Poincaré group
| Algebraic structure → Group theory Group theory |
|---|
|
Modular groups
|
Infinite dimensional Lie group
|
| Group theory → Lie groups Lie groups |
|---|
|
|
The Poincaré group, named after Henri Poincaré,[1] is the group of Minkowski spacetime isometries.[2][3] It is a ten-generator non-abelian Lie group of fundamental importance in physics.
Overview
A Minkowski spacetime isometry has the property that the interval between events is left invariant. For example, if everything was postponed by two hours including two events and the path you took to go from one to the other, then the time interval between the events recorded by a stop-watch you carried with you would be the same. Or if everything was shifted five miles to the west, or turned 60 degrees to the right, you would also see no change in the interval. It turns out that the proper length of an object is also unaffected by such a shift. A time or space reversal (a reflection) is also an isometry of this group.
In Minkowski space (i.e. ignoring the effects of gravity), there are ten degrees of freedom of the isometries, which may be thought of as translation through time or space (four degrees, one per dimension); reflection through a plane (three degrees, the freedom in orientation of this plane); or a "boost" in any of the three spatial directions (three degrees). Composition of transformations is the operator of the Poincaré group, with proper rotations being produced as the composition of an even number of reflections.
In classical physics, the Galilean group is a comparable ten-parameter group that acts on absolute time and space. Instead of boosts, it features shear mappings to relate co-moving frames of reference.
Details
The Poincaré group is the group of Minkowski spacetime isometries. It is a ten-dimensional noncompact Lie group. The abelian group of translations is a normal subgroup, while the Lorentz group is also a subgroup, the stabilizer of the origin. The Poincaré group itself is the minimal subgroup of the affine group which includes all translations and Lorentz transformations. More precisely, it is a semidirect product of the translations and the Lorentz group,
Another way of putting this is that the Poincaré group is a group extension of the Lorentz group by a vector representation of it; it is sometimes dubbed, informally, as the "inhomogeneous Lorentz group". In turn, it can also be obtained as a group contraction of the de Sitter group SO(4,1) ~ Sp(2,2), as the de Sitter radius goes to infinity.
Its positive energy unitary irreducible representations are indexed by mass (nonnegative number) and spin (integer or half integer) and are associated with particles in quantum mechanics (see Wigner's classification).
In accordance with the Erlangen program, the geometry of Minkowski space is defined by the Poincaré group: Minkowski space is considered as a homogeneous space for the group.
The Poincaré algebra is the Lie algebra of the Poincaré group. More specifically, the proper (detΛ=1), orthochronous (Λ00≥1) part of the Lorentz subgroup (its identity component), SO+(1, 3), is connected to the identity and is thus provided by the exponentiation exp(iaμPμ) exp(iωμνMμν/2) of this Lie algebra. In component form, the Poincaré algebra is given by the commutation relations:[4][5]
where P is the generator of translations, M is the generator of Lorentz transformations, and η is the Minkowski metric (see Sign convention).
The bottom commutation relation is the ("homogeneous") Lorentz group, consisting of rotations, Ji = −ϵimnMmn/2, and boosts, Ki = Mi0. In this notation, the entire Poincaré algebra is expressible in noncovariant (but more practical) language as
where the bottom line commutator of two boosts is often referred to as a "Wigner rotation". Note the important simplification [Jm+i Km , Jn−i Kn] = 0, which permits reduction of the Lorentz subalgebra to su(2)⊕su(2) and efficient treatment of its associated representations.
The Casimir invariants of this algebra are PμPμ and Wμ Wμ where Wμ is the Pauli–Lubanski pseudovector; they serve as labels for the representations of the group.
The Poincaré group is the full symmetry group of any relativistic field theory. As a result, all elementary particles fall in representations of this group. These are usually specified by the four-momentum squared of each particle (i.e. its mass squared) and the intrinsic quantum numbers JPC, where J is the spin quantum number, P is the parity and C is the charge-conjugation quantum number. In practice, charge conjugation and parity are violated by many quantum field theories; where this occurs, P and C are forfeited. Since CPT symmetry is invariant in quantum field theory, a time-reversal quantum number may be constructed from of those given.
As a topological space, the group has four connected components: the component of the identity; the time reversed component; the spatial inversion component; and the component which is both time-reversed and spatially inverted.
Poincaré symmetry
Poincaré symmetry is the full symmetry of special relativity. It includes:
- translations (displacements) in time and space (P), forming the abelian Lie group of translations on space-time;
- rotations in space, forming the non-Abelian Lie group of three-dimensional rotations (J);
- boosts, transformations connecting two uniformly moving bodies (K).
The last two symmetries, J and K, together make the Lorentz group (see also Lorentz invariance); the semi-direct product of the translations group and the Lorentz group then produce the Poincaré group. Objects which are invariant under this group are then said to possess Poincaré invariance or relativistic invariance.
See also
- Euclidean group
- Representation theory of the Poincaré group
- Wigner's classification
- Symmetry in quantum mechanics
- Center of mass (relativistic)
- Pauli–Lubanski pseudovector
- Particle physics and representation theory
Notes
- ↑ Poincaré, Henri, "Sur la dynamique de l’électron", Rendiconti del Circolo matematico di Palermo 21: 129–176, doi:10.1007/bf03013466 (Wikisource translation: On the Dynamics of the Electron).
- ↑ Minkowski, Hermann, "Die Grundgleichungen für die elektromagnetischen Vorgänge in bewegten Körpern", Nachrichten von der Gesellschaft der Wissenschaften zu Göttingen, Mathematisch-Physikalische Klasse: 53–111 (Wikisource translation: The Fundamental Equations for Electromagnetic Processes in Moving Bodies).
- ↑ Minkowski, Hermann, "Raum und Zeit", Physikalische Zeitschrift 10: 75–88
- ↑ N.N. Bogolubov (1989). General Principles of Quantum Field Theory (2nd ed.). Springer. p. 272. ISBN 0-7923-0540-X.
- ↑ T. Ohlsson (2011). Relativistic Quantum Physics: From Advanced Quantum Mechanics to Introductory Quantum Field Theory. Cambridge University Press. p. 10. ISBN 1-13950-4320.
References
- Wu-Ki Tung (1985). Group Theory in Physics. World Scientific Publishing. ISBN 9971-966-57-3.
- Weinberg, Steven (1995). The Quantum Theory of Fields 1. Cambridge: Cambridge University press. ISBN 978-0-521-55001-7.
- L.H. Ryder (1996). Quantum Field Theory (2nd ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 62. ISBN 0-52147-8146.

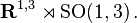
![~[P_\mu, P_\nu] = 0\,](../I/m/64f0eb783043f96e3b71de153a6b6351.png)
![~\frac{ 1 }{ i }~[M_{\mu\nu}, P_\rho] = \eta_{\mu\rho} P_\nu - \eta_{\nu\rho} P_\mu\,](../I/m/044e50e3844a4125d5ea515a3f5cc9ee.png)
![~\frac{ 1 }{ i }~[M_{\mu\nu}, M_{\rho\sigma}] = \eta_{\mu\rho} M_{\nu\sigma} - \eta_{\mu\sigma} M_{\nu\rho} - \eta_{\nu\rho} M_{\mu\sigma} + \eta_{\nu\sigma} M_{\mu\rho}\, ,](../I/m/ad4e98391c828ea987dfbde544331bee.png)
![[J_m,P_n] = i \epsilon_{mnk} P_k ~,](../I/m/c7f293d1f901955fa27db121f244b37b.png)
![[J_i,P_0] = 0 ~,](../I/m/80ad37d62bd564ee4c71c272b42083a4.png)
![[K_i,P_k] = i \eta_{ik} P_0 ~,](../I/m/33ec6017a19d7ab0ba1693f9dcdc64bf.png)
![[K_i,P_0] = -i P_i ~,](../I/m/08ca57cf6bde72e032071858f634efbb.png)
![[J_m,J_n] = i \epsilon_{mnk} J_k ~,](../I/m/62de91dd8cb7073d10e3ee82ffdb671a.png)
![[J_m,K_n] = i \epsilon_{mnk} K_k ~,](../I/m/1f2345593b48c97f361450b5ab986f53.png)
![[K_m,K_n] = -i \epsilon_{mnk} J_k ~,](../I/m/c3441c6898f6be0691f88581d6bd3b21.png)