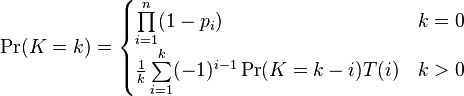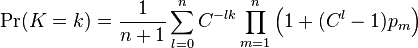Poisson binomial distribution
| Parameters |
![\mathbf{p}\in [0,1]^n](../I/m/13723ad4f4359d6e7c8951dc69ac6b51.png) — success probabilities for each of the n trials — success probabilities for each of the n trials |
|---|---|
| Support | k ∈ { 0, …, n } |
| pmf |
 |
| CDF |
 |
| Mean |
 |
| Variance |
 |
| Skewness |
 |
| Ex. kurtosis |
 |
| MGF |
 |
| CF |
 |
In probability theory and statistics, the Poisson binomial distribution is the discrete probability distribution of a sum of independent Bernoulli trials that are not necessarily identically distributed. The concept is named after Siméon Denis Poisson.
In other words, it is the probability distribution of the
number of successes in a sequence of n independent yes/no experiments with success probabilities 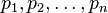 . The ordinary binomial distribution is a special case of the Poisson binomial distribution, when all success probabilities are the same, that is
. The ordinary binomial distribution is a special case of the Poisson binomial distribution, when all success probabilities are the same, that is  .
.
Mean and variance
Since a Poisson binomial distributed variable is a sum of n independent Bernoulli distributed variables, its mean and variance will simply be sums of the mean and variance of the n Bernoulli distributions:
For fixed values of the mean (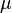 ) and size (n), the variance is maximal when all success probabilities are equal and we have a binomial distribution. When the mean is fixed, the variance is bounded from above by the variance of the Poisson distribution with the same mean which is attained asymptotically as n tends to infinity.
) and size (n), the variance is maximal when all success probabilities are equal and we have a binomial distribution. When the mean is fixed, the variance is bounded from above by the variance of the Poisson distribution with the same mean which is attained asymptotically as n tends to infinity.
Probability mass function
The probability of having k successful trials out of a total of n can be written as the sum [1]
where 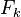 is the set of all subsets of k integers that can be selected from {1,2,3,...,n}. For example, if n = 3, then
is the set of all subsets of k integers that can be selected from {1,2,3,...,n}. For example, if n = 3, then  .
.  is the complement of
is the complement of 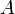 , i.e.
, i.e. 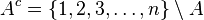 .
.
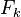 will contain
will contain  elements, the sum over which is infeasible to compute in practice unless the number of trials n is small (e.g. if n = 30,
elements, the sum over which is infeasible to compute in practice unless the number of trials n is small (e.g. if n = 30, 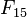 contains over 1020 elements). There are luckily more efficient ways to calculate
contains over 1020 elements). There are luckily more efficient ways to calculate 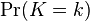 .
.
As long as none of the success probabilities are equal to one, one can calculate the probability of k successes using the recursive formula [2] [3]
where
The recursive formula is not numerically stable, and should be avoided if 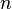 is greater than approximately 20. Another possibility is using the discrete Fourier transform
[4]
is greater than approximately 20. Another possibility is using the discrete Fourier transform
[4]
where  and
and  .
.
Still other methods are described in .[5]
Entropy
There is no simple formula for the entropy of a Poisson binomial distribution, but the entropy can be upper bounded by that entropy of a binomial distribution with the same number parameter and the same mean. Therefore the entropy can also be upper bounded by the entropy of a Poisson distribution with the same mean. [6]
The Shepp-Olkin conjecture, due to Lawrence Shepp and Ingram Olkin in 1981, states that the entropy of a Poisson binomial distribution is a concave function of the success probabilities 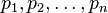 .
[7]
.
[7]
See also
References
- ↑ Wang, Y. H. (1993). "On the number of successes in independent trials". Statistica Sinica 3 (2): 295–312.
- ↑ Shah, B. K. (1994). "On the distribution of the sum of independent integer valued random variables". American Statistician 27 (3): 123–124. JSTOR 2683639.
- ↑ Chen, X. H.; A. P. Dempster; J. S. Liu (1994). "Weighted finite population sampling to maximize entropy". Biometrika 81 (3): 457. doi:10.1093/biomet/81.3.457.
- ↑ Fernandez, M.; S. Williams (2010). "Closed-Form Expression for the Poisson-Binomial Probability Density Function". IEEE Transactions on Aerospace Electronic Systems 46: 803–817. doi:10.1109/TAES.2010.5461658.
- ↑ Chen, S. X.; J. S. Liu (1997). "Statistical Applications of the Poisson-Binomial and conditional Bernoulli distributions". Statistica Sinica 7: 875–892.
- ↑ Harremoës, P. (2001). "Binomial and Poisson distributions as maximum entropy distributions". IEEE Transactions on Information Theory 47 (5): 2039–2041. doi:10.1109/18.930936.
- ↑ Shepp, Lawrence; Olkin, Ingram (1981). "Entropy of the sum of independent Bernoulli random variables and of the multinomial distribution". In Gani, J.; Rohatgi, V.K. Contributions to probability: A collection of papers dedicated to Eugene Lukacs. New York,: Academic Press,. pp. 201–206. ISBN 0-12-274460-8. MR 0618689.
| ||||||||||||||