Phosphorene
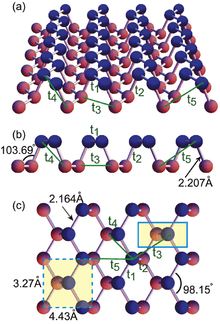
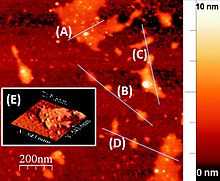
Phosphorene is an allotrope of phosphorus. It is normally used to designate a single layer of black phosphorus, although other allotropes have been predicted. Its two-dimensional structure makes it conceptually similar to the carbon-based graphene, hence the name phosphorene. However, phosphorene has substantially different electronic properties; in particular it possesses a nonzero fundamental band gap. This property makes phosphorene a semiconductor, different from graphene, which is a semimetal. As a semiconductor, it may be used to fabricate digital circuits. Phosphorene isolation was reported for the first time in 2014 by mechanical exfoliation. Liquid exfoliation of phosphorene, which is a potentially scalable process, was reported in the same year.[2]
See also
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Phosphorene. |
- ↑ Ezawa, M. (2014). "Topological origin of quasi-flat edge band in phosphorene". New Journal of Physics 16 (11): 115004. doi:10.1088/1367-2630/16/11/115004.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Brent, J. R.; Savjani, N.; Lewis, E. A.; Haigh, S. J.; Lewis, D. J.; O'Brien, P. (2014). "Production of few-layer phosphorene by liquid exfoliation of black phosphorus". Chem. Commun 50 (87): 13338. doi:10.1039/C4CC05752J.
Sources
- Castellanos-Gomez, Andres; Vicarelli, Leonardo; Prada, Elsa; Island, Joshua O; Narasimha-Acharya, K L; Blanter, Sofya I; Groenendijk, Dirk J; Buscema, Michele; Steele, Gary A; Alvarez, J V; Zandbergen, Henny W; Palacios, J J; van der Zant, Herre S J (2014). "Isolation and characterization of few-layer black phosphorus". 2D Materials 1: 025001. doi:10.1088/2053-1583/1/2/025001.
- Li, Pengke; Appelbaum, Ian (2014). "Electrons and holes in phosphorene". Phys. Rev. B 90 (11): 115439. arXiv:1408.0770. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.90.115439.
- Li, Likai; Yu, Yijun; Ye, Guo Jun; Ge, Qingqin; Ou, Xuedong; Wu, Hua; Feng, Donglai; Chen, Xian Hui; Zhang, Yuanbo (2014). "Black phosphorus field-effect transistors". Nature Nanotechnology 9 (5): 372–377. arXiv:1401.4117. doi:10.1038/nnano.2014.35.
- Xia, Fengnian; Wang, Han; Jia, Yichen (2014). "Rediscovering black phosphorus as an anisotropic layered material for optoelectronics and electronics". Nature Communications 5: 4458. arXiv:1402.0270. doi:10.1038/ncomms5458.
- Liu, Han; Neal, Adam T.; Zhu, Zhen; Luo, Zhe; Xu, Xianfan; Tománek, David; Ye, Peide D. (2014). "Phosphorene: An Unexplored 2D Semiconductor with a High Hole Mobility". ACS Nano (journal) 8 (4): 4033. arXiv:1401.4133. doi:10.1021/nn501226z.
- Qiao, Jingsi; Kong, Xianghua; Hu, Zhi-Xin; Yang, Feng; Ji, Wei (2014). "High-mobility transport anisotropy and linear dichroism in few-layer black phosphorus". Nature Communications 5: 4475. arXiv:1401.5045. doi:10.1038/ncomms5475.
- Rodin, A. S.; Carvalho, A.; Castro Neto, Antonio (2014). "Strain-Induced Gap Modification in Black Phosphorus". Physical Review Letters 112 (17): 176801. arXiv:1401.1801. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.112.176801.
- Low, Tony; Roldan, Rafael; et. al (2014). "Plasmons and Screening in Monolayer and Multilayer Black Phosphorus". Physical Review Letters 113: 106802. arXiv:1404.4035. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.113.106802.
- Low, Tony; Engel, Michael; et. al (2014). "Origin of photoresponse in black phosphorus phototransistors". Physical Review B Rapid 90: 081408. arXiv:1407.7286. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.90.081408.
- Low, Tony; Rodin, AS; Carvalho, A; Jiang, Y; Wang, H; Xia, F; Castro Neto, AH (2014). "Tunable optical properties of multilayer black phosphorus thin films". Physical Review B 90: 075434. arXiv:1404.4030. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.90.075434.
- Zhu, Zhen; Tomanek, David (2014). "Semiconducting layered blue phosphorus: A computational study". Physical Review Letters (journal) 112 (17): 176802. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.112.176802.
- Samuel Reich, Eugenie (2014). "Phosphorene excites materials scientists". Nature (journal) 506 (19): 19. doi:10.1038/506019a. Retrieved February 10, 2014.
- Island, Joshua O; Steele, Gary A; van der Zant, Herre S J; Castellanos-Gomez, Andres (2015). "Environmental instability of few-layer black phosphorus". 2D Materials 2: 011002. doi:10.1088/2053-1583/2/1/011002.