Phyllodulcin
Phyllodulcin
 |
| Names |
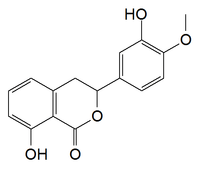
| IUPAC name
(3R)-8-hydroxy-3-(3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-3,4-dihydroisochromen-1-one |
| Other names
Praeruptorin |
| Identifiers |
| |
21499-23-0  Y Y |
| Jmol-3D images |
Image |
| PubChem |
146694 |
COC1=C(C=C(C=C1)C2CC3=C(C(=CC=C3)O)C(=O)O2)O
|
| Properties |
| |
C16H14O5 |
| Molar mass |
286.27 g/mol |
Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) |
 Y verify (what is: Y verify (what is:  Y/ Y/ N?) N?) |
| Infobox references |
|
|
Phyllodulcin is an dihydroisocoumarin found in Hydrangea macrophylla[1] and Hydrangea serrata.[2] It is a sweetener 400-800 sweeter than sugar.[3]
See also
References
- ↑ Effects of phyllodulcin, hydrangenol, and their 8-O-glucosides, and Thunberginols A and F from Hydrangea macrophylla SERINGE var. thunbergii MAKINO on passive cutaneous anaphylaxis reaction in rats. Matsuda H., Shimoda H., Yamahara J. and Yoshikawa M., Biological & pharmaceutical bulletin, 1999, vol. 22, no8, pp. 870-872,
INIST:1959604
- ↑ Accumulation of phyllodulcin in sweet-leaf plants of Hydrangea serrata and its neutrality in the defence against a specialist leafmining herbivore. Mami Ujihara, Masateru Shinozaki and Makoto Kato, Researches on population ecology, Volume 37, Number 2, pp. 249-257, doi:10.1007/BF02515827
- ↑ Chemical and Functional Properties of Food Saccharides. P. Tomasik, CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2003 , isbn : 978-0-8493-1486-5
Food substitutes |
|---|
| | Artificial fat substitutes | |
|---|
| | Artificial protein substitutes |
- Acid-hydrolyzed vegetable protein
|
|---|
| | Artificial sugar substitutes | |
|---|
| | Natural food substitutes | |
|---|
| | Related topics | |
|---|
|
