Persistence of a number
In mathematics, the persistence of a number is the number of times one must apply a given operation to an integer before reaching a fixed point at which the operation no longer alters the number.
Usually, this involves additive or multiplicative persistence of an integer, which is how often one has to replace the number by the sum or product of its digits until one reaches a single digit. Because the numbers are broken down into their digits, the additive or multiplicative persistence depends on the radix. In the remaining article, base ten is assumed.
The single-digit final state reached in the process of calculating an integer's additive persistence is its digital root. Put another way, a number's additive persistence is the measure of how many times we must sum the digits it takes us to arrive at its digital root.
Examples
The additive persistence of 2718 is 2: first we find that 2 + 7 + 1 + 8 = 18, and then that 1 + 8 = 9. The multiplicative persistence of 39 is 3, because it takes three steps to reduce 39 to a single digit: 39 → 27 → 14 → 4. Also, 39 is the smallest number of multiplicative persistence 3.
Smallest numbers of a given persistence
For a radix of 10, there is thought to be no number with a multiplicative persistence > 11: this is known to be true for numbers up to 1050. The smallest numbers with persistence 0, 1, ... are:
- 0, 10, 25, 39, 77, 679, 6788, 68889, 2677889, 26888999, 3778888999, 277777788888899, ... (sequence A003001 in OEIS)
By cleverly using the specific properties of numbers in this sequence, the above terms can be calculated in a fraction of a second.
The additive persistence of a number, however, can become arbitrarily large (proof: For a given number 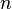 , the persistence of the number consisting of
, the persistence of the number consisting of 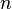 repetitions of the digit 1 is 1 higher than that of
repetitions of the digit 1 is 1 higher than that of 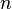 ). The smallest numbers of additive persistence 0, 1, ... are:
). The smallest numbers of additive persistence 0, 1, ... are:
The next number in the sequence (the smallest number of additive persistence 5) is 2 × 102×(1022 − 1)/9 − 1 (that is, 1 followed by 2222222222222222222222 9's). For any fixed base, the sum of the digits of a number is proportional to its logarithm; therefore, the additive persistence is proportional to the iterated logarithm.
References
- Guy, Richard K. (2004). Unsolved problems in number theory (3rd ed.). Springer-Verlag. pp. 398–399. ISBN 978-0-387-20860-2. Zbl 1058.11001.