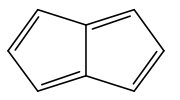
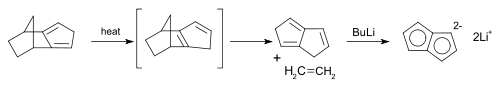Pentalene
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Pentalene | |
| Identifiers | |
| 250-25-9 | |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:33074 |
| ChemSpider | 4574194 |
| |
| Jmol-3D images | Image |
| PubChem | 5460726 |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula |
C8H6 |
| Molar mass | 102.13 g·mol−1 |
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Pentalene is a polycyclic hydrocarbon composed of two fused cyclopentadiene rings.[1] It has chemical formula C8H6. It is antiaromatic, because it has 4n π electrons where n is any integer. For this reason it dimerizes even at temperatures as low as -100 °C.[2][3] The derivative 1,3,5-tri-tert-butylpentalene was synthesized in 1973.[4] Because of the tert-butyl substituents this compound is thermally stable. Pentalenes can also be stabilized by benzannulation for example in the compounds benzopentalene and dibenzopentalene.[1]
Dilithium pentalenide was isolated in 1962, long before pentalene itself in 1997.[5] It is prepared from reaction of dihydropentalene (pyrolysis of an isomer of dicyclopentadiene) with n-butyllithium in solution and forms a stable salt. In accordance with its structure proton NMR shows 2 signals in a 2 to 1 ratio. The addition of two electrons removes the antiaromaticity; it becomes a planar 10 pi aromatic species and is thus a bicyclic analogue of the cyclooctatetraene (COT) dianion C8H82−.
The dianion can also be considered as two fused cyclopentadienyl rings, and has been used as a ligand in organometallic chemistry to stabilise many types of mono- and bimetallic complexes, including those containing multiple metal-metal bonds, and anti-bimetallics with extremely high levels of electronic communication between the centers.[6]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Hopf, Henning (2013). "Pentalenes-From Highly Reactive Antiaromatics to Substrates for Material Science". Angewandte Chemie International Edition 52 (47): 12224. doi:10.1002/anie.201307162.
- ↑ Carey, Francis A.; Sundberg, Richard J. (1984). Advanced Organic Chemistry: Part A Structure and Mechanisms (2nd ed.). New York, NY: Plenum Press. ISBN 0-306-41198-9.
- ↑ Bally T., Chai S., Neuenschwander M., Zhu Z. (1997). "Pentalene: Formation, Electronic, and Vibrational Structure" (REPRINT). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 119 (8): 1869–1875(7). doi:10.1021/ja963439t.
- ↑ Hafner, K. and Süss, H. U. (1973), 1,3,5-Tri-tert-Butylpentalene. A Stabilized Planar 8π-Electron System. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl., 12: 575–577. doi:10.1002/anie.197305751
- ↑ Katz, Thomas J.; Rosenberger, Michael. (1962). "The Pentalenyl Dianion". Journal of the American Chemical Society 84 (5): 865. doi:10.1021/ja00864a038.
- ↑ Summerscales, Owen T.; Cloke, F. Geoffrey N. (2006). "The organometallic chemistry of pentalene". Coordination Chemistry Reviews 250 (9–10): 1122. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2005.11.020.