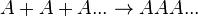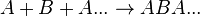Polymerization
In polymer chemistry, polymerization is a process of reacting monomer molecules together in a chemical reaction to form polymer chains or three-dimensional networks.[2][3][4] There are many forms of polymerization and different systems exist to categorize them.
Introduction
|
Homopolymers
Copolymers
|
In chemical compounds, polymerization occurs via a variety of reaction mechanisms that vary in complexity due to functional groups present in reacting compounds[4] and their inherent steric effects. In more straightforward polymerization, alkenes, which are relatively stable due to 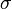 bonding between carbon atoms, form polymers through relatively simple radical reactions; in contrast, more complex reactions such as those that involve substitution at the carbonyl group require more complex synthesis due to the way in which reacting molecules polymerize.[4]
bonding between carbon atoms, form polymers through relatively simple radical reactions; in contrast, more complex reactions such as those that involve substitution at the carbonyl group require more complex synthesis due to the way in which reacting molecules polymerize.[4]
As alkenes can be formed in somewhat straightforward reaction mechanisms, they form useful compounds such as polyethylene and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) when undergoing radical reactions,[4] which are produced in high tonnages each year[4] due to their usefulness in manufacturing processes of commercial products, such as piping, insulation and packaging. In general, polymers such as PVC are referred to as "homopolymers," as they consist of repeated long chains or structures of the same monomer unit, whereas polymers that consist of more than one molecule are referred to as copolymers (or co-polymers).[5]
Other monomer units, such as formaldehyde hydrates or simple aldehydes, are able to polymerize themselves at quite low temperatures (ca. −80 °C) to form trimers;[4] molecules consisting of 3 monomer units, which can cyclize to form ring cyclic structures, or undergo further reactions to form tetramers,[4] or 4 monomer-unit compounds. Further compounds either being referred to as oligomers[4] in smaller molecules. Generally, because formaldehyde is an exceptionally reactive electrophile it allows nucleophillic addition of hemiacetal intermediates, which are in general short-lived and relatively unstable "mid-stage" compounds that react with other molecules present to form more stable polymeric compounds.
Polymerization that is not sufficiently moderated and proceeds at a fast rate can be very hazardous. This phenomenon is known as hazardous polymerization and can cause fires and explosions.
Step-growth
Step-growth polymers are defined as polymers formed by the stepwise reaction between functional groups of monomers, usually containing heteroatoms such as nitrogen or oxygen. Most step-growth polymers are also classified as condensation polymers, but not all step-growth polymers (like polyurethanes formed from isocyanate and alcohol bifunctional monomers) release condensates; in this case, we talk about addition polymers. Step-growth polymers increase in molecular weight at a very slow rate at lower conversions and reach moderately high molecular weights only at very high conversion (i.e., >95%).
To alleviate inconsistencies in these naming methods, adjusted definitions for condensation and addition polymers have been developed. A condensation polymer is defined as a polymer that involves loss of small molecules during its synthesis, or contains heteroatoms as part of its backbone chain, or its repeat unit does not contain all the atoms present in the hypothetical monomer to which it can be degraded.
Chain-growth
Chain-growth polymerization (or addition polymerization) involves the linking together of molecules incorporating double or triple carbon-carbon bonds. These unsaturated monomers (the identical molecules that make up the polymers) have extra internal bonds that are able to break and link up with other monomers to form a repeating chain, whose backbone typically contains only carbon atoms. Chain-growth polymerization is involved in the manufacture of polymers such as polyethylene, polypropylene, and polyvinyl chloride (PVC). A special case of chain-growth polymerization leads to living polymerization.
In the radical polymerization of ethylene, its π bond is broken, and the two electrons rearrange to create a new propagating center like the one that attacked it. The form this propagating center takes depends on the specific type of addition mechanism. There are several mechanisms through which this can be initiated. The free radical mechanism is one of the first methods to be used. Free radicals are very reactive atoms or molecules that have unpaired electrons. Taking the polymerization of ethylene as an example, the free radical mechanism can be divided into three stages: chain initiation, chain propagation, and chain termination.
Free radical addition polymerization of ethylene must take place at high temperatures and pressures, approximately 300 °C and 2000 atm. While most other free radical polymerizations do not require such extreme temperatures and pressures, they do tend to lack control. One effect of this lack of control is a high degree of branching. Also, as termination occurs randomly, when two chains collide, it is impossible to control the length of individual chains. A newer method of polymerization similar to free radical, but allowing more control involves the Ziegler-Natta catalyst, especially with respect to polymer branching.
Other forms of chain growth polymerization include cationic addition polymerization and anionic addition polymerization. While not used to a large extent in industry yet due to stringent reaction conditions such as lack of water and oxygen, these methods provide ways to polymerize some monomers that cannot be polymerized by free radical methods such as polypropylene. Cationic and anionic mechanisms are also more ideally suited for living polymerizations, although free radical living polymerizations have also been developed.
Esters of acrylic acid contain a carbon-carbon double bond which is conjugated to an ester group. This allows the possibility of both types of polymerization mechanism. An acrylic ester by itself can undergo chain-growth polymerization to form a homopolymer with a carbon-carbon backbone, such as poly(methyl methacrylate). Also, however, certain acrylic esters can react with diamine monomers by nucleophilic conjugate addition of amine groups to acrylic C=C bonds. In this case the polymerization proceeds by step-growth and the products are poly(beta-amino ester) copolymers, with backbones containing nitrogen (as amine) and oxygen (as ester) as well as carbon.[6]
Physical polymer reaction engineering
To produce a high-molecular-weight, uniform product, various methods are employed to better control the initiation, propagation, and termination rates during chain polymerization and also to remove excess concentrated heat during these exothermic reactions compared to polymerization of the pure monomer. These include emulsion polymerization, solution polymerization, suspension polymerization, and precipitation polymerization. Although the polymer polydispersity and molecular weight may be improved, these methods may introduce additional processing requirements to isolate the product from a solvent.
Photopolymerization
Most photopolymerization reactions are chain-growth polymerizations which are initiated by the absorption of visible or ultraviolet light. The light may be absorbed either directly by the reactant monomer (direct photopolymerization), or else by a photosensitizer which absorbs the light and then transfers energy to the monomer. In general only the initiation step differs from that of the ordinary thermal polymerization of the same monomer; subsequent propagation, termination and chain transfer steps are unchanged.[7] In step-growth photopolymerization, absorption of light triggers an addition (or condensation) reaction between two comonomers that do not react without light. A propagation cycle is not initiated because each growth step requires the assistance of light.[8]
Photopolymerization can be used as a photographic or printing process, because polymerization only occurs in regions which have been exposed to light. Unreacted monomer can be removed from unexposed regions, leaving a relief polymeric image.[7] Several forms of 3D printing -- including layer-by-layer stereolithography and two-photon absorption 3D photopolymerization -- use photopolymerization.
See also
- Addition polymer
- Condensation polymer
- Cross-link
- Metallocene
- Plasma polymerization
- Polymer characterization
- Polymer physics
- Reversible addition−fragmentation chain transfer polymerization
- Ring-opening polymerization
- Sequence-controlled polymers
- Sol-gel
- Ziegler-Natta catalyst
References
- ↑ Jenkins, A. D.; Kratochvíl, P.; Stepto, R. F. T.; Suter, U. W. (1996). "Glossary of basic terms in polymer science (IUPAC Recommendations 1996)" (PDF). Pure and Applied Chemistry 68 (12): 2287–2311. doi:10.1351/pac199668122287. See definition 3.1, p. 2305.
- ↑ Young, R. J. (1987) Introduction to Polymers, Chapman & Hall ISBN 0-412-22170-5
- ↑ International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry, et al. (2000) IUPAC Gold Book, Polymerization
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 4.7 Clayden, J., Greeves, N. and Warren, S. (2000). Organic chemistry, Oxford University Press ISBN 0198503466 pp. 1450–1466
- ↑ Cowie, J.M.G. (1991) Polymers: Chemistry and Physics of Modern Materials, Chapman and Hall, p. 4 ISBN 0849398134
- ↑ Lynn, David M.; Langer, Robert (2000). "Degradable Poly(β-amino esters): Synthesis, Characterization, and Self-Assembly with Plasmid DNA". Journal of the American Chemical Society 122 (44): 10761. doi:10.1021/ja0015388.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Allcock H.R., Lampe F.W. and Mark J.F. Contemporary Polymer Chemistry (3rd ed. Pearson Prentice-Hall 2003), chap.5. ISBN 0-13-065056-0
- ↑ Soto, Marc; Sebastián, Rosa María; Marquet, Jordi (2014). "Photochemical Activation of Extremely Weak Nucleophiles: Highly Fluorinated Urethanes and Polyurethanes from Polyfluoro Alcohols". J. Org. Chem. 79: 5019–5027. doi:10.1021/jo5005789.