Period-doubling bifurcation
In mathematics, a period doubling bifurcation in a discrete dynamical system is a bifurcation in which a slight change in a parameter value in the system's equations leads to the system switching to a new behavior with twice the period of the original system. With the doubled period, it takes twice as many iterations as before for the numerical values visited by the system to repeat themselves.
A period doubling cascade is a sequence of doublings and further doublings of the repeating period, as the parameter is adjusted further and further.
Period doubling bifurcations can also occur in continuous dynamical systems, namely when a new limit cycle emerges from an existing limit cycle, and the period of the new limit cycle is twice that of the old one.
Examples
- Logistic map
- Logistical map for a modified Phillips curve

Consider the following logistical map for a modified Phillips curve:


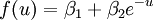
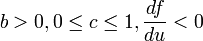
where :
-
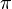 is the actual inflation
is the actual inflation -
 is the expected inflation,
is the expected inflation, - u is the level of unemployment,
-
 is the money supply growth rate.
is the money supply growth rate.
Keeping 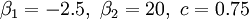 and varying
and varying 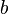 , the system undergoes period doubling bifurcations, and after a point becomes chaotic, as illustrated in the bifurcation diagram on the right.
, the system undergoes period doubling bifurcations, and after a point becomes chaotic, as illustrated in the bifurcation diagram on the right.

Period-halving bifurcation
A period halving bifurcation in a dynamical system is a bifurcation in which the system switches to a new behavior with half the period of the original system. A series of period-halving bifurcations leads the system from chaos to order.
See also
References
- Kuznetsov, Yuri A. (2004). Elements of Applied Bifurcation Theory. Applied Mathematical Sciences 112 (3rd ed.). Springer-Verlag. ISBN 0-387-21906-4. Zbl 1082.37002.
External links
- The Flip (Period Doubling) Bifurcation in Discrete Time, Dynamic Processes