Poles in the United Kingdom
| Total population | |
|---|---|
|
60,711 Polish-born (2001 Census) 579,000 Polish-born (2011 Census) 850,000 resident Poles (May 2012)[1] | |
| Regions with significant populations | |
| Throughout the United Kingdom, mostly in and around London | |
| Languages | |
| English, Polish | |
| Religion | |
| Roman Catholicism · Polish Orthodox Church · Judaism |
Polish migration to the United Kingdom describes the temporary or permanent settlement of Polish people in the United Kingdom. Most Polish migrants arrived in the UK after the 2004 enlargement of the European Union.[2] At the time of the 2011 Census, 521,000 Polish-born people reported being resident in the UK,[3] and there is a wider population of British Poles, including the descendants of over 200,000 immigrants who settled in the UK after World War II.[4]
Poles are the third largest foreign-born community in the UK after Irish and Indian born people [5] and the Polish language is the second most spoken language in England and the third most spoken language in the UK after English and Welsh, with 1% of Britain's population speaking Polish.[6][7] Since 2004 there have been an increasing number of Polish-British citizens in the UK.
History and settlement
Early history
Polabian Slavs (Wends) settled in parts of the Danelaw (north-eastern England ruled by the Danes), apparently as Danish allies.[8]
According to the medieval chroniclers Thietmar of Merseburg and Adam of Bremen, King Canute the Great - who ruled both Denmark and England - was the son of a Polish princess, a daughter of Mieszko I of Poland and sister of Boleslaw I of Poland. An inscription in Liber vitae of the New Minster and Hyde Abbey Winchester mentions King Canute as having a sister named "Santslaue" ("Santslaue soror CNVTI regis nostri"), which without doubt is a Slavic name, and J. Steenstrup suggests this was a rendering of Świętosława. References in medieval chronicles to the involvement of Polish troops in invasions of England are likely related to Canute's Polish ancestry, constituting the earliest evidence of Poles arriving in the country.
In the 16th century, when most grain imports to the British Isles were derived from Poland, Polish travellers came as merchants and diplomats, usually on the Eastland Company trade route from Gdansk to London. Poles are mentioned in Shakespeare's Hamlet (e.g. "sledded polack"), which Israel Gollancz says is an influence of The Counsellor by Wawrzyniec Grzymała Goślicki. As early as 1608 there were enough Poles in England for the Virginia Company to hire a group of them to sail to America to help salvage the Jamestown Colony, where they formed an early trade union.[9] In the 17th century, Irish Catholics serving in the Swedish Army defected to Poland.[10]
After the Battle of Vienna, a pub in London's Soho area was called the King of Poland, and soon afterwards the street on which it stands was named Poland Street - which exists to this day. In the 18th century some Polish Protestants settled around Poland Street as religious refugees from the counter reformation in Poland.
In the 19th century, after the collapse of the November Uprising of 1831 against the Russian Empire, many Polish insurgents came to the UK in search of political sanctuary.[11] After the First World War Poles settled in large numbers in London – many from the London Polish Prisoner-of-War camps in Alexandra Palace and Feltham.
Second World War period
The Poles made an crucial contribution to the Allied war effort, which directly led to the formation of the Polish British community as it exists today. The majority of Poles came to the United Kingdom as political émigrés after the German and Soviet occupation of Poland. In 1940, with the fall of France, the exiled Polish President, Prime Minister and government transferred to London, along with a first wave of at least 20,000 soldiers and airmen.
Poles formed the fourth-largest Allied armed force after the Soviets, the Americans and the combined troops of the British Empire. Poles were the largest group of non-British personnel in the RAF during the Battle of Britain, and the 303 Polish Squadron was the highest-scoring Polish RAF unit in the Battle of Britain. Special Operations Executive had a large section of covert, elite Polish troops and cooperated closely with the Polish resistance. The Polish Army under British high command were instrumental at the Battle of Monte Cassino, the Battle of the Falaise Gap, the Battle of Arnhem, the Siege of Tobruk and the liberation of many European cities including Bologna and Breda.
Perhaps most importantly, the Poles cracked early versions of the Enigma machine, which laid the foundations for subsequent British successes in deciphering German military signals and generating the Ultra intelligence which proved a key factor in many Allied successes during the war.[12] Former Bletchley Park cryptologist Gordon Welchman said: "Ultra would never have got off the ground if we had not learned from the Poles, in the nick of time, the details both of the German military... Enigma machine, and of the operating procedures that were in use."[13]
By July 1945 there were 228,000 troops of the Polish Armed Forces in the West serving under the high command of the British Army.[11] Many of these men and women were originally from the Kresy region of eastern Poland, including cities such as Lwow (now Lviv, Ukraine) and Wilno (now Vilnius, Lithuania). They had been deported from Kresy to the Soviet Gulags when Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union occupied Poland in 1939 in accordance with the Nazi-Soviet Pact. When Churchill and Joseph Stalin formed an alliance against Adolf Hitler two years later, the Kresy Poles were released from the Gulags in Siberia, formed the Anders Army and marched to Persia to create the II Corps (Poland) under British high command.
These Polish troops were vital to the Allied defeat of the Germans in North Africa and Italy, and hoped to return to Kresy in an independent and democratic Poland at the end of the War. But at Yalta, Roosevelt and Churchill agreed that Stalin should keep the Soviet gains Hitler agreed in the Nazi-Soviet Pact, including Kresy, and carry out Polish population transfers (1944–1946). Consequently, Roosevelt and Churchill had agreed that tens of thousands of veteran Polish troops under British command should lose their Kresy homes to the Soviet Union, with the implication that their relatives, including wives and children, would be at the mercy of the NKVD.[14] In reaction, thirty officers and men from the II Corps (Poland) committed suicide.[15]
Churchill explained his actions in a three-day Parliamentary debate starting on 27 February 1945, which ended in a vote of confidence. Many MPs openly criticised Churchill over Yalta and voiced strong loyalty to the UK's Polish allies.[15] Some reporters felt Churchill was not confident Poland would be the independent and democratic country Polish troops could return to, because the prime minister also said: "His Majesty's Government will never forget the debt they owe to the Polish troops... I earnestly hope it will be possible for them to have citizenship and freedom of the British Empire, if they so desire."[16]
During the debate, 25 MPs risked their careers to draft an amendment protesting against the UK's tacit acceptance of Poland's domination by the Soviet Union. These members included: Arthur Greenwood; Commander Sir Archibald Southby, 1st Baronet; Sir Alec Douglas-Home; Lord Willoughby de Eresby and Victor Raikes.[15] After the failure of the amendment, Henry Strauss, 1st Baron Conesford, MP for Norwich, resigned his seat in protest at the British treatment of Poland.[15]
Polish Resettlement Corps 1946-1949
"Following the invasion and fall of Poland in September 1939, many Polish servicemen and women made their way through France, Russia and other countries to the UK or British territories in the Middle East. They were formed into units which fought in the campaigns in North West Europe, Italy, North Africa and the Middle East. "At the end of the war, many of these Poles stayed in the United Kingdom and in order to ease the transition from a Polish military environment to British civilian life, a satisfactory means of demobilisation needed to be devised by the British authorities. This took the form of the raising, as a corps of the British Army, of the Polish Resettlement Corps (PRC), into which such Poles as wished to stay in the UK were allowed to enlist for the period of their demobilisation. "The PRC was formed in 1946 (Army Order 96 of 1946) and was disbanded after fulfilling its purpose in 1949 (Army Order 2 of 1950)." [Source: UK National Archives, Online Catalogue, Series Reference WO315.]
Polish Resettlement Act 1947
When the Second World War ended, a Communist government was installed in Poland. Most Poles felt betrayed by their wartime allies, and refused to return to Poland, because of the Soviet repressions of Polish citizens (1939–1946), Soviet conduct around the 1944 Warsaw Uprising, the Trial of the Sixteen and other executions of pro-democracy Poles, particularly the former members of the Home Army. The result was the Polish Resettlement Act 1947, the UK's first mass immigration law. Initially a very large community was centred around Swindon, due to the fact many military personnel has been stationed there during the war.
Large numbers, after occupying resettlement camps of the Polish Resettlement Corps, later settled in London, many recruited as European Volunteer Workers.[17] Others settled in the British Empire, forming large Polish Canadian and Polish Australian communities.
In the 1951 Census of the UK, the Polish-born population of the UK numbered some 162,339, up from 44,642 in 1931.[18][19]
The relaxation of travel restrictions to and from Poland saw a steady increase in Polish migration to the United Kingdom in the 1950s. Brixton, Earls Court and Lewisham were a few of the London areas where they settled. As these communities grew, it was felt by the Polish Catholic hierarchy and the English and Scottish hierarchies that Polish priests should settle and minister specifically to the spiritual needs of the Polish people. The first such parish was Brockley-Lewisham in 1951 and today there are 10 Polish parishes in London, in places such as Balham and Ealing. Thriving parishes also exist in many other UK towns and cities.
The longer established communities that ensued after the church established itself were mainly set up by former members of the Polish Resettlement Corps in the late 1940s and early 1950s. Around the hub of a Polish church would be Polish clubs, cultural centres as well as a variety of adult and youth organisations such as the Ex-Combatants (SPK), the Polish Youth Group (KSMP) and the Polish Scouting Movement (ZHP pgk). The original aims of these organisations was to ensure a continuation of Polish language, culture and heritage for the children of the ex-PRC members. Many of these groups are still active and steps are being taken to attract newer Polish migrants.
The Polish Government in London was not dissolved until 1991, when a freely elected president took office in Warsaw. The Polish people fought hard to combat communism, and for their right to liberty. Previously a base to fight against the communist regime in Poland, London came to be seen as an important centre to foster business and political relations.
21st century economic migration
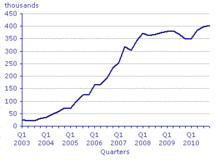
Many of the Polish British community formed after the Second World War had friends and relatives in Poland. Partly because of this bond, there was a steady flow of migrants from Poland to the UK, which accelerated after the fall of communism in 1989. Throughout the 1990s, Poles used the freer travel restrictions to move to the UK and work, sometimes in the grey economy.
At the expansion of the EU including Poland on 1 May 2004, the UK granted free movement to workers from the new member states.[21]
There were restrictions, covered by the Worker Registration Scheme, on benefits that Polish immigrants could claim, but they were abolished in 2011 in accordance with the Treaty of Accession 2003.[22] Most of the other longer-standing EU member states exercised their right to maintain immigration controls, but these ended in 2011 in line with the Treaty of Accession of 2003,[23] over entrants from these accession states,[24] although some states had removed these restrictions earlier.[25]

The Home Office publishes quarterly statistics on applications to the Worker Registration Scheme. Figures published in August 2007 indicated that some 656,395 persons were accepted on to the scheme between 1 May 2004 and 30 June 2007, of whom 430,395 were Polish nationals. However, as the scheme is voluntary, offers no financial incentive and is not enforced immigrants are free to ignore the scheme. They may work legally in the UK provided they have a Polish identity card or passport and a National Insurance number. This has led to some estimates of Polish nationals in the UK being much higher.[26]
The Polish magazine Polityka launched a 'Stay With Us' scheme offering young academics a £5,000 bonus to encourage them to stay and work at home in Poland. Additionally on 20 October 2007, a campaign was launched by the British Polish Chamber of Commerce called 'Wracaj do Polski' ('Come Back to Poland') which encouraged Poles living and working in the UK to return home.
By the end of 2007, stronger economic growth in Poland, falling unemployment and the rising strength of the złoty had reduced the economic incentive for Poles to migrate to the UK.[27] Labour shortages in Poland's cities and in sectors such as construction, IT and financial services have also played a part in stemming the flow of Poles to the UK.[28] According to the August 2007 Accession Monitoring Report, fewer Poles migrated in the first half of 2007 than in the same period in 2006.
There was a baby boom under Martial Law in Poland in the early 1980s. Consequently the 2000s saw an over-supply of new workers on the Polish job market. Unemployment rose and emigration was chosen by many young Poles. As Poland's demographic bulge slimmed, new entrants to the domestic labour market reduced and emigration slowed. Some commentators say the Polish baby-boomers began returning to Poland as they reach child-rearing age themselves.[27]
Demographics
Population size
The 2001 UK Census recorded 60,711 Polish-born people resident in the UK.[29] 60,680 of these were resident in Great Britain (the UK minus Northern Ireland), compared to 73,951 in 1991.[30] With the migration that has followed Poland's accession to the EU, the Polish-born population in the whole of the UK is estimated to have risen to 515,000 in the year to March 2010.[20] Unofficial estimates have put the number of Poles living in the UK higher, at up to one million.[31][32][33]
Geographic distribution

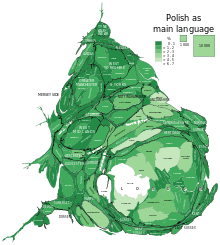
According to 2011 Census in England and Wales there are 0.5 million residents whose main language is Polish which makes 1% of the whole population aged 3 and over. In London there were 147,816 Polish speakers. The main hub of the London Polish community is Ealing in west London. Elsewhere in London the biggest Polish communities are in London Boroughs of: Haringey, Brent, Hounslow, Waltham Forest, Barnet. Besides London, the biggest Polish communities are in Birmingham, Southampton, Slough, Luton, Leeds, Peterborough, Nottingham, Manchester, Leicester, Coventry. The biggest concentrations are in London Borough of Ealing (21,507; 6.4% of all usual residents), Slough (8,341; 5.9%) and Borough of Boston (2.975; 4.6%).[34]
Scotland has seen a significant influx of Polish immigrants with estimates of Poles currently living in Scotland ranging from 40,000 according to General Register Office for Scotland up to 50,000 as per Polish Council,.[35] The creation of a bilingual English-Polish newspaper[36] supports the estimated 5,000 Poles[37] now living in the Highlands. Edinburgh has around 13,000 Poles which is 2.7% of the city's population and is one of the largest Polish communities in the UK.
The activities revolve around the Polish Social and Cultural Association and the Federation of Poles in Great Britain (ZPWB) that were established to promote the interests of the Polish ethnic minority in Great Britain and to promote Polish history and culture among the British people. Currently, the federation creates more than 70 Polish organisations in UK. Polish food shops are increasingly apparent following Poland's entry into the European Union in May 2004. The local newspaper in Blackpool is one of a handful of British newspapers to have its own online edition in Polish called Witryna Polska .[38] Polish workers are employed in agriculture[39] and light industry in the countrysides of low-population density regions such as East Anglia and East Midlands[40]
Official figures on the number of Polish people in Northern Ireland are difficult to obtain. The total number of Polish nationals who applied for a National Insurance Number is 12,020 as of 2005, and the number of people reporting Polish as a first language in the 2011 census was 17,100[41] but the actual number of residents is likely to be much higher.[42] A Police Service of Northern Ireland (PSNI) recruitment drive in November 2006 attracted applications from 968 Poles, with language exams being held both in Northern Ireland and Warsaw, but as of 2008, none have entered the PSNI's ranks.[43][44]
Social issues
Education
Many Poles who have migrated to the UK since the enlargement of the EU have brought children with them. This has created some pressure on school places and English language support services.[45] Despite language difficulties, research shows these pupils perform well in British schools and the presence of Polish pupils in schools has improved the performance of other pupils in those schools.[46]
Ethnic tensions
Polish people living in the UK reported 42 "racially motivated violent attacks" against them in 2007, compared with 28 in 2004.[47] On 11 July 2012, the Polish Association of Northern Ireland called for action after Polish flags were burned on Eleventh Night bonfires in several locations across Belfast.[48]
On 26 July 2008, The Times published a comment piece by restaurant reviewer Giles Coren containing anti-Polish sentiment including alleged Polish antisemitism. Coren used the racial slur 'Polack' to describe Polish immigrants in the UK, arguing that "if England is not the land of milk and honey it appeared to them three or four years ago, then, frankly, they can clear off out of it".[49] The article has been subject to major criticism.
The far-right British National Party (BNP) have used anti-Polish sentiment,[50] and campaigned for a ban on all Polish migrant workers in the UK.[51] In one highly publicised incident, the party used a poster that showed a nostalgic picture of a Second World War Spitfire fighter plane under the slogan "Battle for Britain", during the party's 2009 European Elections campaign. However, apparently unknowingly, the photograph they used was accidentally that of a Spitfire belonging to the Polish 303 Squadron of the Royal Air Force. John Hemming, MP for Yardley, Birmingham, ridiculed the party for accidentally using an image of "Polish heroism" in their campaign: "They have a policy to send Polish people back to Poland – yet they are fronting their latest campaign using this plane."[52]
In January 2014, a Polish man, whose helmet was emblazoned with the flag of Poland,[53] claimed he was attacked by a group of 15 men outside a pub in Dagenham, London.[54] The victim blamed xenophobic speeches of the conservative Prime Minister David Cameron.[55] During the same month in Belfast there were 7 attacks on Polish homes within 10 days, in which stones and bricks were thrown at the windows.[56]
Notable individuals
The following individuals are notable Poles who have lived in the United Kingdom, or British people of Polish ancestry.
Businessmen
- Sir Jack Cohen, the founder of Tesco, was the son of Polish Jewish immigrants.[57]
- Michael Marks, Polish: Michał Marks, M&S, (1859, 1863 or 1864 – 31 December 1907), was one of the two co-founders of the retail chain Marks & Spencer.
Artists
- Iwona Blazwick, art critic
- Henryk Gotlib, painter[58]
- Jan Pieńkowski, children's illustrator[59]
- Andrzej Krauze, cartoonist, illustrator, painter and poster designer[60]
- Waldemar Januszczak, art critic
- Adam Kossowski, painter
- Witold Rybczynski, architect
- Richard Wawro, landscape painter
Musicians and performers
- Kathryn Apanowicz, actress
- Daniela Denby-Ashe (born Pszkit), actress
- Robert Donat, actor
- Chris Dreja, guitarist with The Yardbirds
- Anulka Dziubinska, actress and model
- Janick Gers, guitarist in Iron Maiden
- Coky Giedroyc, director
- Mel Giedroyc, actress and comedienne, one half of 'Mel and Sue'[61]
- Sir John Gielgud, actor and director
- Maina Gielgud, ballet dancer
- Val Gielgud, pioneer of radio drama
- Stefan Golaszewski, comedian
- J. J. Jeczalik, musician
- Marek Kanievska, director
- Richard Kwietniowski, director and screenwriter
- Rula Lenska, actress
- Gerald Lepkowski, actor
- Kasia Madera, newsreader
- Andrzej Panufnik, orchestral conductor and composer
- Emily Ratajkowski, model and actress
- Janek Schaefer, sound artist
- Leopold Stokowski, orchestral conductor
- Peter Serafinowicz, comedian
- Chris Urbanowicz, guitar player in Editors
- Tracey Ullman, Comedienne, actress, and singer
- Katy Carr, Musician, songwriter and aviator
Writers
- Joseph Conrad, novelist[58]
- Marianna Palka, screenwriter
Politicians
- Daniel Kawczynski, Conservative MP for Shrewsbury and Atcham, whose family fled Poland in 1940[62]
- Mark Lazarowicz, Labour and Co-operative MP for Edinburgh North and Leith, whose father was Polish[63]
- Denis MacShane (né Matyjaszek), former Minister for Europe, whose father was Polish[64]
- David Miliband, former Foreign Secretary, whose mother was born in Poland[65]
- Ed Miliband, leader of the Labour Party, whose mother was born in Poland[65]
- Edward Bernard Raczyński, aristocrat, diplomat, writer, politician and President of Poland in exile (between 1979 and 1986)[58]
- Szmul Zygielbojm was a Jewish-Polish socialist politician, Bund leader, and member of the National Council of the Polish Government in Exile. He committed suicide to protest the indifference of the Allied governments in the face of the Holocaust.[58]
Science
- Sir Leszek Borysiewicz (born 1951) - physician, immunologist and scientific administrator, the 345th Vice-Chancellor of the University of Cambridge (in office since 2010).[66]
- Jacob Bronowski (1908-1974) - Polish-Jewish British mathematician, biologist, historian of science, theatre author, poet and inventor. Presenter and writer of the 1973 BBC television documentary series, The Ascent of Man.
- Maria Czaplicka (1884-1921) - cultural anthropologist who is best known for her ethnography of Siberian shamanism.
- Helen Czerski, physicist and oceanographer
- James Gimzewski, physicist
- Janusz Jankowski, medical doctor, scientist and academic administrator
- Leszek Kołakowski (1927-2009) - philosopher and historian of ideas, senior research fellow at All Souls College, Oxford, the first winner of the John W. Kluge Prize for Lifetime Achievement in the Humanities.
- Józef Kosacki (1909–1990) - inventor of the Polish mine detector, first used in Second Battle of El Alamein.
- W. S. Lach-Szyrma, historian
- Bronisław Malinowski (1884–1942) - one of the most important 20th-century anthropologists
- Zbigniew Pelczynski (born 1925) - political scientist, fellow of Pembroke College, Oxford, founder of School for Leaders in Poland
- Sir Leon Radzinowicz, criminologist
- Karol Sikora, oncologist
- Jack Szostak (born 1952) - Nobel prize winning geneticist who helped to understand telomeres & create the human genome.
- Władysław Świątecki (1895 – 1944)- invented the slip bomb device. The slip bomb device was the most successful bomb device used in WW2 up to the Atomic bomb.
- Paweł Strzelecki (24 June 1797 – 6 October 1873) was a Polish explorer and geologist who in 1845 also became a British subject.
- Zbigniew Szydlo, chemist
Sportspeople
- Paweł Abbott, British born former Poland under-21 international footballer
- Michael Bisping, Mixed martial artist
- Andy Drzewiecki, former weightlifter
- Carl Froch, professional boxer and is a two-time former WBC Super Middleweight Champion
- Lisa Dobriskey, English middle distance athlete
- Robert Grabarz, high-jumper
- Phil Jagielka, England international footballer
- Andrew Johnson, former England international footballer
- Lukas Jutkiewicz, footballer
- Paul Konchesky, former England international footballer
- Craig Kopczak, rugby league player
- Robert Kozluk, footballer
- Dick Krzywicki, former Wales international footballer
- Anthony Malarczyk, former cyclist
- Eddie Niedzwiecki, former Wales international footballer
- Anton Otulakowski, former footballer
- Kris Radlinski, former Wigan Warriors and Great Britain rugby league player
- Kevin Rutkiewicz, footballer
- Kevin Spiolek, former darts player
- Alex Szostak, rugby league player
See also
- Anglo-Polish Radio ORLA.fm
- Polish diaspora
- Dziennik Polski
- Goniec Polski
- Polish Radio London
- Londyńczycy
- BBC Polish Section
- Polish Government in London
- Western betrayal
- Lists of UK locations with large ethnic minority populations
- Federation of Poles in Great Britain
- World War II Behind Closed Doors: Stalin, the Nazis and the West
- History of the Jews in Poland
- Rescue of Jews by Poles during the Holocaust
- British Jews
- Oxford University Polish Society
- Great Polish Map of Scotland
- Lipka Tatars
- Scottish migration to Poland - large Scottish migration to Poland between 15th and 18th century
References
- ↑ "Poland’s British baby boom". News Poland. 25 May 2012. Retrieved 28 January 2014.
- ↑ Daily Mail article on Polish population boom
- ↑ Office for National Statistics graph of Polish population growth
- ↑ Polish Resettlement Act 1947
- ↑ http://www.thenews.pl/1/9/Artykul/121253,Census-confirms-Poles-as-UKs-second-biggest-foreign-community
- ↑ http://dawn.com/2013/02/01/polish-now-englands-second-language/
- ↑ http://www.mirror.co.uk/news/uk-news/2011-census-polish-language-becomes-1564957
- ↑ Shore, Thomas William (2008). Origin of the Anglo-Saxon Race – A Study of the Settlement of England and the Tribal Origin of the Old English People. READ BOOKS. pp. 84–102. ISBN 1-4086-3769-3.
- ↑ http://www.polamcon.org/jamestown/roles-and-accomp.htm
- ↑ http://home.earthlink.net/~rggsibiba/html/sib/sib2.html
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 BBC London, Polish London. accessdate 2008-01-02.
- ↑ Peter, Laurence (20 July 2009). "How Poles cracked Nazi Enigma secret". BBC News. Retrieved 22 May 2010.
- ↑ Gordon Welchman, The Hut Six Story, p. 289.
- ↑ http://www.pbs.org/behindcloseddoors/about/index.html
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 15.2 15.3 pp.374-383 Olson and Cloud 2003
- ↑ http://news.google.com/newspapers?id=BTsNAAAAIBAJ&sjid=_mkDAAAAIBAJ&pg=4479,4501733
- ↑ Kay, Diana; Miles, Robert (1998). "Refugees or migrant workers? The case of the European Volunteer Workers in Britain (1946–1951)". Journal of Refugee Studies 1 (3-4): 214–236. doi:10.1093/jrs/1.3-4.214.
- ↑ Holmes, Colin (1988). John Bull's Island: Immigration and British Society 1871-1971. Basingstoke: Macmillan.
- ↑ Burrell, Kathy (2002). "Migrant memories, migrant lives: Polish national identity in Leicester since 1945" (PDF). Transactions of the Leicestershire Archaeological and Historical Society (76): 59–77.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 "Polish people in the UK: Half a million Polish-born residents". Office for National Statistics. 25 November 2010. Retrieved 30 December 2010.
- ↑ Tesco caters for an estimated 1.1 million Poles visiting the UK or living and working there
- ↑ Home Office, Border & Immigration Agency, The Worker Registration Scheme Accessed 2007-12-27.
- ↑ Freedom of movement for workers after enlargement Europa
- ↑ Barriers still exist in larger EU, BBC News, 1 May 2005
- ↑ EU free movement of labour map, BBC News, 4 January 2007, accessed 26 August 2007
- ↑ Home Office, Department for Work and Pensions, HM Revenue & Customs and Communities and Local Government, Accession Monitoring Report: A8 Countries, May 2004-June 2007, 21 August 2007, accessed 26 August 2007.
- ↑ 27.0 27.1 Tchorek, Kamil (16 February 2008). "Building a future in a land where life is affordable". The Times (London). Retrieved 22 May 2010.
- ↑ Pollard, Naomi; Latorre, Maria; Sriskandarajah, Dhananjayan (April 2008). "Floodgates or turnstiles? Post-EU enlargement migration to (and from) the UK". Institute for Public Policy Research. p. 21. Retrieved 2008-06-15.
- ↑ "Country-of-birth database". Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development. Retrieved 2009-10-04.
- ↑ "Born abroad: Poland". BBC News. 7 September 2005. Retrieved 2009-10-04.
- ↑ de Quetteville, Harry (8 October 2007). "Poland's politicians fly to UK ahead of election". The Daily Telegraph (London). Retrieved 22 May 2010.
- ↑ Kaczmarek, Julita (3 September 2007). "Radio moves to Polish position". The Guardian (London). Retrieved 22 May 2010.
- ↑ Smithers, Rebecca (11 July 2007). "'Swiat Wedlung Clarksona, poprosz (World According to Clarkson, please)". The Guardian (London). Retrieved 22 May 2010.
- ↑ "Table QS203EW: 2011 Census: Country of birth (detailed), local authorities in England and Wales". Census 2011. Office for National Statistics. Retrieved 22 March 2014.
- ↑ Polish immigrants swell Scotland's new baby boom
- ↑ Gazeta z Highland Polish language newspaper for Scottish Highlands-based Poles
- ↑ BBC article about Polish/English bi-lingual newspaper for 'north Poles'
- ↑ Polish Gazette in the TV spotlight
- ↑ Hiranthi Jayaweera and Bridget Anderson (2007) "Migrant workers and vulnerable employment: an analysis of existing data" Report for TUC Commission on Vulnerable Employment
- ↑ Polish demographic patterns in the UK
- ↑ BBC article: "Census figures: NI Protestant population continuing to decline"
- ↑ University Of Ulster Project on Polish Minority
- ↑ Almost 1,000 Poles apply to PSNI
- ↑ BBC News - No Poles make it into PSNI ranks
- ↑ http://www.ces.ed.ac.uk/PDF%20Files/Brief054.pdf
- ↑ Bingham, John (22 May 2012). "Polish children boosting standards among English pupils, study suggests". Daily Telegraph (London). Retrieved 18 February 2015.
- ↑ "BBC denies MP's anti-Polish claim". BBC News. 4 June 2008. Retrieved 22 May 2010.
- ↑ BBC article: "Poland flags burned on bonfires across Belfast on 11 July"
- ↑ Coren, Giles (26 July 2008). "Two waves of immigration, Poles apart". The Times (London). Retrieved 26 September 2010.
- ↑ BNP advances on Middle England to exploit ‘fear’ of Polish migrants Andrew Norfolk, The Times, 23 April 2007
- ↑ BNP shot down after it uses a Spitfire to front its anti-immigration campaign Daily Mail, 4 March 2009
- ↑ BNP uses Polish Spitfire in anti-immigration poster 4 Mar 2009, The Telegraph
- ↑ http://www.thenews.pl/1/10/Artykul/163186,UK-Poles-in-Downing-Street-antidiscrimination-protest
- ↑ http://www.barkinganddagenhampost.co.uk/news/crime-courts/gang_of_15_attacks_dagenham_motorcyclist_outside_pub_because_he_is_polish_1_3233943
- ↑ http://wyborcza.pl/1,75477,15295210,Pobili_Polaka_w_Londynie___Kopali_i_krzyczeli__ze.html?utm_source=HP&utm_medium=AutopromoHP&utm_content=cukierek1&utm_campaign=wyborcza#Cuk
- ↑ http://www.belfasttelegraph.co.uk/news/local-national/northern-ireland/seven-attacks-in-10-days-as-racist-gang-targets-polish-community-in-east-belfast-29924518.html
- ↑ Sir John Edward Cohen at Oxford Dictionary of National Biography
- ↑ 58.0 58.1 58.2 58.3 Lachowicz, Marysia (21 February 2007). "Poles in London history". Untold London. Retrieved 15 December 2009.
- ↑ Alison Flood (22 December 2008). "Meg, Mog and other monsters". theguardian.com. Retrieved 2014-07-22.
- ↑ "Andrzej Krauze". British Cartoon Archive. Retrieved 2014-07-22.
- ↑ http://www.express.co.uk/posts/view/184227/Mel-Giedroyc-Dad-s-tragic-childhood-has-made-me-a-better-person
- ↑ "Daniel Kawczynski: The tallest MP in in Parliament". The Daily Telegraph (London). 22 January 2009. Retrieved 26 February 2011.
- ↑ "Report from Parliament (North Edinburgh News, June 2009)". Mark Lazarowicz. June 2009. Retrieved 26 February 2011.
- ↑ Helm, Toby (1 May 2004). "MacShane's passion for Europe driven by memories of war". The Daily Telegraph (London). Retrieved 26 February 2011.
- ↑ 65.0 65.1 Mendick, Robert; Day, Matthew (16 May 2010). "The miraculous escape of Marion Miliband". The Daily Telegraph (London). Retrieved 26 February 2011.
- ↑ "New Vice-Chancellor for Cambridge". University of Cambridge. Retrieved 2010-10-06.
Further reading
- A Remarkable School in Exile 1941-1951, Veritas Foundation Publication, ISBN 0-9545100-0-3
- S.Barnes, A Long Way From Home, Staffordshire University 2003
- Kathy Burrell, Polish Migration to the UK in the 'New' European Union, Ashgate 2009, ISBN 978-0-7546-7387-3
- Dr Diana M Henderson(Editor), The Lion and The Eagle, Cualann Press ISBN 0-9535036-4-X.
- Robert Gretzyngier Poles in Defence of Britain, Grub 2001, ISBN 1-902304-54-3
- Michael Hope, The Abandoned Legion, Veritas Foundation Publication ISBN 1-904639-09-7.
- Michael Hope, Polish deportees in the Soviet Union, Veritas Foundation Publication, ISBN 0-948202-76-9
- W. Jedrzejewicz, Poland in the British Parliament 1939-1945, White Eagle Printing
- G. Kay & R.Negus, Polish Exile Mail in Great Britain 1939-1949, J.Barefoot, ISBN 0-906845-52-1
- Ignacy Matuszewski, Did Britain Guarantee Poland's frontiers?, Polish Bookshop
- Ignacy Matuszewski, Great Britain's Obligations Towards Poland, National Committee of Americans, 1945
- Wiktor Moszczynski, Hello, I'm Your Polish Neighbour: All about Poles in West London, AuthorHouse, 2010, ISBN 1-4490-9779-0,
- Robert Ostrycharz,Polish War Graves in Scotland A Testament to the Past, ISBN 1-872286-48-8.
- Prazmowska, Anita, Britain and Poland 1939-1943, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0-521-48385-9
- Tim Smith & Michelle Winslow, Keeping the Faith The Polish Community in Britain, Bradford Heritage, ISBN 0-907734-57-X
- Peter Stachura(Editor), The Poles in Britain 1940-2000, Frank Cass ISBN 0-7146-8444-9.
- R. Umiastowski, Poland, Russia and Great Britain 1941-1945, Hollis & Carter 1946
- Ian Valentine, Station 43 Audley End House and SOE's Polish section, Sutton 2004, ISBN 0-7509-4255-X
- Various, Intelligence co-operation between Poland and Great Britain during World War II, Vallentine Mitchell 2005, ISBN 0-85303-656-X
- Jonathan Walker, Poland Alone, History Press 2008, ISBN 978-1-86227-474-7
Memoirs and fiction
- Michał Giedroyc, Crater's Edge: A Family's Epic Journey Through Wartime Russia, Bene Factum Publishing Ltd (1 May 2010)
- Matthew Kelly, Finding Poland, Jonathan Cape Ltd (4 Mar 2010)
- Michael Moran, A Country in the Moon: Travels in Search of the Heart of Poland, Granta Books; Reprint edition (2 Mar 2009)
- Joanna Czechowska, The Black Madonna of Derby, Silkmill Press 2008
- Andrew Tarnowski, The Last Mazurka: A Tale of War, Passion and Loss, Aurum Press Ltd (9 May 2006)
- Kasimir Czerniak, Gabi Czerniak, William Czerniak-Jones, The Wisdom of Uncle Kasimir, Bloomsbuy 2006
- Annette Kobak, Joe's War - My Father Decoded: A Daughter's Search for Her Father's War, 2004
- Dr John Geller, Through Darkness To Dawn, Veritas (1 Jan 1989)
- Denis Hills, Return to Poland, The Bodley Head Ltd; First Edition (28 Jan 1988)
- Slavomir Rawicz, The Long Walk: The True Story of a Trek to Freedom, Robinson Publishing (26 April 2007)
Academic papers
- Małgorzata Irek, New Wave, Old Ways? Post-accession Migration from Poland Seen from the Perspective of the Social Sciences, Studia Sociologica IV (2012), vol. 2, p. 21–30
- Michał P. Garapich, Between Cooperation and Hostility – Constructions of Ethnicity and Social Class among Polish Migrants in London, Studia Sociologica IV (2012), vol. 2, p. 31-45
- (Polish) Małgorzata Krywult-Albańska, Profil demograficzny polskich imigrantów poakcesyjnych w Wielkiej Brytanii, Studia Sociologica IV (2012), vol. 2, p. 72-80
External links
- Emito.net - UK's Polish Community Online
- Anglo-Polish Radio ORLA.fm
- Polish Weekly Magazine in the UK
- Portal for the Polish Minority in the UK
- The oldest Polish Newspaper in the UK - Polish Daily/Soldier's Daily
- Polish Embassy in the UK, London
- Portal for Polish people in Leeds, West Yorkshire
- Leeds-Manchester.pl - Portal for the Polish Community in Northern England
- Polish Resettlement Act, as revised
- The National Archives: Polish Resettlement
- Federation of Poles in Great Britain
- POSK Polish Social and Cultural Association
- Reassessing what we collect website – Polish London History of Polish London with objects and images
- Return to Poland - employers' website
- Polish Residents in Scotland, 1861-2001
- Conservative Friends of Poland - website
- Social Network for Poles within the UK - website
- Jagiellonian University Polish Research Centre in London
- Help for Poles in the UK Foundation
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||