Posterior compartment of the forearm
| Posterior compartment of the forearm | |
|---|---|
|
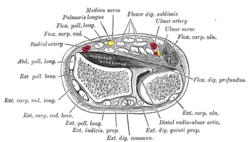
Cross-section through the middle of the forearm. (Anterior compartment is at top; posterior compartment is at bottom.) | |
| Details | |
| Latin | compartimentum antebrachii posterius |
| radial artery, radial recurrent artery , profunda brachii, posterior interosseous artery | |
| radial nerve,[1] posterior interosseous nerve | |
| Identifiers | |
| TA | A04.6.01.007 |
| FMA | 38411 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The posterior compartment of the forearm (or extensor compartment)[2] contains 12 muscles which are chiefly responsible for extension of the wrist and digits, and supination of the forearm. It is separated from the anterior compartment by the interosseous membrane between the radius and ulna.
The brachioradialis, flexor of the elbow, is unusual in that it is located in the posterior compartment, but it is actually in the anterior portion of the forearm. The anconeus, assisting in extension of the elbow joint, is by some considered part of the posterior compartment of the arm.
Muscles
| Level | Muscle | E/I |
| superficial | brachioradialis | I |
| superficial | extensor carpi radialis longus | E |
| superficial | extensor carpi radialis brevis | E |
| superficial | extensor carpi ulnaris | E |
| superficial | anconeus | I |
| intermediate | extensor digitorum | E |
| intermediate | extensor digiti minimi | E |
| deep | abductor pollicis longus | E |
| deep | extensor pollicis longus | E |
| deep | extensor pollicis brevis | E |
| deep | extensor indicis | E |
| deep | supinator | I |
- "E/I" refers to "extrinsic" or "intrinsic".
Innervation
The muscles of the posterior compartment of the forearm are innervated by the radial nerve. The radial nerve arises from the posterior cord of the plexus. The somatomotor fibers of the radial nerve branch from the main radial nerve at the level of the radial groove of the humerus.
See also
Additional images
References
- ↑ lesson5musofpostforearm at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University)
- ↑ "Dissector Answers - Forearm & Wrist". Retrieved 2008-01-17.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||