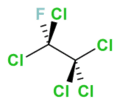
Pentachlorofluoroethane
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1,1,1,2,2-Pentachloro-2-fluoroethane | |||
| Other names
Pentachloromonofluoroethane CFC-111 R-111 | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| 354-56-3 | |||
| ChemSpider | 55058 | ||
| |||
| Jmol-3D images | Image | ||
| PubChem | 61107 | ||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| Molecular formula |
C2Cl5F | ||
| Molar mass | 220.28 g·mol−1 | ||
| Melting point | 101.5 °C (214.7 °F; 374.6 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 135 °C (275 °F; 408 K) | ||
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |||
| | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Pentachlorofluoroethane is a chlorofluorocarbon once used as a propellant and refrigerant. Its production and consumption has been banned since January 1, 1996 under the Montreal Protocol because of its ozone-depleting potential.[1]
.png)