Phenyl acetate
Not to be confused with phenylacetate, the conjugate base of phenylacetic acid.
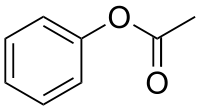 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Phenyl acetate | |
| Other names
Phenol acetate; (Acetyloxy)benzene; Acetoxybenzene | |
| Identifiers | |
| 122-79-2 | |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:8082 |
| ChemSpider | 28969 |
| |
| Jmol-3D images | Image |
| PubChem | 31229 |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula |
C8H8O2 |
| Molar mass | 136.15 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.075 g/mL[1] |
| Melting point | 50 °C (122 °F; 323 K) |
| Boiling point | 195–196 °C (383–385 °F; 468–469 K)[1] |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 76 °C (169 °F; 349 K)[1] |
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Phenyl acetate is the ester of phenol and acetic acid. One way that it can be produced by decarboxylation of aspirin. Another way that it can be produced is by reacting phenol with acetic anhydride.
Phenyl acetate can be separated into phenol and an acetate salt, via saponification: heating the phenyl acetate with a strong base, such as sodium hydroxide, will produce phenol and sodium acetate. The two chemicals can then be separated by heat and decantation or heat and filtration.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Phenyl acetate, Alfa Aesar