Plastoquinone
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| 4299-57-4 | |
| Jmol-3D images | Image |
| PubChem | 6433402 |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula |
C53H80O2 |
| Molar mass | 749.20 g·mol−1 |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds |
1,4-benzoquinone quinone Coenzyme Q10 |
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Plastoquinone (PQ) is a quinone molecule involved in the electron transport chain in the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. Plastoquinone is reduced (accepts two protons (H+) from the stromal matrix of the chloroplast, coupled to two electrons (e−) from photosystem II), forming plastoquinol. It transports the protons to the lumen of thylakoid discs, while the electrons continue through the electron transport chain into the cytochrome b6f protein complex.
The prefix plasto- means either plastid or chloroplast, alluding to its location within the cell.[1]
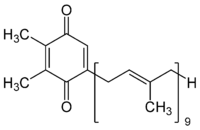
Structurally it is a 2,3-dimethyl-1,4-benzoquinone molecule with a side chain of nine isoprenyl units.
Derivatives
Some derivatives designed to penetrate cell membranes (SkQ1 (plastoquinonyl-decyl-triphenylphosphonium), SkQR1 (the rhodamine-containing analog of SkQ1), SkQ3) have anti-oxidant and protonophore activity.[2]
SkQ1 is proposed as an anti-aging treatment.[3][4]
SkQ1 is starting clinical trials for glaucoma in Russia.
See also
- Coenzyme Q10 has similar chemical structure.
References
- Berg, J; Tymoczko, J; Stryer, L (2002). Biochemistry (Fifth Edition). W H Freeman and Company. ISBN 0-7167-4684-0.
- ↑ http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/Plastoquinone Definition of plastoquinone
- ↑ F.F. Severina; I.I. Severina, Y.N. Antonenkoa, T.I. Rokitskayaa, D.A. Cherepanovb, E.N. Mokhovaa, M.Yu. Vyssokikha, A.V. Pustovidkoa, O.V. Markovaa, L.S. Yaguzhinskya, G.A. Korshunovaa, N.V. Sumbatyana, M.V. Skulacheva, V.P. Skulacheva (2009). "Penetrating cation/fatty acid anion pair as a mitochondria-targeted protonophore.". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 107 (2): 663–8. doi:10.1073/pnas.0910216107. PMC 2818959. PMID 20080732.
- ↑ "An attempt to prevent senescence: A mitochondrial approach.". 2008.
- ↑ http://protein.bio.msu.ru/biokhimiya/contents/v73/pdf/bcm_1329.pdf Mitochondria-Targeted Plastoquinone Derivatives as Tools to Interrupt Execution of the Aging Program. 5. SkQ1 Prolongs Lifespan and Prevents Development of Traits of Senescence. Anisimov etal. 2008
External links
- Plastoquinones History, absorption spectra, and analogs.