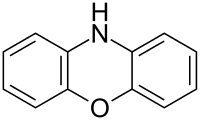
Phenoxazine
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
10H-Phenoxazine | |
| Identifiers | |
| 135-67-1 | |
| ChemSpider | 60610 |
| |
| Jmol-3D images | Image |
| PubChem | 67278 |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula |
C12H9NO |
| Molar mass | 183.21 g·mol−1 |
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Phenoxazine is a heterocyclic compound. The structure of phenoxazine consists of an oxazine fused to two benzene rings. It occurs as the central core of a number of naturally occurring chemical compounds such as the antibiotic actinomycins,[1] litmus, and orcein. The dyes Nile blue and Nile red are also phenoxazine derivatives.
Phenoxazine dyes were once widely used for silk dyeing, but due to their lack of lightfastness they have disappeared over time from the market. However, since their light resistance is significantly better on acrylic fibers, these dyes have experienced a renaissance.