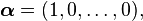Phase-type distribution
| Parameters |
 subgenerator matrix subgenerator matrix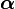 , probability row vector , probability row vector |
|---|---|
| Support |
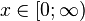 |
 See article for details | |
| CDF |
 |
| Mean |
 |
| Median | no simple closed form |
| Mode | no simple closed form |
| Variance |
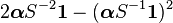 |
| MGF |
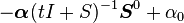 |
| CF |
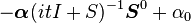 |
A phase-type distribution is a probability distribution constructed by a convolution of exponential distributions.[1] It results from a system of one or more inter-related Poisson processes occurring in sequence, or phases. The sequence in which each of the phases occur may itself be a stochastic process. The distribution can be represented by a random variable describing the time until absorption of a Markov process with one absorbing state. Each of the states of the Markov process represents one of the phases.
It has a discrete time equivalent the discrete phase-type distribution.
The set of phase-type distributions is dense in the field of all positive-valued distributions, that is, it can be used to approximate any positive-valued distribution.
Definition
Consider a continuous-time Markov process with m + 1 states, where m ≥ 1, such that the states 1,...,m are transient states and state 0 is an absorbing state. Further, let the process have an initial probability of starting in any of the m + 1 phases given by the probability vector (α0,α) where α0 is a scalar and α is a 1 × m vector.
The continuous phase-type distribution is the distribution of time from the above process's starting until absorption in the absorbing state.
This process can be written in the form of a transition rate matrix,
where S is an m × m matrix and S0 = –S1. Here 1 represents an m × 1 vector with every element being 1.
Characterization
The distribution of time X until the process reaches the absorbing state is said to be phase-type distributed and is denoted PH(α,S).
The distribution function of X is given by,
and the density function,
for all x > 0, where exp( · ) is the matrix exponential. It is usually assumed the probability of process starting in the absorbing state is zero (i.e. α0= 0). The moments of the distribution function are given by
Special cases
The following probability distributions are all considered special cases of a continuous phase-type distribution:
- Degenerate distribution, point mass at zero or the empty phase-type distribution - 0 phases.
- Exponential distribution - 1 phase.
- Erlang distribution - 2 or more identical phases in sequence.
- Deterministic distribution (or constant) - The limiting case of an Erlang distribution, as the number of phases become infinite, while the time in each state becomes zero.
- Coxian distribution - 2 or more (not necessarily identical) phases in sequence, with a probability of transitioning to the terminating/absorbing state after each phase.
- Hyper-exponential distribution (also called a mixture of exponential) - 2 or more non-identical phases, that each have a probability of occurring in a mutually exclusive, or parallel, manner. (Note: The exponential distribution is the degenerate situation when all the parallel phases are identical.)
- Hypoexponential distribution - 2 or more phases in sequence, can be non-identical or a mixture of identical and non-identical phases, generalises the Erlang.
As the phase-type distribution is dense in the field of all positive-valued distributions, we can represent any positive valued distribution. However, the phase-type is a light-tailed or platikurtic distribution. So the representation of heavy-tailed or leptokurtic distribution by phase type is an approximation, even if the precision of the approximation can be as good as we want.
Examples
In all the following examples it is assumed that there is no probability mass at zero, that is α0 = 0.
Exponential distribution
The simplest non-trivial example of a phase-type distribution is the exponential distribution of parameter λ. The parameter of the phase-type distribution are : S = -λ and α = 1.
Hyper-exponential or mixture of exponential distribution
The mixture of exponential or hyper-exponential distribution with λ1,λ2,...,λn>0 can be represented as a phase type distribution with
with 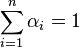 and
and
This mixture of densities of exponential distributed random variables can be characterized through
or its cumulative distribution function
with 
Erlang distribution
The Erlang distribution has two parameters, the shape an integer k > 0 and the rate λ > 0. This is sometimes denoted E(k,λ). The Erlang distribution can be written in the form of a phase-type distribution by making S a k×k matrix with diagonal elements -λ and super-diagonal elements λ, with the probability of starting in state 1 equal to 1. For example E(5,λ),
and
For a given number of phases, the Erlang distribution is the phase type distribution with smallest coefficient of variation.[2]
The hypoexponential distribution is a generalisation of the Erlang distribution by having different rates for each transition (the non-homogeneous case).
Mixture of Erlang distribution
The mixture of two Erlang distribution with parameter E(3,β1), E(3,β2) and (α1,α2) (such that α1 + α2 = 1 and for each i, αi ≥ 0) can be represented as a phase type distribution with
and
Coxian distribution
The Coxian distribution is a generalisation of the hypoexponential. Instead of only being able to enter the absorbing state from state k it can be reached from any phase. The phase-type representation is given by,
and
where 0 < p1,...,pk-1 ≤ 1. In the case where all pi = 1 we have the hypoexponential distribution. The Coxian distribution is extremely important as any acyclic phase-type distribution has an equivalent Coxian representation.
The generalised Coxian distribution relaxes the condition that requires starting in the first phase.
Generating samples from phase-type distributed random variables
BuTools includes methods for generating samples from phase-type distributed random variables.[3]
Approximating other distributions
Any distribution can be arbitrarily well approximated by a phase type distribution.[4][5] In practice, however, approximations can be poor when the size of the approximating process is fixed. Approximating a deterministic distribution of time 1 with 10 phases, each of average length 0.1 will have variance 0.1 (because the Erlang distribution has smallest variance[2]).
- BuTools a MATLAB and Mathematica script for fitting phase-type distributions to 3 specified moments
- momentmatching a MATLAB script to fit a minimal phase-type distribution to 3 specified moments[6]
Fitting a phase type distribution to data
Methods to fit a phase type distribution to data can be classified as maximum likelihood methods or moment matching methods.[7] Fitting a phase type distribution to heavy-tailed distributions has been shown to be practical in some situations.[8]
- PhFit a C script for fitting discrete and continuous phase type distributions to data[9]
- EMpht is a C script for fitting phase-type distributions to data or parametric distributions using an expectation–maximization algorithm.[10]
- HyperStar was developed around the core idea of making phase-type fitting simple and user-friendly, in order to advance the use of phase-type distributions in a wide range of areas. It provides a graphical user interface and yields good fitting results with only little user interaction.[11]
- jPhase is a Java library which can also compute metrics for queues using the fitted phase type distribution[12]
See also
- Discrete phase-type distribution
- Continuous-time Markov process
- Exponential distribution
- Hyper-exponential distribution
- Queueing theory
References
- ↑ Harchol-Balter, M. (2012). "Real-World Workloads: High Variability and Heavy Tails". Performance Modeling and Design of Computer Systems. p. 347. doi:10.1017/CBO9781139226424.026. ISBN 9781139226424.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Aldous, David; Shepp, Larry (1987). "The least variable phase type distribution is erlang". Stochastic Models 3 (3): 467. doi:10.1080/15326348708807067.
- ↑ Horváth, G. B.; Reinecke, P.; Telek, M. S.; Wolter, K. (2012). "Efficient Generation of PH-Distributed Random Variates". Analytical and Stochastic Modeling Techniques and Applications. Lecture Notes in Computer Science 7314. p. 271. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-30782-9_19. ISBN 978-3-642-30781-2.
- ↑ Bolch, Gunter; Greiner, Stefan; de Meer, Hermann; Trivedi, Kishor S. (1998). "Steady-State Solutions of Markov Chains". Queueing Networks and Markov Chains. pp. 103–151. doi:10.1002/0471200581.ch3. ISBN 0471193666.
- ↑ Cox, D. R. (2008). "A use of complex probabilities in the theory of stochastic processes". Mathematical Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society 51 (2): 313. doi:10.1017/S0305004100030231.
- ↑ Osogami, T.; Harchol-Balter, M. (2006). "Closed form solutions for mapping general distributions to quasi-minimal PH distributions". Performance Evaluation 63 (6): 524. doi:10.1016/j.peva.2005.06.002.
- ↑ Lang, Andreas; Arthur, Jeffrey L. (1996). "Parameter approximation for Phase-Type distributions". In Chakravarthy, S.; Alfa, Attahiru S. Matrix Analytic methods in Stochastic Models. CRC Press. ISBN 0824797663.
- ↑ Ramaswami, V.; Poole, D.; Ahn, S.; Byers, S.; Kaplan, A. (2005). "Ensuring Access to Emergency Services in the Presence of Long Internet Dial-Up Calls". Interfaces 35 (5): 411. doi:10.1287/inte.1050.0155.
- ↑ Horváth, András S.; Telek, Miklós S. (2002). "PhFit: A General Phase-Type Fitting Tool". Computer Performance Evaluation: Modelling Techniques and Tools. Lecture Notes in Computer Science 2324. p. 82. doi:10.1007/3-540-46029-2_5. ISBN 978-3-540-43539-6.
- ↑ Asmussen, Søren; Nerman, Olle; Olsson, Marita (1996). "Fitting Phase-Type Distributions via the EM Algorithm". Scandinavian Journal of Statistics 23 (4): 419–441. JSTOR 4616418.
- ↑ Reinecke, P.; Krauß, T.; Wolter, K. (2012). "Cluster-based fitting of phase-type distributions to empirical data". Computers & Mathematics with Applications 64 (12): 3840. doi:10.1016/j.camwa.2012.03.016.
- ↑ Pérez, J. F.; Riaño, G. N. (2006). "jPhase: an object-oriented tool for modeling phase-type distributions". Proceeding from the 2006 workshop on Tools for solving structured Markov chains (SMCtools '06). doi:10.1145/1190366.1190370. ISBN 1595935061.
- M. F. Neuts. Matrix-Geometric Solutions in Stochastic Models: an Algorithmic Approach, Chapter 2: Probability Distributions of Phase Type; Dover Publications Inc., 1981.
- G. Latouche, V. Ramaswami. Introduction to Matrix Analytic Methods in Stochastic Modelling, 1st edition. Chapter 2: PH Distributions; ASA SIAM, 1999.
- C. A. O'Cinneide (1990). Characterization of phase-type distributions. Communications in Statistics: Stochastic Models, 6(1), 1-57.
- C. A. O'Cinneide (1999). Phase-type distribution: open problems and a few properties, Communication in Statistic: Stochastic Models, 15(4), 731-757.
![{Q}=\left[\begin{matrix}0&\mathbf{0}\\\mathbf{S}^0&{S}\\\end{matrix}\right],](../I/m/9127e1f9c7a998b7f83973f121614a2f.png)
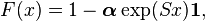

![E[X^{n}]=(-1)^{n}n!\boldsymbol{\alpha}{S}^{-n}\mathbf{1}.](../I/m/19e8713d20d3995d2fce8c5ea77c67f3.png)

![{S}=\left[\begin{matrix}-\lambda_1&0&0&0&0\\0&-\lambda_2&0&0&0\\0&0&-\lambda_3&0&0\\0&0&0&-\lambda_4&0\\0&0&0&0&-\lambda_5\\\end{matrix}\right].](../I/m/ccc5fcfa1fdef2a2c089ab6035f28f69.png)

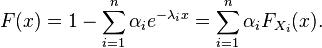
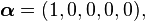
![{S}=\left[\begin{matrix}-\lambda&\lambda&0&0&0\\0&-\lambda&\lambda&0&0\\0&0&-\lambda&\lambda&0\\0&0&0&-\lambda&\lambda\\0&0&0&0&-\lambda\\\end{matrix}\right].](../I/m/1371fb1acbbfe4bffdfdcb0deeba1522.png)
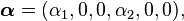
![{S}=\left[\begin{matrix}
-\beta_1&\beta_1&0&0&0&0\\
0&-\beta_1&\beta_1&0&0&0\\
0&0&-\beta_1&0&0&0\\
0&0&0&-\beta_2&\beta_2&0\\
0&0&0&0&-\beta_2&\beta_2\\
0&0&0&0&0&-\beta_2\\
\end{matrix}\right].](../I/m/e7de1c30fc36928f23b60329add9e3fe.png)
![S=\left[\begin{matrix}-\lambda_{1}&p_{1}\lambda_{1}&0&\dots&0&0\\
0&-\lambda_{2}&p_{2}\lambda_{2}&\ddots&0&0\\
\vdots&\ddots&\ddots&\ddots&\ddots&\vdots\\
0&0&\ddots&-\lambda_{k-2}&p_{k-2}\lambda_{k-2}&0\\
0&0&\dots&0&-\lambda_{k-1}&p_{k-1}\lambda_{k-1}\\
0&0&\dots&0&0&-\lambda_{k}
\end{matrix}\right]](../I/m/f874e4a4fbf3f504783e78748311d79f.png)