Plunketts Creek Bridge No. 3
| Plunketts Creek Bridge No. 3 | |
| Bridge in Plunketts Creek Township (NRHP) | |
| Historic American Engineering Record, National Register of Historic Places | |
 View from southeast in January 1996, with flood damage | |
| Official name: Plunketts Creek Bridge No. 3 (HAER) | |
| Named for: Plunketts Creek | |
| Country | United States |
|---|---|
| State | Pennsylvania |
| County | Lycoming |
| Township | Plunketts Creek |
| Road | State Route 1005 (single lane) |
| Crosses | Plunketts Creek |
| Elevation | 780 ft (238 m) |
| Coordinates | 41°24′32″N 76°48′10″W / 41.40889°N 76.80278°WCoordinates: 41°24′32″N 76°48′10″W / 41.40889°N 76.80278°W [1] |
| Length | 75 ft (23 m) [2] |
| Roadway width | 15.25 ft (4.6 m) [2] |
| Design | Rubble masonry arch bridge |
| Material | Stone |
| Built | between 1840 and 1875 |
| - Destroyed | 1996 |
| Owned and Maintained by | Pennsylvania Department of Transportation |
| HAER Number | PA-418 [2] |
| Added to NRHP | June 22, 1988 |
| NRHP Ref# | 88000830 |
| MPS | Highway Bridges Owned by the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, Department of Transportation, TR |
| Removed from NRHP | July 22, 2002 |
|
Location within Pennsylvania
| |
| Wikimedia Commons: Plunketts Creek Bridge No. 3 | |
Plunketts Creek Bridge No. 3 was a rubble masonry stone arch bridge over Plunketts Creek in Plunketts Creek Township, Lycoming County in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania. It was built between 1840 and 1875, probably closer to 1840, when the road along the creek between the unincorporated villages of Barbours and Proctor was constructed. Going upstream from the mouth, the bridge was the third to cross the creek, hence its name.
The bridge was 75 feet (23 m) long, with an arch that spanned 44 feet (13 m), a deck 18 feet 8 inches (5.69 m) wide, and a roadway width of 15 feet 3 inches (4.65 m). It carried a single lane of traffic. In the 19th century, the bridge and its road were used by the lumber, leather, and coal industries active along the creek. By the early 20th century, these industries had almost entirely left, and the villages declined. The area the bridge served reverted mostly to second growth forest and it was used to access Pennsylvania State Game Lands and a state pheasant farm.
Plunketts Creek Bridge No. 3 was considered "significant as an intact example of mid-19th century stone arch bridge construction",[2] and was added to the National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) on June 22, 1988. Although it was repaired after a major flood in 1918, a record flood on January 21, 1996, severely damaged the bridge, and it was demolished in March 1996. Before the 1996 flood about 450 vehicles crossed it each day. Later that year, a replacement bridge was built and the old stone structure was documented by the Historic American Engineering Record. It was removed from the NRHP on July 22, 2002.
History
Early inhabitants and name
Plunketts Creek is in the West Branch Susquehanna River drainage basin, the earliest recorded inhabitants of which were the Susquehannocks. Their numbers were greatly reduced by disease and warfare with the Five Nations of the Iroquois, and by 1675 they had died out, moved away, or been assimilated into other tribes. The West Branch Susquehanna River valley was subsequently under the nominal control of the Iroquois,[3] who invited displaced tribes, including the Lenape (Delaware) and Shawnee to live in the lands vacated by the Susquehannocks. The French and Indian War (1754–1763) led to the migration of many Native Americans westward to the Ohio River basin.[3] On November 5, 1768, the British acquired the New Purchase from the Iroquois in the Treaty of Fort Stanwix, including what is now Plunketts Creek.[4] The first settlement along the creek by European colonists took place between 1770 and 1776.[2]
Plunketts Creek is named for Colonel William Plunkett, a physician, who was the first president judge of Northumberland County after it was formed in 1772. During conflicts with Native Americans, he treated wounded settlers and fought the natives. Plunkett led a Pennsylvania expedition in the Pennamite-Yankee War to forcibly remove settlers from Connecticut, who had claimed and settled on lands in the Wyoming Valley also claimed by Pennsylvania. For his services, Plunkett was granted six tracts of land that totaled 1,978 acres (800 ha) on November 14, 1776, although the land was not actually surveyed until September 1783. Plunkett's land included the creek's mouth, so Plunketts Creek was given his name.[2][5] He died in 1791, aged about 100, and was buried in Northumberland without a grave marker or monument (except for the creek that bears his name).[2][5]
Lycoming County was formed from Northumberland County in 1795. When Plunketts Creek Township was formed in Lycoming County in 1838, the original name proposed was "Plunkett Township", but Plunkett's lack of active support for the American Revolution some years earlier had led some to believe his loyalty lay with the British Empire. The lingering suspicion of his loyalist sympathies led to the proposed name being rejected. Naming the township for the creek rather than its namesake was seen as an acceptable compromise.[2][5]
Villages and road
In 1832, John Barbour built a sawmill on Loyalsock Creek near the mouth of Plunketts Creek. This developed into the village of Barbours Mills, today known as Barbours. In the 19th century, Barbours had several blacksmiths, a temperance hotel, post office, many sawmills, a school, store and wagon maker. In 1840, a road was built north from Barbours along Plunketts Creek, crossing it several times. This is the earliest possible date for construction of the bridge, but the surviving county road docket on the construction mentions neither bridges nor fords for crossing the creek.[2]
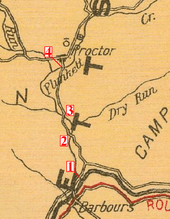
The bridge is at the mouth of Coal Mine Hollow,[1] and the road it was on was used by the lumber and coal industries that were active in Plunketts Creek Township during the 19th and early 20th centuries.[2] Creeks in the township supplied water power to 14 mills in 1861, and by 1876 there were 19 sawmills, a shingle mill, a woolen factory, and a tannery.[2][6] By the latter half of the 19th century, these industries supported the inhabitants of two villages in Plunketts Creek Township.
In 1868 the village of Proctorville was founded as a company town for Thomas E. Proctor's tannery, which was completed in 1873.[2][7] Proctor, as it is now known, is 1.66 miles (2.67 km) north of Barbours along Plunketts Creek,[8] and the main road to it crossed the bridge. The bark from Eastern hemlock trees was used in the tanning process, and the village originally sat in the midst of vast forests of hemlock.[2] The tannery employed "several hundred" workers at wages between 50 cents and $1.75 a day. These employees lived in 120 company houses, which each cost $2 a month to rent.[5][7][9] In 1892, Proctor had a barber shop, two blacksmiths, cigar stand, Independent Order of Odd Fellows hall, leather shop, news stand, a post office (established in 1885), a two-room school, two stores, and a wagon shop.[5][7]
The road between Barbours and Proctor crosses Plunketts Creek four times and the four bridges are numbered in order, starting from the southernmost in Barbours near the mouth and going upstream. While evidence such as maps indicates that the third bridge was constructed close to 1840, the first definitive proof of its existence is a survey to relocate the road between the second and third bridges in 1875. The first bridge over Plunketts Creek was replaced with a covered bridge in 1880, and the second bridge was replaced in 1886. That same year, the road between the second and third bridges was moved again, returning to its original position on the west side of the creek.[2]
Finished sole leather was hauled over the bridge by horse-drawn wagon south about 8 miles (13 km) to Little Bear Creek, where it was exchanged for "green" hides and other supplies brought north from Montoursville.[7] These were then hauled north across the bridge into Proctor. The hides, which were tanned to make leather, came from the United States, and as far away as Mexico, Argentina, and China. Hemlock bark, used in the tanning process, was hauled to the tannery from up to 8 miles (13 km) away in both summer and winter, using wagons and sleds.[10] The lumber boom on Plunketts Creek ended when the virgin timber ran out. By 1898, the old growth hemlock was exhausted and the Proctor tannery, then owned by the Elk Tanning Company, was closed and dismantled.[9]
20th century

Small-scale lumbering continued in the watershed in the 20th century, but the last logs were floated under the bridge down Plunketts Creek to Loyalsock Creek in 1905.[7] In 1918, a flood on the creek damaged the road for 100 feet (30 m) on both sides of the bridge, and caused "settling and cracking of the bridge itself".[2] The bridge had needed repairs and reconstruction. In 1931, the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania passed legislation that gave the state responsibility for the costs of road and bridge maintenance for many highways belonging to local municipalities. This took effect in 1932, relieving Plunketts Creek Township and Lycoming County of the responsibility.[2]
Without timber and the tannery, the populations of Proctor and Barbours declined, as did traffic on the road and bridges between them. The Barbours post office closed in the 1930s and the Proctor post office closed on July 1, 1953. Both villages also lost their schools and almost all of their businesses.[9][11] Proctor celebrated its centennial in 1968, and a 1970 newspaper article on its 39th annual "Proctor Homecoming" reunion called it a "near-deserted old tannery town".[9][10] In the 1980s, the last store in Barbours closed, and the former hotel (which had become a hunting club) was torn down to make way for a new bridge across Loyalsock Creek.[6]
Plunketts Creek has been a place for lumber and tourism since its villages were founded, and as industry declined, nature recovered.[6] Second growth forests have since covered most of the clear-cut land. Pennsylvania's state legislature authorized the acquisition of abandoned and clear-cut land for Pennsylvania State Game Lands in 1919, and the Pennsylvania Game Commission (PGC) acquired property along Plunketts Creek for State Game Lands Number 134 between 1937 and 1945.[2][12] The main entrance to State Game Lands 134 is just north of the bridge site, on the east side of the creek.[2][13]
The PGC established the Northcentral State Game Farm in 1945 on part of State Game Lands 134 to raise wild turkey. The farm was converted to ringneck pheasant production in 1981, and, as of 2007, it was one of four Pennsylvania state game farms that produced about 200,000 pheasants each year for release on land open to public hunting.[14] The Northcentral State Game Farm is chiefly in the Plunketts Creek valley, just south of Proctor and north of the bridge.[2][13] The opening weekend of the trout season brings more people into the village of Barbours at the mouth of Plunketts Creek than any other time of the year.[6]
On June 22, 1988, the bridge was added to the National Register of Historic Places (NRHP), as part of the Multiple Property Submission (MPS) of Highway Bridges Owned by the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, Department of Transportation, TR. The MPS included 135 bridges owned by the Pennsylvania Department of Transportation (PennDOT), 58 of which were of the stone arch type. While the individual NRHP form for the bridge cites a 1932 inspection report (the year that the state took over its maintenance),[15] the MPS form mistakenly gives the bridge's date of construction as 1932.[16][17]
Flood and destruction

In January 1996, there was major flooding throughout Pennsylvania. The 1995–1996 early winter was unusually cold, and considerable ice buildup formed in local streams. A major blizzard on January 6–8 produced up to 40 inches (100 cm) of snow, which was followed on January 19–21 by more than 3 inches (76 mm) of rain with temperatures as high as 62 °F (17 °C) and winds up to 38 miles per hour (61 km/h). The rain and snowmelt caused flooding throughout Pennsylvania and ice jams made this worse on many streams. Elsewhere in Lycoming County, flooding on Lycoming Creek in and near Williamsport killed six people and caused millions of dollars in damage.[18]
On Plunketts Creek, ice jams led to record flooding, which caused irreparable major damage to the mid-19th century stone arch bridge.[2] Downstream in Barbours, the waters were 4 feet (1.2 m) deep in what was then called the village's "worst flood in history".[6][Note a] Plunketts Creek Bridge No. 3 was one of two destroyed in Lycoming County, and on January 31 a photograph of the damaged bridge was featured on the front page of the Williamsport Sun-Gazette with the caption "This old stone arch bridge over Plunketts Creek must be replaced."[19] In neighboring Sullivan County, the Sonestown Covered Bridge, also on the NRHP, was so damaged by the flood that it remained closed for repairs until late December 1996.[20] Throughout Pennsylvania, these floods led to 20 deaths and 69 municipal- or state-owned bridges being either "destroyed or closed until inspections could verify their safety".[18]
When it became clear that the bridge could not be repaired, PennDOT awarded an emergency contract for a temporary bridge before the end of January, citing "emergency vehicles that can no longer travel directly from Barbours" to Proctor and beyond.[19] The temporary bridge cost $87,000 and was 24 feet (7.3 m) wide.[19] The photographs for the bridge's inclusion in the Historic American Engineering Record (HAER) were taken in January, and the HAER "documentation package was prepared as mitigation for the emergency demolition" of the bridge, which was collapsed in March.[2] The permanent replacement bridge was completed in 1996,[15] and the old bridge was removed from the NRHP on July 22, 2002.[21]
Description and construction

Plunketts Creek Bridge No. 3 was a rubble masonry stone arch bridge, oriented roughly east–west over Plunketts Creek. Its overall length was 75 feet (23 m) and its single semi-circular arch spanned 44 feet (13 m).[15] The bridge deck width was 18 feet 8 inches (5.69 m), and its roadway was 15 feet 3 inches (4.65 m) wide, which could accommodate only a single lane of traffic.[2] Just before the flood that led to the bridge's destruction, about 450 vehicles crossed the bridge daily.[19] The outside corners of the wing walls were 25 feet (7.6 m) apart, which combined with the overall length of 75 feet (23 m) led to a total area of 1,875 square feet (174.2 m2) being listed on the NRHP.[15]
The bridge rested on abutments which had been jacketed with concrete after its original construction. The arch was supported by voussoirs made of "irregular rubble stone", without a keystone.[2] There was also no stone giving the date or other construction information. The approaches were flanked by wing walls constructed of riprap stones, and the spandrel walls were topped by parapets made of "rough, crenellated stones".[2] The bridge's road deck rested directly on the top of its arch. This led to a "narrow wall at the arch crown" and a "protruding rock parapet" atop this spandrel wall on either side.[15] Most stone arch bridges have solid parapets without decoration; this bridge's parapet crenellation was an ornamental feature.[2] The parapet construction and appearance made the bridge unique among the 58 Pennsylvania stone arch bridges with which it was nominated for the NRHP.[15]
Pennsylvania has a long history of stone arch bridges, including the oldest such bridge in use in the United States, the 1697 Frankford Avenue Bridge over Pennypack Creek in Philadelphia.[2] Such bridges typically used local stone, with three types of finishing possible. Rubble or third-class masonry construction used stones just as they came from the quarry; squared-stone or second-class masonry used stones that had been roughly dressed and squared; and ashlar or first-class masonry used stones which had been finely dressed and carefully squared. Rubble masonry was the quickest and cheapest for construction, and had the largest tolerances. Many of the oldest stone bridges in Pennsylvania were built using rubble masonry techniques.[2]
Stone bridge construction started with the excavation of foundations for the abutments. Then a temporary structure known as a center or centering would be built of wood or iron. This structure supported the stone arch during construction. Once the stone arch was built, the spandrel walls and wing walls could be added. Then the road bed was built, with fill (loose stones or dirt) added to support it as needed. Wall and arch stones were generally set in place dry to ensure a good fit, then set in mortar. Once the bridge was complete and the mortar had properly hardened, the center was gradually lowered and then removed. In March 1996, after standing for between 156 and 121 years, the arch of Bridge No. 3 finally collapsed.[2]
Note
- a. ^ The January 1996 flood which destroyed Plunketts Creek Bridge No. 3 was surpassed by flooding associated with remnants of Tropical Storm Lee in September 2011. In the nearby village of Shunk in Fox Township, Sullivan County, Lee dumped 11.36 inches (289 mm) of rainfall.[22] Plunketts Creek has no stream gauge, but just downstream of its mouth the gauge on the Loyalsock Creek bridge at Barbours was a record 34.0 feet (10.4 m) on September 7, 2011 (for comparison, the January 20–21, 1996 flood crest was 24.9 feet (7.6 m)).[23] The 2011 flooding destroyed a small stone bridge on Wallis Run Road in Proctor over a tributary of Plunketts Creek.[24]
See also
- List of bridges documented by the Historic American Engineering Record in Pennsylvania
- List of bridges on the National Register of Historic Places in Pennsylvania
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 United States Geological Survey. "USGS Barbours (PA) Topo Map". MSR Maps and the National Map. Retrieved June 5, 2013.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 2.8 2.9 2.10 2.11 2.12 2.13 2.14 2.15 2.16 2.17 2.18 2.19 2.20 2.21 2.22 2.23 2.24 2.25 2.26 2.27 Scherkoske, Deborah A. (August 1996). "Plunkett's Creek Bridge No. 3, Spanning Plunkett's Creek at State Route 1005, Barbours vicinity, Lycoming County, PA" (PDF). Historic American Engineering Record and Library of Congress. Retrieved March 13, 2013. Metadata including black and white photographs and descriptive captions is here.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Wallace, Paul A. W. (2000) [1961]. Indians in Pennsylvania. Harrisburg, Pennsylvania: Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, The Pennsylvania Historical and Museum Commission. pp. 4–12, 84–89, 99–105, 145–148, 157–164. ISBN 978-0-89271-017-1.
Note: For a general overview of Native American History in the West Branch Susquehanna watershed, see Meginness, John Franklin (1892). "Chapter I. Aboriginal Occupation.". History of Lycoming County, Pennsylvania: including its aboriginal history; the colonial and revolutionary periods; early settlement and subsequent growth; organization and civil administration; the legal and medical professions; internal improvement; past and present history of Williamsport; manufacturing and lumber interests; religious, educational, and social development; geology and agriculture; military record; sketches of boroughs, townships, and villages; portraits and biographies of pioneers and representative citizens, etc. etc. (1st ed.). Chicago, IL: Brown, Runk & Co. ISBN 0-7884-0428-8. Retrieved on September 30, 2008. Note: ISBN refers to the Heritage Books July 1996 reprint. URL is to a scan of the 1892 version with some OCR typos. - ↑ Donehoo, Dr. George P. (1999) [1928]. A History of the Indian Villages and Place Names in Pennsylvania (PDF) (Second Reprint ed.). Lewisburg, Pennsylvania: Wennawoods Publishing. pp. 154–155, 215–219. ISBN 1-889037-11-7. Retrieved on September 30, 2008. Note: ISBN refers to a 1999 reprint edition, URL is for the Susquehanna River Basin Commission's web page of Native American Place names, quoting and citing the book.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 Meginness, John Franklin (1892). "Chapter XLII. Plunkett's Creek, Lewis, Cascade, and Gamble.". History of Lycoming County, Pennsylvania: including its aboriginal history; the colonial and revolutionary periods; early settlement and subsequent growth; organization and civil administration; the legal and medical professions; internal improvement; past and present history of Williamsport; manufacturing and lumber interests; religious, educational, and social development; geology and agriculture; military record; sketches of boroughs, townships, and villages; portraits and biographies of pioneers and representative citizens, etc. etc. (1st ed.). Chicago, IL: Brown, Runk & Co. ISBN 0-7884-0428-8. Retrieved June 5, 2013. Note: ISBN refers to the Heritage Books July 1996 reprint. URL is to a scan of the 1892 version with some OCR typos.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 Barr, James P (January 12, 1997). "Sock Country casts Spell on Residents of Tiny Barbours". Williamsport Sun-Gazette. pp. B9–10.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 (No author) (October 1966). "Proctorville – Historic Village". Now and then (The Journal of the Muncy, Pennsylvania Historical Society) XV (5): p. 277. Note: the article has a note that it was written in 1959, but the author's name was lost prior to publication in 1966.
- ↑ Pennsylvania Department of Environmental Protection; Bureau of Watershed Management, Division of Water Use Planning (2001). Pennsylvania Gazetteer of Streams (PDF). Prepared in Cooperation with the United States Department of the Interior Geological Survey. Retrieved June 2, 2013.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 (No author) (August 18, 1968). "History Recalled as Proctor Plans to Celebrate Centennial". Williamsport Sun-Gazette. p. 11.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 (No author) (August 9, 1970). "Near-Deserted Old Tannery Town Schedules 39th Annual Homecoming". Grit (Williamsport Edition). p. 20.
- ↑ Pollom, Leon J (August 18, 1994). "Community Profile: Is there a Better Place in God's Country than the Village of Barbours?". Williamsport Sun-Gazette. p. 11.
- ↑ Pennsylvania Game Commission (January 24, 2007). "2007 Press Release: Release #012-07: Board Approves Acquisition of Nearly 160 Acres" (PDF). Retrieved June 5, 2013.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 State Game Lands 134, Lycoming and Sullivan Counties (PDF) (Map). Pennsylvania Game Commission. July 1993. Archived from the original (PDF) on April 3, 2006. Retrieved June 5, 2013.
- ↑ "Pheasant Program – A guide to pheasant releases and more". Pennsylvania Game Commission. Archived from the original on June 3, 2008. Retrieved June 5, 2013.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 15.2 15.3 15.4 15.5 "Bridge in Plunketts Creek Township". National Park Service (June 22, 1988). Note: this file contains not only the NRHP Nomination Form, but also the May 31, 2002 letter from the Pennsylvania Historical and Museum Commission requesting removal of the bridge from the NRHP.
- ↑ "NPS Focus". National Register of Historic Places. National Park Service. Retrieved June 5, 2013.
- ↑ "Highway Bridges Owned by the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, Department of Transportation TR (Thematic Resources)" (PDF). National Park Service. June 22, 1988. Retrieved June 5, 2013.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 Thompson, R.E., Jr. (April 10, 1996). "Statewide Floods in Pennsylvania, January 1996". United States Geological Survey. Retrieved June 5, 2013.
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 19.2 19.3 Pollom, Leon J. (January 31, 1996). "Road, Bridge Costs Climb". Williamsport Sun-Gazette. pp. A1, A6.
- ↑ Moore, Catherine (December 12, 1996). "Covered Bridge to Reopen". Williamsport Sun-Gazette. p. A3.
- ↑ "National Register of Historic Places Listings August 2, 2002". National Park Service. August 2, 2002. Retrieved June 5, 2013.
- ↑ Brown, Daniel P. (December 15, 2011). "Tropical Cyclone Report: Tropical Storm Lee" (PDF). National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 7, 2013.
- ↑ "County Stream Gauge Details; Watershed: Loyalsock Creek; Gauge Site: Barbours (Stream Gauge 5143)". Lycoming County, Pennsylvania. Retrieved June 7, 2013.
- ↑ "Wallis Run Road bridge reopens in Proctor". Williamsport Sun-Gazette. September 13, 2011. Retrieved June 7, 2013.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||