Planes minutus
| Planes minutus | |
|---|---|
 | |
| An individual on Réunion Island | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Subphylum: | Crustacea |
| Class: | Malacostraca |
| Order: | Decapoda |
| Infraorder: | Brachyura |
| Family: | Grapsidae |
| Genus: | Planes |
| Species: | P. minutus |
| Binomial name | |
| Planes minutus (Linnaeus, 1758) | |
| Synonyms [1] | |
| |
Planes minutus is a species of pelagic crab that lives in the North Atlantic Ocean. It is typically less than 10 mm (0.4 in) long across the back, and is variable in colouration, to match its background. It may have been the crab seen by Christopher Columbus on Sargassum weed in the Sargasso Sea in 1492.
Description
Planes minutus is a small crab, reaching a maximum carapace length of 17.5 millimetres (0.7 in), and typically less than 10 mm (0.4 in). It has conspicuous eyes in wide orbits at the corners of the wide front edge of the carapace.[2] The first pair of pereiopods (walking legs) bear a symmetrical pair of chelae with cutting teeth;[3] the other four pairs are adorned with spines on the last two segments of each leg.[2] It differs from the larger P. major in that males have a broadly triangular abdomen, rather than one which narrows abruptly after the third segment, and from P. marinus in having flattened legs with a fringe of setae that aid in swimming.[4]
The colouration of Planes minutus is very variable, and camouflages the crab against the Sargassum weed it often lives on. The base colour is typically brown, sometimes tending towards yellow or red. This is often supplemented with large patches of white, apparently imitating the calcareous tubes attached by annelid worms to Sargassum.[5] Although the colour pattern tends to match that of the substrate on which the crab is found, the colouration is only able to change slowly after a change of substrate.[5]
Distribution
Planes minutus is found in the North Atlantic Ocean, between the latitudes of 11° N and 32° N, and also from the west coast of Africa.[6] Related species, such as Planes major (formerly P. cyaneus) and Planes marinus, occur in other parts of the world's oceans[6]
Ecology
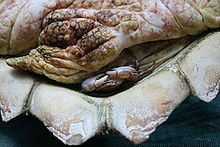
Planes minutus is exclusively pelagic, inhabiting a wide variety of substrates, including Sargassum weed, floating timbers and the hulls of ships.[2] It is often found in association with turtles, especially the loggerhead sea turtle, Caretta caretta. It had been thought that the crab fed on the turtle's faeces, but it is now thought to fill a cleaning role.[7][8]
Although proficient at swimming, Planes minutus has little endurance, being capable of swimming for less than 45 minutes at 28 °C (82 °F) before sinking.[3] It uses all its legs while swimming, the first two pairs holding the crab up in the water, and the remaining legs propelling it forwards.[3] The legs may begin to beat before the crab releases itself from its resting place, allowing it to accelerate more quickly. Attacks on passing animals only normally occur within 5 cm (2 in) of the crab's substrate.[3] The diet of P. minutus is very varied, including small fish, krill, isopods, sea skaters and squid, and food items may be stored for later consumption.[3]
Taxonomic history
| External identifiers for Planes minutus | |
|---|---|
| Encyclopedia of Life | 343924 |
| ITIS | 99055 |
| NCBI | 106762 |
| WoRMS | 107462 |
The first record of Planes minutus may have been made by Christopher Columbus during his first voyage to the New World. On September 17, 1492, in the Sargasso Sea near 28°N 37°W / 28°N 37°W, he recorded "much more weed appearing, like herbs from rivers, in which they found a live crab, which the Admiral kept. He says that these crabs are certain signs of land". It is thought that this is likely to refer to Planes, rather than the larger Portunus sayi, which rarely occurs so far east.[4] As a result, crabs of the genus Planes are sometimes known as "Columbus crabs".[4]
Sporadic records followed from different oceans, but the first name to be accepted under the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature is the name "Cancer minutus", published by Carl Linnaeus in his 1758 10th edition of Systema Naturae.[4] In 1825, Thomas Edward Bowdich described the species under the name "Planes clypeatus"; Bowdich's genus is now used for all the Columbus crabs, but Linnaeus' species name has priority, and so the species is now known as Planes minutus.[4]
Notes
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Charles Fransen & Michael Türkay (2012). "Planes minutus". World Register of Marine Species. Retrieved June 10, 2012.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Mario de Kluijver & Sarita Ingalsuo. "Planes minutus". Macrobenthos of the North Sea – Crustacea. Retrieved June 10, 2012.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 John Davenport (1992). "Observations on the ecology, behaviour, swimming mechanism and energetics of the neustonic grapsid crab, Planes minutus". Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom 72 (3): 611–620. doi:10.1017/S0025315400059385.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 Fenner A. Chace, Jr. (1951). "The oceanic crabs of the genera Planes and Pachygrapsus". Proceedings of the United States National Museum 101 (3272): 65–103. doi:10.5479/si.00963801.101-3272.65.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Harold B. Hitchcock (1941). "The coloration and color changes of the Gulf-weed crab, Planes minutus" (PDF). The Biological Bulletin 80 (1): 26–30. JSTOR 1537704.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 M. Pons, A. Verdi & A. Domingo (2011). "The pelagic crab Planes cyaneus (Dana, 1851) (Decapoda, Brachyura, Grapsidae) in the southwestern Atlantic Ocean in association with loggerhead sea turtles and buoys". Crustaceana 84 (4): 425–434. doi:10.1163/001121611X557064.
- ↑ John Davenport (1994). "A cleaning association between the oceanic crab Planes minutus and the loggerhead sea turtle Caretta caretta". Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom 74 (3): 735–737. doi:10.1017/S0025315400047780.
- ↑ Michael G. Frick, Kristina L. Williams, Alan B. Bolten, Karen A. Bjorndal & Helen R. Martins (2004). "Diet and fecundity of Columbus crabs, Planes minutus, associated with oceanic-stage loggerhead sea turtles, Caretta caretta, and inanimate flotsam" (PDF). Journal of Crustacean Biology 24 (2): 350–355. doi:10.1651/c-2440. JSTOR 1549917.