Phonological opacity
| Linguistics |
|---|
| Theoretical |
| Descriptive |
| Applied and experimental |
| Related articles |
| Linguistics portal |
Phonological opacity is a term used in phonology. It was first defined by Kiparsky[1] as a measure of how far the context or the consequences of a phonological process may be determined only by examining the surface structure. Kiparsky defined it in the following way:
A phonological rule P, 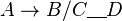 , is opaque if any of the following surface structures exists:
, is opaque if any of the following surface structures exists:
- instance of A in the
 environment;
environment; - instance of B created by P in an environment other than
 ;
; - instance of B not derived from P that occur in the context
 .
.
Counter-feeding and counter-bleeding opacity
Phonological opacity is often the result of the counterfeeding or counterbleeding order of two or more phonological rules, which is called "counter-feeding opacity" or "counter-bleeding opacity". An example of both can be seen in the future-marking suffix -en in the Yokutsan languages. Its vowel is supposed to be an underlying high vowel, though it surfaces as a mid vowel. Vowel rounding always applies before vowel lowering. Due to this order of phonological rules, the interaction of the suffix vowel with rounding harmony is opaque. There is still vowel harmony between the suffix vowel and a preceding high vowel as these vowels agree in roundedness, while a vowel with the feature [-high] would usually be exempt from rounding harmony. As a result of counter-bleeding opacity, the apparent motivation for the vowel harmony has disappeared here. Moreover, as a result of counter-feeding opacity, it cannot be told from the surface structure of the suffix vowel why it fails to harmonize in rounding with preceding mid vowels.[2]
References
- ↑ Kiparsky, Paul (1973). "Abstractness, opacity and global rules (Part 2 of 'Phonological representations')". In Fujimura, Osamu. Three Dimensions of Linguistic Theory. Tokyo Institute for Advanced Studies of Language. pp. 57–86.
- ↑ John A. Goldsmith, Jason Riggle, Alan C. L. Yu, The Handbook of Phonological Theory, 2Nd Edition, 2011