Phosphorus sesquisulfide
| |||
 | |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC names
tetraphosphorus trisulfide or 3,5,7-trithia-1,2,4,6-tetraphosphatricyclo[2.2.1.02,6]heptane | |||
| Other names
phosphorus trisulfide, phosphorus sesquisulfide, phosphorus sulfide | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| 1314-85-8 | |||
| ChemSpider | 14134 | ||
| |||
| Jmol-3D images | Image | ||
| PubChem | 14818 | ||
| RTECS number | TH4330000 | ||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| P4S3 | |||
| Molar mass | 220.093 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | yellow, yellow-green or gray solid | ||
| Density | 2.08 g.cm3,[1] solid | ||
| Melting point | 172.5 °C (342.5 °F; 445.6 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 408 °C (766 °F; 681 K) | ||
| Structure | |||
| Crystal structure | orthorhombic, Schönflies notation D2h | ||
| Space group | Pmnb | ||
| Point group | C3v | ||
| Related compounds | |||
| Related compounds |
P4S10 P4O6 | ||
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |||
| | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Phosphorus sesquisulfide is the inorganic compound with the formula P4S3. It was developed by Henri Sevene and Emile David Cahen in 1898 as part of their invention of friction matches that did not pose the health hazards of white phosphorus.[2] This yellow solid is one of two commercially produced phosphorus sulfides. It is a component of "strike anywhere" matches.
Depending on purity, samples can appear yellow-green to grey. The compound was discovered by G. Lemoine and first produced safely in commercial quantities in 1898 by Albright and Wilson. It dissolves in an equal weight of carbon disulfide (CS2). Unlike some other phosphorus sulfides, P4S3 is slow to hydrolyze and has a well-defined melting point.
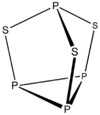
Structure and synthesis
The molecule has C3v symmetry. It is a derivative of the tetrahedral (P4) unit from insertion of sulfur into three P-P bonds. The P-S and P-P distances are 2.090 and 2.235 Å, respectively. P4Se3 and P4S3 adopt the same structures.[1] These compounds can be melted together and form mixed crystals of one dissolved in the other.[3] Under higher temperatures, mixed chalcogenide molecules P4S2Se and P4SSe2 will form.[4]
P4S3 is produced by the reaction of red or white phosphorus with sulfur. Excess sulfur gives phosphorus pentasulfide (P4S10). It is estimated that 150 ton/y were produced in 1989.[5]
Applications
P4S3 and potassium chlorate, together with other materials, comprises the heads of "strike-anywhere matches".[6]
Safety
Its flash point is about 100 °C.
Health Effects
Exposure to "strike anywhere" matches containing phosphorus sesquisulfide can cause contact dermatitis, usually in the pocket area but also on the face.[7] Exposure over a long period of time to burning match tips (containing phosphorus sesquisulfide) can result in a recurring severe primary dermatitis about the eyes and face. Loosening of the teeth has also been reported which may have been due to phosphorus poisoning.[8]
References
This article contains public domain text from the NOAA as cited.
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Leung, Y. C.; Waser, J.; van Houten, S.; Vos, A.; Wiegers, G. A.; Wiebenga, E. H. (1957). "The Crystal Structure of P4S3". Acta Crystallographica 10 (9): 574–582. doi:10.1107/S0365110X57002042.
- ↑ US patent 614350, Seyene, H.; Cahen, E. D., "Match Composition", issued 1898-11-15
- ↑ Burns, G.R., and Sarfati, J.D., "Raman spectra of tetraphosphorus triselenide doped in tetraphosphorus trisulphide", Solid State Communications 66(4):347–49, April 1988 | doi:10.1016/0038-1098(88)90854-X
- ↑ Burns, G.R., Rollo, J.R., and Sarfati, J.D.: "Raman spectra of the tetraphosphorus trichalcogenide cage molecules P4S2Se and P4SSe2", Inorganica Chimica Acta 161(1):35–38, 3 July 1989 | doi:10.1016/S0020-1693(00)90111-7
- ↑ Bettermann, G.; Krause, W.; Riess, G.; Hofmann, T. (2005), "Phosphorus Compounds, Inorganic", Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Weinheim: Wiley-VCH, doi:10.1002/14356007.a19_527
- ↑ Corbridge, D. E. C. (1995). Phosphorus: An Outline of its Chemistry, Biochemistry, and Technology (5th ed.). Amsterdam: Elsevier. pp. 115–116. ISBN 0-444-89307-5.
- ↑ BURGESS, J. F.; FORSEY, R. ROY (1951). "CONTACT DERMATITIS OF THE FACE DUE TO MATCHES.". AMA Arch Derm Syphilol. (American Medical Association) 64 (5): 636–637. doi:10.1001/archderm.1951.01570110106016. Retrieved 2013-12-06.
- ↑ BURGESS, J. Frederick (December 1951). "Phosphorus Sesquisulphide Poisoning". Can Med Assoc J. (Canadian Medical Association) 65 (6): 567–568. PMC 1822299. PMID 14886853. Retrieved 2013-12-06.
| ||||||