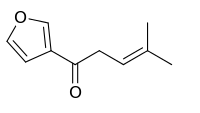
Perilla ketone
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1-(3-Furanyl)-4-methyl-1-pentanone | |
| Other names
beta-Furyl isoamyl ketone | |
| Identifiers | |
| 553-84-4 | |
| Jmol-3D images | Image |
| PubChem | 68381 |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula |
C10H14O2 |
| Molar mass | 166.22 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Liquid |
| Density | 0.9920 g/cm³ |
| Melting point | <25 °C |
| Boiling point | 196 °C (385 °F; 469 K) |
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Perilla ketone is a natural terpenoid that consists of a furan ring with a six-carbon side chain containing a ketone functional group. It is a colorless oil that is sensitive to oxygen, becoming colored upon standing. The ketone was identified in 1943 by Sebe as the main component of the essential oil of Perilla frutescens.[1] Perilla ketone is present in the leaves and seeds of purple mint (Perilla frutescens), which is toxic to some animals.[2] When cattle and horses consume purple mint when grazing in fields in which it grows, the perilla ketone causes pulmonary edema leading to a condition sometimes called perilla mint toxicosis.[2]
Synthesis
Perilla ketone was synthesized in 1957 by Matsuura from 3-furoyl chloride and an organocadmium compound similar to the Gilman reagent made from an isoamyl Grignard reagent and cadmium chloride.[3] Perilla ketone (3-Furyl isoamyl ketone) has been prepared in 74% yield via the Stille reaction from a 3-furyl-organotin compound and isocaproyl chloride in tetrahydrofuran solvent.[4]
See also
References
- ↑ Vittorio Farina (1943). "Perilla ketone". Nippon Kagaku Kaishi 64: 1130–6.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Perilla: Botany, Uses and Genetic Resources
- ↑ Teruo Matsuura (1957). "Natural furan derivatives. I. The synthesis of perilla ketone". Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan 30: 430–1. doi:10.1246/bcsj.30.430.
- ↑ Vittorio Farina; Krishnamurthy, Venkat; Scott, William J. (1997). "The Stille reaction". Organic Reactions (Hoboken, NJ, United States) 50.