Energy Conversion & Management, 76 (2013): 155-161.
- ↑ Jumie Yuventi, Roshan Mehdizadeh. “A critical analysis of Power Usage Effectiveness and its use in communicating data center energy consumption.” Energy and Building 64 (2013) 90-94 : Web. 17 November 2014.
- ↑ Gemma A. Brady, Nikil Kapur, Jonathan L. Summers, Harvey M. Thompson “A case study and critical assessment in calculating power usage effectiveness for a data centre”Energy Conversion and Management 74 December 2013 155-181: Web. 18 November 2014.
- ↑ Tuf, Steve. "Power Usage Effectiveness." It.toolbox. Toolbox, n.d. Web. 17 Nov. 2014.
- ↑ https://www.ovh.com/ca/en/about-us/green-it.xml