Physical address
In computing, a physical address (also real address, or binary address), is a memory address that is represented in the form of a binary number on the address bus circuitry in order to enable the data bus to access a particular storage cell of main memory, or a register of memory mapped I/O device.
Use by central processing unit
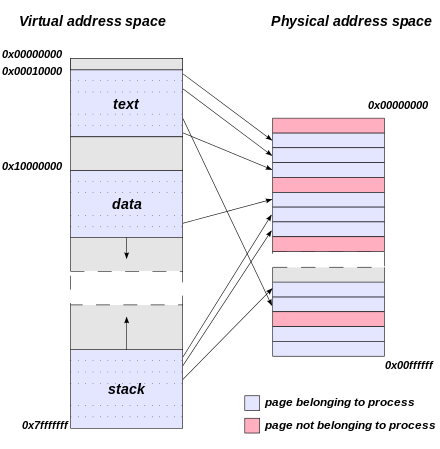
In a computer supporting virtual memory, the term physical address is used mostly to differentiate from a virtual address. In particular, in computers utilizing a memory management unit (MMU) to translate memory addresses, the virtual and physical addresses refer to an address before and after translation performed by the MMU, respectively.[1]09/cse120/lectures/Lecture7.pdf
| title = Lecture 7: Memory Management | work = CSE 120: Principles of Operating Systems | year = 2009 | accessdate = 2013-12-04 | author = Frank Uyeda | publisher = UC San Diego | format = PDF
}}</ref>
Unaligned addressing
Depending upon its underlying computer architecture, the performance of a computer may be hindered by unaligned access to memory. As an example, a 16 bit computer with a 16 bit memory data bus such as an Intel 8086 generally has less overhead if the access is aligned to an even address. In that case fetching one 16 bit value requires a single memory read operation, a single transfer over a data bus.[2][3]
Obviously, if the 16 bit data value starts at an odd address, the processor may actually need to perform two memory read cycles to load the value into it, i.e. one for the low address (throwing half of it away) and then a second to load the high address (again throwing half of the retrieved data away). In fact, on some architectures (such as the Motorola 68000 family), unaligned memory accesses will result in an exception being raised (usually resulting in a software exception being raised like POSIX's SIGBUS).[2]
Use by other devices
The direct memory access (DMA) feature allows other devices in the mother board but CPU to address the main memory. Such devices, therefore, also need to have a knowledge of physical addresses.
See also
- Address constant
- Addressing mode
- Address space
- Page address register
- Pointer (computer science)
- Primary storage, also known as main memory
- Virtual memory
- Virtual address, also known as logical address
- Page table
- Memory management unit (MMU)
References
- ↑ a | publisher = UC San Diego w format = PDF }}
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Daniel Drake (2007-12-04). "Memory access and alignment". LWN.net. Retrieved 2013-12-04.
- ↑ Daniel Drake; Johannes Berg. "Documentation/unaligned-memory-access.txt". kernel.org. Retrieved 2013-12-04.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||