Pepstatin
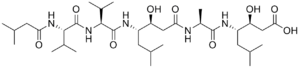 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Pepstatin A | |
| Identifiers | |
| 26305-03-3 | |
| ChemSpider | 4586014 |
| |
| Jmol-3D images | Image |
| KEGG | D03818 |
| PubChem | 5478883 |
| |
| Properties | |
| C34H63N5O9 | |
| Molar mass | 685.892 |
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Pepstatin is a potent inhibitor of aspartyl proteases. It is a hexa-peptide containing the unusual amino acid statine (Sta, (3S,4S)-4-amino-3-hydroxy-6-methylheptanoic acid), having the sequence Isovaleryl-Val-Val-Sta-Ala-Sta (Iva-Val-Val-Sta-Ala-Sta).[1] It was originally isolated from cultures of various species of Actinomyces[1] due to its ability to inhibit pepsin at picomolar concentrations.[2] Pepstatin A is well known to be an inhibitor of aspartic proteinases such as pepsin, cathepsins D and E. Except for its role as a proteinase inhibitor, however, the pharmacological action of pepstatin A upon cells remain unclear. Pepstatin A suppresses receptor activator of NF-κB ligand (RANKL)–induced osteoclast differentiation. Pepstatin A suppresses the formation of multinuclear osteoclasts dose-dependently. This inhibition of the formation only affected osteoclast cells, i.e., not osteoblast-like cells. Furthermore, pepstatin A also suppresses differentiation from pre-osteoclast cells to mononuclear osteoclast cells dose-dependently. This inhibition seems to be independent of the activities of proteinases such as cathepsin D, because the formation of osteoclasts was not suppressed with the concentration that inhibited the activity of cathepsin D. Cell signaling analysis indicated that the phosphorylation of ERK was inhibited in pepstatin A-treated cells, while the phosphorylation of IκB and Akt showed almost no change. Furthermore, pepstatin A decreased the expression of nuclear factor of activated T cells c1 (NFATc1). These results suggest that pepstatin A suppresses the differentiation of osteoclasts through the blockade of ERK signaling and the inhibition of NFATc1 expression.
Pepstatin is practically insoluble in water, chloroform, ether, and benzene, however it can be dissolved in methanol, ethanol and DMSO with acetic acid,[3] to between 1 and 5 mg/ml.

References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Umezawa H, Aoyagi T, Morishima H, Matsuzaki M, Hamada M (1970). "Pepstatin, a new pepsin inhibitor produced by Actinomycetes". J. Antibiot. 23 (5): 259–62. doi:10.7164/antibiotics.23.259. PMID 4912600.
- ↑ Marciniszyn J, Hartsuck JA, Tang J (1976). "Mode of inhibition of acid proteases by pepstatin". J. Biol. Chem. 251 (22): 7088–94. PMID 993206.
- ↑ The Merck Index - An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals (14th Edition - Version 14.4), Monograph 07147, ISBN 978-1-60119-491-6