Phenylacetone
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1-Phenylpropan-2-one | |
| Other names
Benzyl methyl ketone; Methyl benzyl ketone; Phenyl-2-propanone | |
| Identifiers | |
| 103-79-7 | |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:52052 |
| ChemSpider | 21106366 |
| |
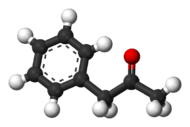
| Jmol-3D images | Image |
| KEGG | C15512 |
| PubChem | 7678 |
| |
| UNII | O7IZH10V9Y |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula |
C9H10O |
| Molar mass | 134.18 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless, pleasant odor |
| Density | 1.006 g/mL |
| Melting point | −15 °C (5 °F; 258 K) |
| Boiling point | 214 °C (417 °F; 487 K) |
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
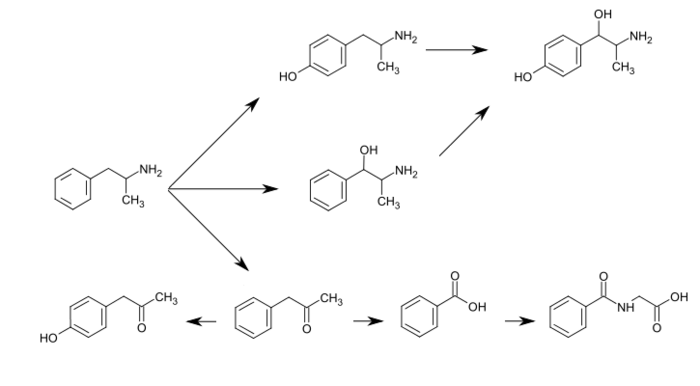
Phenylacetone is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5CH2C(O)CH3. It is a colorless oil that is soluble in organic solvents. This substance is used in the manufacture of methamphetamine and amphetamine, where it is commonly known as P2P. Due to the illicit uses in clandestine chemistry, it was declared a schedule II controlled substance in the United States in 1980.[1] In humans, phenylacetone occurs as a metabolite of amphetamine via oxidative deamination.
Preparation
It is prepared commercially by ketonization of phenylacetic acid and acetic acid over alumina at 400-500 °C. The aluminum oxide serves as a catalyst for the dehydration and decarboxylation:[2]
- C6H5CH2CO2H + CH3CO2H → C6H5CH2C(O)CH3 + CO2 + H2O
Due to its status as a controlled substance, other laboratory scale methods have been reported.[3] It can be produced by the condensation of benzaldehyde with nitroethane, which yields phenyl-2-nitropropene followed by reduction, usually in the presence of acid, to phenylacetone.
A conceptually simple example of phenylacetone organic synthesis is the Friedel-Crafts alkylation of benzene with chloroacetone.
This is, however, typically not used due to overalkylation commonly associated with Friedel-Crafts alkylation.
Applications
Phenyl acetone is used as an intermediate in the production of pesticides and anticoagulants.
Amphetamine metabolism
See also
- MDP2P - related compound with a methylenedioxy group, and a precursor to MDMA.
- Cyclohexylacetone - the cyclohexane derivative of phenylacetone
- Phenylacetones
References
- ↑ "Lists of: Scheduling Actions, Controlled Substances, Regulated Chemicals" (PDF). U.S. Department of Justice, Drug Enforcement Administration.
- ↑ Siegel, H.; Eggersdorfer, M. (2005), "Ketones", Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Weinheim: Wiley-VCH, doi:10.1002/14356007.a15_077
- ↑ Synthesis of Phenyl-2-Propanone (P2P)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||